Article contents
A simple model of plate-like crystallization with constant plate thickness
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 19 April 2013
Abstract
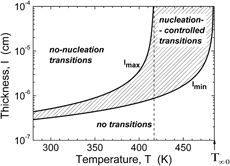
A kinetic model of crystallization based on two-dimensional nucleation and growth of plate-like crystals with constant thickness is analyzed. It is shown that plate thickness required for nucleation is limited. The lower limit is determined by zero Gibbs’ free energy of transition, the upper one corresponds to the conditions when the critical cluster volume of nucleation is equal to two elementary kinetic units. Effects of plate thickness on crystallization kinetics are discussed. In the lower temperature range, creation of thicker plates is preferred. For a given plate thickness, frequency of the phase transition decreases with increasing temperature. Numerical calculations for α-polypropylene concern kinetics of primary nucleation and global phase transition in a system of one or several fractions of plate-like kinetic elements.
- Type
- Articles
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Materials Research Society 2013
References
REFERENCES
- 1
- Cited by


