Published online by Cambridge University Press: 12 February 2015
Microstructures and mechanical properties of directionally solidified (DS) MoSi2 / Mo5Si3 / Mo5Si3C ternary eutectic composites were investigated. Ternary eutectic microstructure of a script-lamellar type that is characterized by rod-shaped Mo5Si3 and Mo5Si3C phases extending along the growth direction in the MoSi2 single crystalline matrix was developed simply by directional solidification at a growth rate of 10 mm/h. Compression tests along 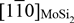 $[{\rm{1}}\mathop 1\limits^- 0]_{MoSi_2 }$ nearly parallel to the growth direction revealed that the DS ternary eutectic composites were plastically deformed above 1000 °C. Yield stresses of the DS ternary eutectic composites were much higher than those of binary composites mainly because of a smaller average thickness of MoSi2 matrix.
$[{\rm{1}}\mathop 1\limits^- 0]_{MoSi_2 }$ nearly parallel to the growth direction revealed that the DS ternary eutectic composites were plastically deformed above 1000 °C. Yield stresses of the DS ternary eutectic composites were much higher than those of binary composites mainly because of a smaller average thickness of MoSi2 matrix.