Introduction
The Chelonia face an extinction crisis, particularly in Asia, because of the burgeoning demands for the pet, food and traditional Chinese medicine markets (Gibbons et al., Reference Gibbons, Scott, Ryan, Buhlmann, Tuberville and Metts2000; van Dijk et al., Reference van Dijk, Stuart and Rhodin2000). Unsustainable harvests, and habitat fragmentation and loss accompanying rapid urbanization and land development all pose threats to turtles. These threats are particularly acute for those species with a high commercial value. Of the chelonian species traded in Asia, the yellow-margined box turtle Cuora flavomarginata is one of the most threatened (Zhou & Jiang, Reference Zhou and Jiang2008).
This species predominantly inhabits mesic forests on low-elevation hills (Mao, Reference Mao1971; Zhao, Reference Zhao1998). Although C. flavomarginata is widely distributed in central and southern mainland China, Taiwan and the southern Ryukyus of Japan (Mao, Reference Mao1971; Iverson, Reference Iverson1992; Fong et al., Reference Fong, Parham and Fu2002), its status in China and Taiwan is poorly known (Zhao, Reference Zhao1998; Chen et al., Reference Chen, Lin, Chang, van Dijk, Stuart and Rhodin2000) and it faces an uncertain future in Taiwan. The species is categorized as Endangered on the IUCN Red List (Asian Turtle Trade Working Group, 2000) because of extensive habitat loss and commercial exploitation; it was also added to Appendix II of CITES in 2000 to limit overexploitation by international trade. Since 1989 the Taiwanese populations have been protected by the Wildlife Conservation Act as a rare and valuable species.
The status of a given species is usually determined by its distribution and abundance, and the changing rate of these two components (McGowan et al., Reference McGowan, Gillman and Dodd1998). For turtle species with high economic value, such as C. flavomarginata, range countries have been urged to assess the status, ecology and demography of populations in the wild (Zhao, Reference Zhao1998; Zhou & Jiang, Reference Zhou and Jiang2008). We therefore performed a large-scale trapping survey to evaluate the status and distribution of C. flavomarginata in Taiwan and to highlight conservation measures required for the survival of the species there.
Study area
The trapping survey was conducted at 68 localities throughout Taiwan (Fig. 1), during 2001–2008. At three of these localities (Feitsui, Keelung and Hushan) the survey was extensive (see below). C. flavomarginata had previously been studied in a tributary watershed at the Feitsui Reservoir Protected Area (Chen & Lue, Reference Chen and Lue1999, Reference Chen and Lue2002, Reference Chen and Lue2008; Lue & Chen, Reference Lue and Chen1999), which has been blocked from public access, to protect water resources, since 1984; this site provided an opportunity to examine any population changes over time. The habitat consists mainly of primary and secondary evergreen forests (see detailed description in Lue & Chen, Reference Lue and Chen1999). The site at Keelung is in secondary forest in a mountain basin near a recent development. In the Hushan Reservoir Planning Zone turtles were trapped intensively for translocation within the submerged and construction areas; the original habitat consisted mainly of well-developed secondary forest and cultivated bamboo (mainly Sinocalamus latiflorus). Elsewhere, we identified potentially suitable habitats for C. flavomarginata, such as primary evergreen forest or well-developed secondary forest at elevations < 500 m, using 1 : 25,000 maps published by the Ministry of Interior, Republic of China and satellite images from Google Earth (2008).

Fig. 1 Sampling sites for the yellow-margined box turtle Cuora flavomarginata in Taiwan. White circles indicate sites where no turtles were captured, black circles sites where turtles were captured (Table 1), and grey circles evidence of presence obtained from other reliable sources (see text for further details). Black stars indicate two historical collection sites.
Methods
To select trapping sites the existence of C. flavomarginata in these locations was confirmed by interviews with local residents. We also examined published records and anecdotal reports. Turtles were captured using commercial rodent traps (29 × 17 × 14 cm) in the season when C. flavomarginata is active (April–October). Traps were baited with banana and set under vegetation to avoid overheating of any captured turtles. At each site at least five traps were set and they were checked 1–2 times per week. If no turtles were captured or encountered in 2 weeks of trapping we assumed the site had no turtles or that they occurred at a low density. We moved the traps to a new site after 2–4 weeks of trapping. Because of the high frequency of trap loss in Hualien, Gukeng (near Douliou) and Sheding (near Hengchun) we collected turtles by searching under vegetation and along trails. At Yufong turtles were captured opportunistically by local volunteers during 2001–2003. Information at Nanjenshan was obtained from Tsai (Reference Tsai2007), and at Jiialeshuei by H.-C. Lin (pers. comm.).
