Published online by Cambridge University Press: 02 March 2012
What experiences have infuenced Chinese educators' environmental consciousness and their involvement in environmental education work? Using the autobiographical inquiry approach the author explored this question with fourteen master environmental educators from various regions of China and examined in depth their signifcant life experiences (SLE). Participants described several paths to become involved in environmental education work. Multiple factors impacted their environmental consciousness. Out of ten main categories of SLE three themes emerged: serendipity, 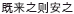 , and a strong sense of responsibility toward the environment and toward environmental education work. This study illuminates the Chinese-ness of environmental education from the angle of life experiences and reflections of environmental educators in mainland China, which also has relevance to and implications for the wider international environmental education community.
, and a strong sense of responsibility toward the environment and toward environmental education work. This study illuminates the Chinese-ness of environmental education from the angle of life experiences and reflections of environmental educators in mainland China, which also has relevance to and implications for the wider international environmental education community.