Published online by Cambridge University Press: 17 June 2013
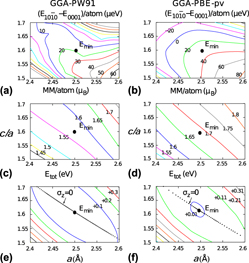
The magnetic anisotropy energy (MAE) of the bulk hcp Co under mechanical deformation is calculated by ab initio density functional theory (DFT) calculations based on the projector augmented wave method. We present a thorough investigation with respect to the choice of exchange-correlation functionals. The generalized gradient approximation (GGA) succeeds in predicting the easy axis of magnetization but underestimates the MAE in comparison to the experimental value, whereas the local density approximation gives a wrong magnetic easy axis. The DFT+U method offers an alternative to increase the MAE value. Unfortunately, as the MAE reaches the experimental value, strong distortions of the lattice parameters are observed. Our results with GGA suggest that a simultaneous reduction of the c/a ratio and increase of the lateral lattice parameter a will strongly enhance the MAE of the material, as observed experimentally. We also found that the MAE in hcp Co is reduced by shear strain.