A programming error occurred in deriving a variable for time of survey completion, which was used to form the time of questionnaire 1 completion in gestational weeks. The time of questionnaire return was used instead of time of questionnaire completion. This error downwardly biases all estimates of incidence, remission, and continuation rates by eating disorder subtypes. An updated version of Table 3 is given below. When replacing the time of questionnaire return with time of questionnaire completion all elements of the discussion and statistically significant tests at an alpha level of 0.05 remain the same.
Table 3. Age-adjusted rates of remission, continuation and incidence in 1000 person-weeks (95% confidence interval)
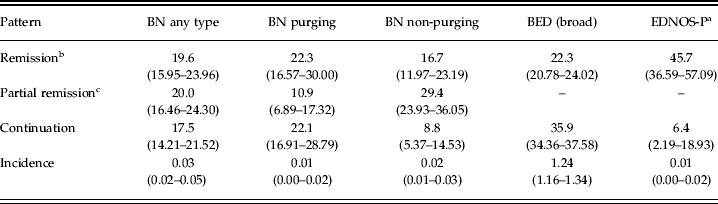
BN, Bulimia nervosa; BED, binge eating disorder; EDNOS-P, eating disorders not otherwise specified (purging at least weekly in the absence of binge eating).
a EDNOS-P and incidence calculations except for BED not age adjusted because of small sample size.
b Remission indicates rate of no eating disorder at time of survey completion during pregnancy.
c Partial remission in BN indicates absence of compensatory behaviors during early pregnancy.



