Article contents
Optical properties of the composite film from P3HT and hydrothermally synthesized porous carbon nanospheres
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 04 May 2015
Abstract
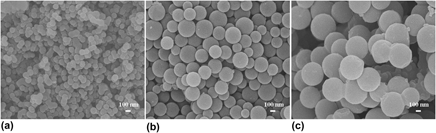
Porous carbon nanospheres (PCNSs), with a diameter of about 100 nm and porous structure, were synthesized by a hydrothermal method. Then, poly(3-hexylthiophene):PCNS (P3HT:PCNS) composite films were prepared by a spin-coating method using PCNS and P3HT mixtures in a chlorobenzene solution. The effects of mixture ratio, revolving speed, suspension concentration during spin coating, and annealing on the optical properties of P3HT:PCNS composite films were investigated. The results indicate that PCNSs exhibit an energy level matching with P3HT and the optical properties of the P3HT:PCNSs depend strongly on mixture ratio, revolving speed, and suspension concentration during spin coating. A 2:1 ratio of P3HT to PCNSs, suspension concentration of 20 mg/mL (P3HT), and spinning rate of 2000 rpm are appropriate for fabricating P3HT:PCNS composite films, and annealing increases the crystallinity of P3HT, resulting in enhanced visible light absorption and increased charge transport in composite films.
- Type
- Articles
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Materials Research Society 2015
References
REFERENCES
- 1
- Cited by


