Published online by Cambridge University Press: 27 October 2020
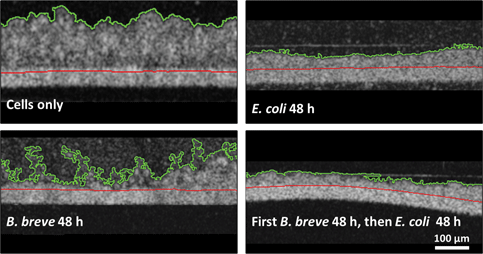
Imaging of cellular layers in a gut-on-a-chip system has been confined to two-dimensional (2D)-imaging through conventional light microscopy and confocal laser scanning microscopy (CLSM) yielding three-dimensional- and 2D-cross-sectional reconstructions. However, CLSM requires staining and is unsuitable for longitudinal visualization. Here, we compare merits of optical coherence tomography (OCT) with those of CLSM and light microscopy for visualization of intestinal epithelial layers during protection by a probiotic Bifidobacterium breve strain and a simultaneous pathogen challenge by an Escherichia coli strain. OCT cross-sectional images yielded film thicknesses that coincided with end-point thicknesses derived from cross-sectional CLSM images. Light microscopy on histological sections of epithelial layers at the end-point yielded smaller layer thicknesses than OCT and CLSM. Protective effects of B. breve adhering to an epithelial layer against an E. coli challenge included the preservation of layer thickness and membrane surface coverage by epithelial cells. OCT does not require staining or sectioning, making OCT suitable for longitudinal visualization of biological films, but as a drawback, OCT does not allow an epithelial layer to be distinguished from bacterial biofilms adhering to it. Thus, OCT is ideal to longitudinally evaluate epithelial layers under probiotic protection and pathogen challenges, but proper image interpretation requires the application of a second method at the end-point to distinguish bacterial and epithelial films.