This trapping was conducted in conjunction with detailed population studies, for > 1 year, at Feitsui, Keelung and Hushan. At Feitsui turtles were trapped intensively during September–November 2002 and April–November 2003. At Keelung turtles were trapped during the active season (April–October) from 2006 to 2008. At Hushan turtles were trapped intensively during September–October 2007 and May–September 2008, and those captured were kept in semi-natural enclosures in nearby abandoned orchards and later translocated to suitable habitats after completion of the construction of the reservoir. At these three sites at least 15 traps were set during each trapping period.
Most of the captured turtles were individually notched on the marginal scutes, for later identification, with a hand saw or triangle file (Cagle, Reference Cagle1939). AVID (AVID Inc., Norco, USA) passive integrated transponder tags were implanted in the Hushan population. Each trapped turtle was sexed on the basis of external secondary sexual characteristics (mainly the position of the cloacal opening). Any turtle without male characteristics and with a carapace length > 100 mm was assumed to be female. Turtles were released at their capture location after handling and measurement, except at Hushan (see above). In the analyses of population structure we include only sites where > 20 turtles were captured. In comparisons of body size among different populations we used the measurements of individual turtles from the time of first captures only. We used G-tests (Sokal & Rohlf, Reference Sokal and Rohlf1995) to compare sex ratios and capture rates among different sites or sampling periods.
Results
We captured a total of 527 individual C. flavomarginata at 23 of the 68 sites (Fig. 1, Table 1) and obtained, in addition, information from Nanjenshan and Jiialeshuei (see above). There were four clusters of localities in which C. flavomarginata were captured: Taipei–Ilan (northern), Nantou-Yunlin (central), Hengchun Peninsula (southern) and northern Hualien-Taitung Valley (eastern). At Feitsui, Keelung and Hushan we captured > 50 individuals, in broad-leaf evergreen forest at low elevations. However, the capture success at most sites was low (Table 1). C. flavomarginata appears to be locally abundant and restricted to primary and well-developed secondary forest and to the forest edge.
Table 1 Numbers of the yellow-margined box turtle Cuora flavomarginata trapped in northern, central, southern and eastern Taiwan (Fig. 1) from 2001 to 2008.

1 Collected by random searches or accidental encounters
2 Collection data provided by H.-C. Lin
3 Data obtained from Tsai (Reference Tsai2007)
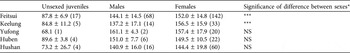
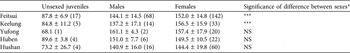
The overall sex ratio of captured C. flavomarginata was highly female-biased (G = 71.39, P < 0.001) and body size composition was dominated by adults (Fig. 2). The proportion of unsexed juveniles was low (7.4% of total captures). In those sites where > 20 turtles were captured the sex ratio was also significantly female-biased (Feitsui: G = 26.65, P < 0.001; Keelung: G = 7.91, P < 0.01; Yufong: G = 17.09, P < 0.001; Huben: G = 10.63, P < 0.01; Hushan: G = 24.90, P < 0.001).

Fig. 2 Frequency distribution of the carapace length of yellow-margined box turtles trapped during 2001–2008.
At Feitsui 227 turtles were captured a total of 892 times, of which 68.6% of the captured turtles had been marked during 1996–2000 (Chen & Lue, Reference Chen and Lue1999, Reference Chen and Lue2002). The proportions of unsexed juveniles and both sexes did not change significantly between 1996–2000 and 2002–2003 (G = 0.90, P = 0.639). The distribution of carapace length seems to be relatively stable (Fig. 3). At Keelung 52 turtles were captured a total of 193 times but the capture success was relatively low (Table 1). The mean carapace length of females was significantly larger than those of males at Feitsui and Keelung (Table 2) but there were no significant differences in carapace length between the sexes at Yufong, Huben and Hushan. The trapping success at Feitsui varied seasonally (Fig. 4), being highest in June and lowest in November.

Fig. 3 Frequency distribution of the carapace length of yellow-margined box turtles collected at the Feitsui Reservoir Protected Area (Fig. 1) in (a) 1996–2000 (data from Chen & Lue, Reference Chen and Lue1999, Reference Chen and Lue2002) and (b) 2002–2003 (this study).

