Article contents
Implicit role of Cairns distributed ions and weak relativistic effects of electrons in the formation of dust acoustic waves in plasma
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 03 March 2016
Abstract
In this model of a dusty plasma, we have investigated dust acoustic waves consisting of electrons with weak relativistic effects, Cairns distributed cold ions and negatively charged mobile dust. Dust acoustic (DA) compressive and rarefactive solitons of various amplitudes are established. The parameter 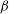 ${\it\beta}$ involved in Cairns distribution is related to the non-thermal parameter
${\it\beta}$ involved in Cairns distribution is related to the non-thermal parameter  ${\it\alpha}$. However, the increase of
${\it\alpha}$. However, the increase of 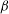 ${\it\beta}$, which is independent of temperature, becomes instrumental for complete linear increase or decrease of the amplitudes of both the compressive and rarefactive relativistic solitons. Hence it is worthwhile to note that the increase of
${\it\beta}$, which is independent of temperature, becomes instrumental for complete linear increase or decrease of the amplitudes of both the compressive and rarefactive relativistic solitons. Hence it is worthwhile to note that the increase of 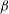 ${\it\beta}$ is solely due to the rest energy and not due to kinetic energy in this relativistic plasma. This is one of the most significant results of our investigation. Also, the flux of negative charges from the dust particles, together with the effect of the relativistic electrons, appears to balance the positive charges of Cairns distributed ions for nearly constant growth of amplitudes.
${\it\beta}$ is solely due to the rest energy and not due to kinetic energy in this relativistic plasma. This is one of the most significant results of our investigation. Also, the flux of negative charges from the dust particles, together with the effect of the relativistic electrons, appears to balance the positive charges of Cairns distributed ions for nearly constant growth of amplitudes.
- Type
- Research Article
- Information
- Copyright
- © Cambridge University Press 2016
References
- 7
- Cited by



