Article contents
Wet-chemical preparation of digold bismuthide, gold diantimonide, and gold ditelluride particles
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 29 July 2013
Abstract
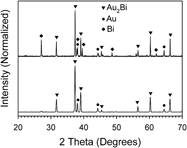
The intermetallic materials digold bismuthide, gold diantimonide, and gold ditelluride were chemically synthesized with a bottom-up wet chemical approach, which has not been achieved before. These gold-based materials display a nano- to microparticle grain size and a well-defined composition-based structure. True intermetallic nanoparticle-based materials have traditionally proven challenging to obtain via wet chemical approaches, making the materials created here significant from a fundamental synthesis standpoint. The knowledge gained by developing reliable synthesis approaches toward intermetallic nanoparticles may be used to develop new materials and enhance the understanding of how to refine the characteristics and enhanced properties of emerging nanoparticle semiconductor materials in advanced applications such as for thermoelectrics.
- Type
- Articles
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Materials Research Society 2013
References
REFERENCES
- 3
- Cited by


