No CrossRef data available.
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 15 March 2011
We present the results of molecular dynamics simulations of pairs of alkylsilane monolayers on silica surfaces under shear. In particular, we investigate the effects of shear velocity on the friction for chains of 6, 8, 12, and 18 carbon atoms covalently bonded to a crystalline surface. Our studies are performed at loads close to 0.2 and 2 GPa for relative velocities of 0.2, 2.0, and 20.0 m/s. We find that for perfect (defect-free) monolayers, the effects of chain length and velocity are weak, indicating that the experimentally measured dependence of friction on these properties is primarily due to defects in the monolayer. We have investigated possible finite size effects by varying our system dimensions from 43 Å ×50 Å Å to 174 Å × 201 Å. We find that increasing the surface area by a factor of N reduces the noise in the shear stress by a factor of 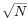 , and has a comparable effect to averaging the smaller system data over bins of
, and has a comparable effect to averaging the smaller system data over bins of 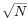 points. This indicates that finite size effects are negligible in our simulations.
points. This indicates that finite size effects are negligible in our simulations.