Published online by Cambridge University Press: 19 January 2011
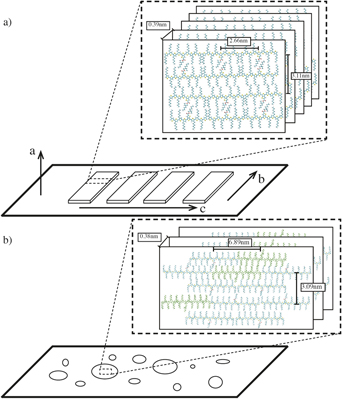
Thin-film aggregation characteristics of a series of oligothiophenes with a central thieno[3,4-b]thiophene ester unit and 4 (M5), 8 (M9), and 16 (M17) regioregular hexylthiophene units were investigated. These oligomers exhibited length-dependent self-assembly characteristics upon spin coating. M9 formed long fibers, while M5 and M17 formed random domains. Grazing incidence x-ray diffraction was performed to understand the reason for this length dependence. The M5 had a dominant ester–ester interaction that disrupted long-range order. The M9 morphology was due to a balance of orthogonal backbone and ester effects, which imposed long-range order on the M9 aggregates. Meanwhile, the M17 ester chain had a smaller relative contribution to packing and functioned as a molecular defect, disrupting long-range order. As a result, though the local self-assembly between monomers was very similar for the molecules, backbone length dependent changes in intermolecular forces dominated long-range structure. The analysis of self-assembly characteristics in these materials provides guidance in the design of organic conjugated materials for use in semiconductor devices.