To the Editor—Rapid laboratory detection of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) is of outmost importance nowadays and affects clinical and epidemiological decisions regarding therapy initiation, carrier isolation, and adoption of public health measures. The implementation of rapid antigen tests even in the form of self-testing has been recently applied in some countries to reduce the turnaround time to result required to perform real-time reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR).
However, molecular techniques remain the gold standard. Reference Lim and Lee1
Isothermal amplification technology (IAT) provides an alternative that improves dramatically the time to result, reduces costs, and maintains the molecular basis of SARS-CoV-2 identification in clinical samples. IAT is the amplification of nucleic acids without thermocycling, and unlike PCR, it does not require skilled personnel and specialized laboratory equipment. Reference James and Alawneh2
The Abbott ID NOW COVID-19 3 is a loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) assay Reference James and Alawneh2 that was recently evaluated in our hospital as a rapid alternative to the already present real-time RT-PCR–based techniques that are used in everyday practice. We obtained 30 nasopharyngeal samples from patients with clinical suspicion of COVID-19 admitted at the emergency department of our hospital, which is one of the referral settings for COVID-19 in northern Greece. The samples were tested in parallel with the Abbott ID NOW, the NeuMoDx SARS-CoV-2, and the Abbott RealTime SARS-CoV-2 assays according to the manufacturers’ respective instructions. Regarding the ID NOW, a dry swab without transport medium (as recommended by the US Food and Drug Administration) was used. 4
In our evaluation, the performance of ID NOW was identical to that of NeuMoDx and was comparable to that of the Abbott RealTime SARS-CoV-2 assay, except for 2 cases (cases 14 and 28, Table 1). Compared to the Abbott RealTime SARS-CoV-2 assay, the sensitivity of ID NOW was 85.71%, the specificity was 100%, the positive predictive value was 100%, the negative predictive value was 88.89%, and the κ coefficient of agreement was 0.805 (P < .005). The time to result of ID NOW was 5 minutes or less for positive samples and 10–15 minutes for negative samples. The rapid times to positive results of the ID NOW were achieved regardless of the Ct values obtained by NeuMoDx and Abbott RealTime assays for the respective positive samples.
Table 1. Result Comparison Between Abbott ID NOW, NeuMoDx SARS-CoV-2 Assay, and Abbott RealTime SARS-CoV-2 Assay
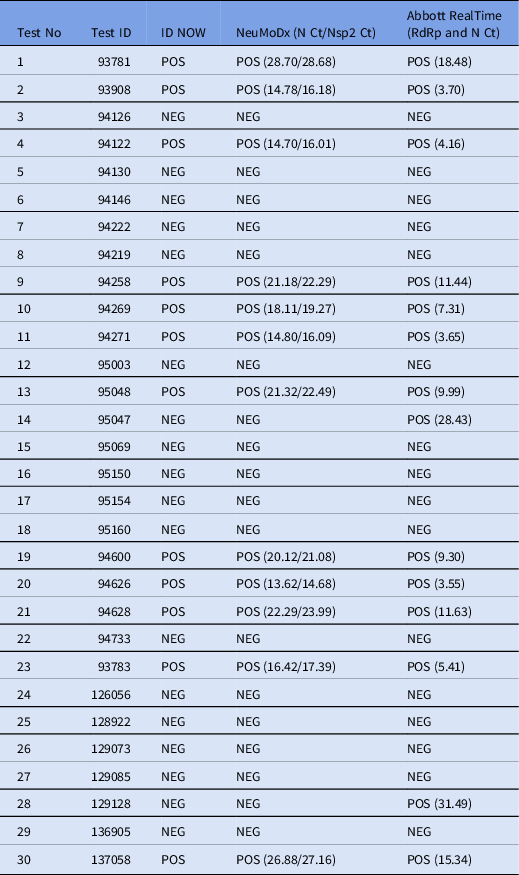
Note. POS, positive; NEG, negative; Ct, cycle threshold; N, nucleocapside gene; Nsp2, nonstructural protein 2 gene; RdRp, RNA-dependent RNA polymerase gene.
Previous studies have reported low sensitivity for the ID NOW test using nasopharyngeal swabs in transport media. Reference Basu, Zinger and Inglima5–Reference Zhen, Smith, Manji, Schron and Berry8 In a recent large study by Sepulveda et al Reference Sepulveda, Abdulbaki and Sands9 in which dry swabs were used, ID NOW showed very high sensitivity for detection of patients with high levels of SARS-CoV-2 RNA but lower overall sensitivity compared with the Xpert SARS-CoV-2 assay. In our evaluation, the 2 cases of disagreement with the Abbott RealTime SARS-CoV-2 assay had high Ct values, indicating the presence of low viral loads.
Considering that low-viral-load samples are commonly unable for viral growth in cell cultures, Reference Sepulveda, Abdulbaki and Sands9 the clinical impact of ID NOW should be approached with respect to the advantage of saving time in detecting infected patients and the disadvantage of false negatives with lower viral loads. Even though IATs are not yet ready to entirely replace real-time RT-PCR, the implementation of assays such as ID NOW could be beneficial in reducing turnaround times, especially in emergency departments, as well as the overall costs of SARS-CoV-2 detection.
Acknowledgments
Financial support
No financial support was provided relevant to this article.
Conflicts of interest
All authors report no conflicts of interest relevant to this article.




