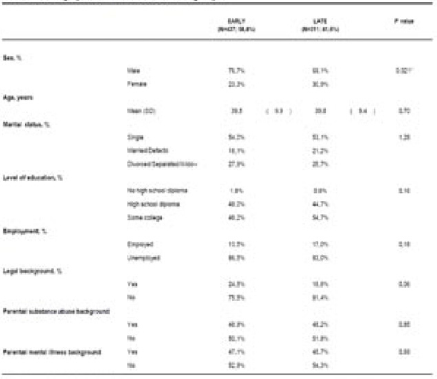
Table 1 Demographic characteristics of both groups.
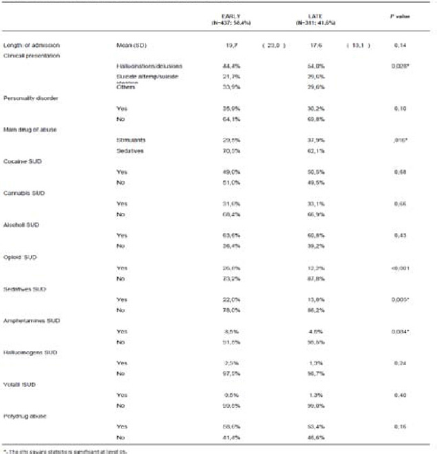
Table 2 Clinical and functional variable at admission in both groups.
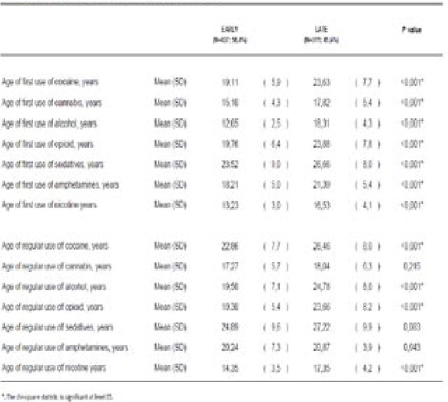
Table 3 Historical data about age of drug use in both groups.
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 23 March 2020
Describe the distinguishing characteristics between patients with early onset of alcohol use (EARLY, age < 15) and late onset of alcohol use (LATE, age > 16), both affected of acute non-substance use psychiatric disorders (non-SUD) and any substance use disorder admitted in a dual diagnosis unit.
Data on demographic, family, and clinical factors were gathered among subjects admitted to our dual diagnosis unit along three years, all of them meeting DSM-IV criteria of any non-substance related Axis I or II disorder and comorbid substance use disorder (SUD). Statistical analysis was performed by using SPSS program.
We show results of 748 patients (437 of EARLY group and 311 of LATE group). Predominantly male (73,53%) with a mean age of 39,60 ± 9,7 years. Most prevalent non-SUD psychiatric disorders were psychotic disorder (39,97%) and personality disorder (39,30%). In our sample, most common substances of abuse were Alcohol (45,05%) and Cocaine (30,35%). EARLY patients had an earlier first contact all substances as well as an earlier age of problematic consumption of cocaine, alcohol, opioids and nicotine; they also had major prevalence of opioid SUD, sedatives SUD and amphetamines SUD (see Tables 1, 2 and 3).
Patients who began earlier their consumptions of alcohol had major prevalence of opioid, sedatives and amphetamine use. They also had earlier consumptions of other substances and earlier problematic consumptions of cocaine, alcohol, opioids and nicotine, what probably means greater severity of drug addiction in the long run.
The authors have not supplied their declaration of competing interest.

Table 1 Demographic characteristics of both groups.

Table 2 Clinical and functional variable at admission in both groups.

Table 3 Historical data about age of drug use in both groups.

Table 1 Demographic characteristics of both groups.

Table 2 Clinical and functional variable at admission in both groups.

Table 3 Historical data about age of drug use in both groups.
Comments
No Comments have been published for this article.