No CrossRef data available.
Article contents
Submillimeter Observations of NGC 4151: Evidence for Thermal Dust Emission
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 07 August 2017
Extract
Observations of NGC 4151 were made with the JCMT on UT 20 April 1988. The detector was the UKT14 system, a dual-beam, 3He cooled, composite doped Germanium bolometer. A bandpass filter was used to define a central wavelength of 438 μm (685 GHz) with a bandwidth of 84 GHz. The beam was approximately Gaussian, with a FWHM of 11′, and the pointing was good to 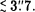 A very significant 5σ upper limit of 200 mJy was obtained. The Figure shows the continuum energy distribution for NGC 4151, made without correcting for beam size. When combined with the measured 155 μm flux density of 4.8 Jy, a lower limit on the spectral index of α155–438μm ≥ +3.06 is derived. Since the steepest cut off allowed by synchrotron self-absorption is α = +2.5, these observations can place an upper limit on the flux at 155 μm arising from a synchrotron self-absorbed source, with the rest arising from a thermal dust source.
A very significant 5σ upper limit of 200 mJy was obtained. The Figure shows the continuum energy distribution for NGC 4151, made without correcting for beam size. When combined with the measured 155 μm flux density of 4.8 Jy, a lower limit on the spectral index of α155–438μm ≥ +3.06 is derived. Since the steepest cut off allowed by synchrotron self-absorption is α = +2.5, these observations can place an upper limit on the flux at 155 μm arising from a synchrotron self-absorbed source, with the rest arising from a thermal dust source.
- Type
- Part 7: Dust, Molecules, Infrared and MM Radiation
- Information
- Symposium - International Astronomical Union , Volume 134: Active Galactic Nuclei , 1989 , pp. 398 - 399
- Copyright
- Copyright © Kluwer 1989


