Published online by Cambridge University Press: 04 March 2018
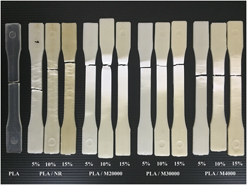
Admicellar polymerization, a novel technique for surface modification, was used in this work to enhance the compatibility between polymers with obviously different polarities, e.g., natural rubber (NR) and polylactic acid (PLA). The admicellar polymerization of methyl methacrylate over NR substrates (using potassium peroxodisulfate as an initiator) so-called poly(methyl methacrylate)–natural rubber (PMMA-ad-NR) was prepared and mixed with PLA at different contents (5, 10, and 15 wt%) in comparison to the simple PLA/NR blends. The monomer to initiator ratio was varied: 25:1, 50:1, and 100:1 corresponding to the admicelled PMMA molecular weight of 20,000, 30,000, and 40,000 g/mol, respectively. All PLA/PMMA-ad-NR blends showed good compatibility as evident by FE-SEM results revealing smooth boundary of PMMA-ad-NR domains in the PLA matrix. Moreover, the mechanical properties and thermal stability of PLA/PMMA-ad-NR blends were higher than those of PLA/NR blends, especially with increasing PMMA-ad-NR content up to 10 wt%. It was clear that the lowest molecular weight of the admicelled PMMA gave the highest toughness of PLA/PMMA-ad-NR blends.
Contributing Editor: Amit Bandyopadhyay