Fig. 4 Mean monthly trapping success (± SD) for the yellow-margined box turtle at the Feitsui Reservoir Protected Area during April–November of 2002–2003.
Discussion
C. flavomarginata was described by Gray (Reference Gray1863) on the basis of a specimen collected by R. Swinhoe from Tamsui (Fig. 1) in northern Taiwan. In the original description C. flavomarginata was reported to be abundant in ponds in the Tamsui area. Some authors (e.g. Stejneger, Reference Stejneger1907; Smith, Reference Smith1931) therefore regarded this turtle as semi-aquatic. Chen (Reference Chen1969) noted that it could be found in wetland and high-elevation mountainous areas. However, this species is highly terrestrial, and is found in and around primary and well-developed secondary evergreen forest at low elevations (Chen & Lue, Reference Chen and Lue1999; Lue & Chen, Reference Lue and Chen1999). In central Taiwan Lin (Reference Lin1996) noted that this turtle was rarely found at altitudes > 500 m. In China C. flavomarginata seems to prefer hilly environments (200–500 m) and is usually found around the edges of humid forests or bushy areas (Wang, Reference Wang and Chen1991). In southern Ryukyus, Japan, the species prefers mesic evergreen forest rather than montane forests (Ota & Hamaguchi, Reference Ota and Hamaguchi2003). Horikawa (Reference Horikawa1934) noted that C. flavomarginata was usually seen in forest on low hills and in the foothills, and was sometimes active in nearby wetlands and grasslands. We found C. flavomarginata in wet meadows near forest, such as at Keelung and Su-ao.
Our survey shows that C. flavomarginata is still widely distributed in Taiwan and the population at Feitsui, in contiguous forested habitats with minimal human disturbance, appears to be stable.
The low capture success at most sites, however, suggests that C. flavomarginata survives at low population densities. We believe that the historical range of C. flavomarginata in Taiwan encompassed the low-elevation evergreen broad-leaf forests. However, its range has contracted and populations in lowland areas may have been extirpated because of habitat loss caused by land development. A specimen stored in Kaohsiung High School was from a low-elevation (20–30 m) area at Fudingjin near Kaohsiung City in the 1930s (B.-H. Lin, pers. comm.). We did not find the species near its type locality (Tamsui) although we found remnant populations in suburban areas near the coast, such as at Keelung and Hualien.
Historical collection data for C. flavomarginata in Taiwan includes specimens from Hualien (eastern), Nantou (central) and Pingtung (southern) counties (Field Museum of Natural History, Chicago, USA; Kuntz & Dien, Reference Kuntz and Dien1970), and from Hengchun (Pintung County, southern; California Academy of Sciences, San Francisco, USA). The specimens in the National Museum of Natural Science, Taichung, Taiwan, were collected from Hengchun. Chen (Reference Chen1969) reported that this turtle occurred in Ilan, Hualien, Hengchun, Puli (Nantou County) and Pasenshan (Taichung County). However, the locality at Pasenshan may be dubious because of its high altitude (750–1,100 m). We captured some individuals in most of the former collection localities but the abundance of the species may have decreased greatly because the capture success was low at most sites, probably because habitats have been greatly altered since the time of the earlier collections.
Gray (Reference Gray1870) noted that C. flavomarginata may be least abundant in southern Taiwan. We did not collect any individuals near the lowland and hilly areas in south-western Taiwan but, in the low-elevation forests in the Hengchun Peninsula, Horikawa (Reference Horikawa1934) reported that he could collect three individuals in 1 hour. Mao (Reference Mao1971) noted that c. 100 turtles had been found in one morning in broad-leaf forest near Hengchun. We were only able to collect three individuals in two mornings searching at Sheding (near Hengchun), although it is difficult to compare collection efficiency. Combining the results of Chen & Lue (Reference Chen and Lue1999, Reference Chen and Lue2002) and this study a total of 401 C. flavomarginata were captured from 1996 to 2003 at Feitsui. However, only about three individuals were found there in 6 hours by intensive searching in forest in 1996–1997 (Chen, Reference Chen1998).
Unbalanced sex ratios have been commonly reported in freshwater turtle populations (Gibbons, Reference Gibbons1970; Bury, Reference Bury, Harless and Morlock1979), and this is often attributed to sampling biases (Gibbons, Reference Gibbons and Gibbons1990). We found the sex ratio of C. flavomarginata to be significantly female-biased, and it did not change between 1996–1997 and 2002–2003 in the Feitsui population. The causes of the female-biased sex ratio of C. flavomarginata are unclear. The body size of the C. flavomarginata collected shows that individuals captured were predominantly adults. Terrestrial turtles may suffer high mortality in early stage of their life history (Frazer et al., Reference Frazer, Gibbons, Greene and Gibbons1990; Iverson, Reference Iverson1991). Nevertheless, juveniles were probably underrepresented in our data because of the difficulties of finding them in the dense forest understorey.
Habitat loss, expansion of the road network and habitat fragmentation have contributed to the decline of the terrestrial box turtle Terrapene carolina in the USA (Stickel, Reference Stickel1978; Williams & Parker, Reference Williams and Parker1987; Nazdrowicz et al., Reference Nazdrowicz, Bowman and Roth2008). The situation for C. flavomarginata in Taiwan seems to be similar. Deforestation and habitat fragmentation in low altitude evergreen forest seem to be the main threats to this species (Chen et al., Reference Chen, Lin, Chang, van Dijk, Stuart and Rhodin2000). In addition, female C. flavomarginata usually move to open habitats near the border of evergreen forests in summer (Lue & Chen, Reference Lue and Chen1999) and this may make the species more vulnerable to illegal collection.
The illegal cross-border trade may pose a serious threat to the long-term survival of C. flavomarginata, especially illegal collection for the pet and food markets in China. Many cases of cross-border trade to continental China have been reported; > 2,300 individuals of C. flavomarginata were confiscated in 2006–2009 (T.-H. Chen, pers. obs.). With low reproductive rates and late maturity (Iverson, Reference Iverson1991), the unregulated exploitation of C. flavomarginata is unsustainable.
The low capture success in our survey and the loss of habitat for the remaining populations indicates that most populations of C. flavomarginata require conservation attention. Most of the major localities of C. flavomarginata in Taiwan are not included in the existing protected area system. Even in protected areas, such as the Kenting National Park (near Hengchun), the pressure of illegal poaching is high (Tsai, Reference Tsai2007). Although it is difficult to protect habitats near highly developed areas such as Keelung and Huanlien, preservation of some habitats for C. flavomarginata in rural areas should be considered.
The most essential measure for the conservation of C. flavomarginata in Taiwan is to secure and conserve some relatively undisturbed habitats at low elevations, such as the Feitsui Reservoir Protected Area (which is protected for its water resources rather than for wildlife) or within national parks, where some box turtle populations are found. It is also important to monitor illegal capture and trade in this species, especially when such activities are conducted commercially. To develop an effective and comprehensive conservation programme for C. flavomarginata more detailed field surveys are needed to assess and monitor population trends, especially in highly developed lowland regions.
Acknowledgements
We thank E.Y. Tsoa and three anonymous reviewers for their valuable comments, and the following, who assisted with fieldwork: S.-L. Liu, Y.-D. Lue, S.-L. Chen, F.-S. Chen and S. Wang. This study was supported financially by the National Science Council, Council of Agriculture, Ministry of Economic Affairs (Water Resources Agency, Central Region Water Resources Office), Taiwan Endemic Species Research Institute, Republic of China (Grants to T.-H. Chen: NSC92-2311-B-396-002, NSC93-2311-B-396-001, 92AS-4.1.4-FC-R1, 93AS-4.1.1-FB-e2, 94AS-9.1.7-FB-e1, 95AS-11.5.3-FB-e1; T.-E. Lin: WRA97-150) and conducted under the permits from the Council of Agriculture (Permits to T.-H. Chen: 900115339, 0910116910, 0920127668, 0931614045, 0941611580; TESRI: 0931606790, 0970139786, 0971610794).
Biographical sketches
Yi-Fu Lin is working on the conservation ecology of threatened box turtles in Taiwan. Sheng-Hai Wu is interested in the comparative anatomy, ecology and systematics of vertebrates, especially of the herpetofauna. Te-En Lin researches the ecology and physiological ecology of the herpetofauna of Taiwan, including introduced amphibians and reptiles. Jean-Jay Mao devotes most of his research to the population ecology of reptiles. Tien-Hsi Chen has worked mainly on the ecology and conservation of the freshwater turtles of Taiwan.