To the Editor—Clostridium difficile ribotype (RT) 078 has been known as the predominant strain in animals (swine and cattle), and it has been increasingly identified in human C. difficile infection causing severe disease and increased mortality, especially in the community settingReference Goorhuis, Bakker and Corver 1 , Reference Keessen, