Article contents
Epithelial Distribution of E-Cadherin, p63, and Mitotic Figures in ApoTome Images to Determine the Oncogenic Potentiality of Oral Submucous Fibrosis
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 14 October 2020
Abstract
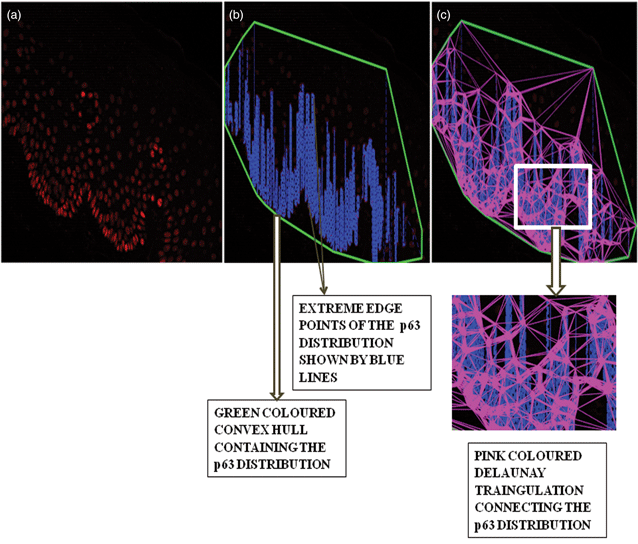
The exact process of the malignant conversion of oral submucous fibrosis (OSF) to oral cancer is not fully understood. This study aimed to detect and analyze E-cadherin expression, p63 expression, and number of mitotic figures, all correlated to cancer development, in ApoTome images of oral tissues to determine the oncogenic potentiality of OSF. ApoTome images of the study groups (6 normal, 16 OSF with dysplasia, and 10 OSF without dysplasia) were recorded. Cytoplasmic and membranous E-cadherin expression, breakages of the cell membrane, and p63 expression were detected in MATLAB 2016b. The number of mitotic figures detected by MATLAB was correlated with the number of chromosomes detected by ImageJ. A Mann–Whitney U test was done to determine a significant difference between the study groups for cytoplasmic and membranous E-cadherin distribution points. Statistical significant differences were found for cytoplasmic E-cadherin distribution between normal and OSF (with dysplasia) (p = 0.0278). There was an increase in mitotic figures, p63 expression, and cytoplasmic E-cadherin expression and a decrease in membranous E-cadherin expression from normal to diseased condition. Hence, automated detection and quantification of E-cadherin, p63, and mitotic figures in ApoTome images of oral biopsies can help in determining the oncogenic potentiality of OSF.
- Type
- Biological Applications
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © The Author(s), 2020. Published by Cambridge University Press
References
- 3
- Cited by


