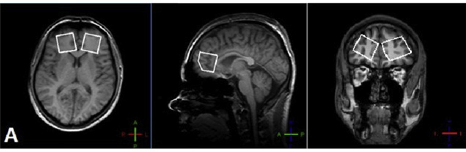
Fig. 1 1H MRS VOI localizations.
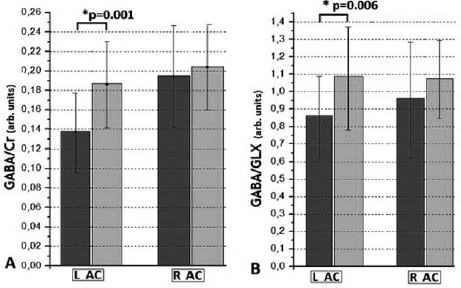
Fig. 2 Reduced GABA (A) and GABA/GLX (B) in the left ACC.
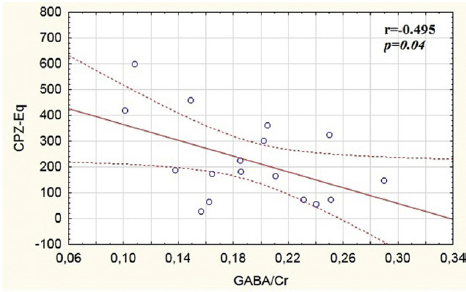
Fig. 3 Association between GABA/Cr and treatment.
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 23 March 2020
Some previous findings indicate participation disturbance of balance between excitatory (GABA) and inhibitory (Glu) neurotransmitters in pathogenesis of schizophrenia. The aim of this study was to evaluate GABA and GLX levels in the brain of medicated UHR subjects.
Twenty-one (18–25 years, mean = 19.4, SD = 3.5) right-handed medicated UHR men and 26 (18–25 years, mean = 19.8, SD = 2.2) mentally healthy volunteers participated in this study. The patients were included in the UHR group in accordance with criteria of prodromal states.
1H MRS (MEGA-PRESS pulse sequence [Mescher, NMR Biomed 1998;11:266]) was used for GABA and GLX detection. Volumes of interest in size of 30 × 30 × 30 mm were placed in the left and right frontal lobes in the areas of the anterior cingulate cortex (ACC) (Fig. 1).
The main effects on the GABA/Cr (t[45] = 4.17, P < 0.01) (Fig. 2A) and GABA/GLX (t[45] = 2.84, P < 0.01) (Fig. 2B), were found in the left ACC (t[45] = 4.17, P < 0.01), with the patients having lower GABA/Cr and GABA/GLX ratios as compared to the control group. Also significant negative correlation (r = −0.49, P = 0.04) between GABA/Cr in the right ACC and the current daily dosage of antipsychotic medication in CPZ-Eq was found (Fig. 3).
This study reveals for the first time a significant reduction of (GABA) (25%) and GABA/GLX ratio (20%) in left AC of UHR subjects. According to (de la Fuente-Sandoval, Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 2015;19[3]) and association of (GABA) with daily dosage of medication found, this reduction may be caused by the antipsichotic treatment.
The authors have not supplied their declaration of competing interest.

Fig. 1 1H MRS VOI localizations.

Fig. 2 Reduced GABA (A) and GABA/GLX (B) in the left ACC.

Fig. 3 Association between GABA/Cr and treatment.

Fig. 1 1H MRS VOI localizations.

Fig. 2 Reduced GABA (A) and GABA/GLX (B) in the left ACC.

Fig. 3 Association between GABA/Cr and treatment.
Comments
No Comments have been published for this article.