Article contents
Three-Dimensional Analysis of Interstitial Cells in the Smooth Muscle Layer of Murine Vas Deferens Using Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy and FIB/SEM
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 26 January 2022
Abstract
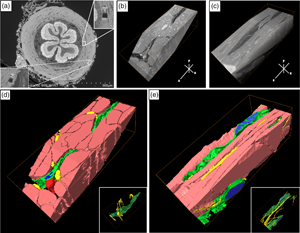
The smooth muscle contraction of the vas deferens has the important function of transporting sperm. Interstitial cells (ICs) play a critical role in the pacing and modulation of various smooth muscle organs by interactions with nerves and smooth muscle. Elucidating the three-dimensional (3D) architecture of ICs is important for understanding their spatial relationship on the mesoscale between ICs, smooth muscle cells (SMCs), and nerves. In this study, the 3D ultrastructure of ICs in the smooth muscle layer of murine vas deferens and the spatial relationships between ICs, nerves, and smooth muscles were observed using confocal laser scanning microscopy and focused ion beam/scanning electron microscopy. ICs have sheet-like structures as demonstrated by 3D observation using modern analytical techniques. Sheet-like ICs have two types of 3D structures, one flattened and the other curled. Multiple extracellular vesicle (EV)-like structures were frequently observed in ICs. Various spatial relations were observed in areas between ICs, nerves, and SMCs, which formed a complex 3D network with each other. These results suggest that ICs in the smooth muscle layer of murine vas deferens may have two subtypes with different sheet-like structures and may be involved in neuromuscular signal transmission via physical interaction and EVs.
- Type
- Micrographia
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © The Author(s), 2022. Published by Cambridge University Press on behalf of the Microscopy Society of America
References
- 4
- Cited by



