Published online by Cambridge University Press: 09 August 2022
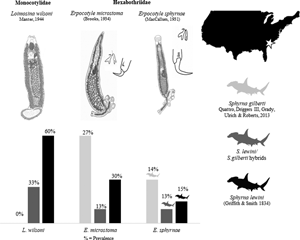
Neonates of hammerhead sharks (Sphyrnidae), Sphyrna lewini (Griffith and Smith, 1834), the sympatric cryptic species, Sphyrna gilberti Quattro et al., 2013, and their hybrids were captured in the western North Atlantic, along the coast of South Carolina, USA, between 2018 and 2019 and examined for gill monogenoids. Parasites were identified and redescribed from the gills of 79 neonates, and DNA sequences from partial fragments of the nuclear 28S ribosomal RNA (rDNA) and cytochrome c oxidase I mitochondrial DNA (COI) genes were generated to confirm species identifications. Three species of monogenoids from Hexabothriidae Price, 1942 and Monocotylidae Taschenberg, 1879 were determined and redescribed. Two species of Hexabothriidae, Erpocotyle microstoma (Brooks, 1934) and Erpocotyle sphyrnae (MacCallum, 1931), infecting both species of Sphyrna and hybrids; and 1 species of Monocotylidae, Loimosina wilsoni Manter, 1944, infecting only S. lewini and hybrids. Loimosina wilsoni 28S rDNA sequences matched those of Loimosina sp. from the southern coast of Brazil. Based on limited morphological analysis, Loimosina parawilsoni is likely a junior synonym of L. wilsoni. This is the first taxonomic study of monogenoids infecting S. gilberti and hybrids of S. gilberti and S. lewini.