Published online by Cambridge University Press: 25 February 2011
In this study, transmission electron microscopy (TEM) was used to investigate the growthconditions which produce the highest quality GaAs(111)B films by molecular beam epitaxy (MBE). Low-temperature growth using both As4 and arsine as an As2 source produced highly twinned structures, although the use of As4 provided for a smoother surface and slightly different defect structure. Two distinct twin boundaries, (112)A and (112)B, were identified by cross-sectional transmission electron microscopy (XTEM). The (112)A defect could be over-grown by a subsequent high temperature growth but the roughness associated with the (112)B defects only increased with further growth. High temperature growth of GaAs and AlAs films, while maintaining the GaAs(11)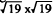 surface reconstruction, resulted in substantial reduction in the number of twins boundaries. We also found that GaAs(111)B layer quality and surface morphology can be further improved by a high temperature growth with low arsenic to Ga flux ratio of I to 1.5 ona slightly misoriented substrate.
surface reconstruction, resulted in substantial reduction in the number of twins boundaries. We also found that GaAs(111)B layer quality and surface morphology can be further improved by a high temperature growth with low arsenic to Ga flux ratio of I to 1.5 ona slightly misoriented substrate.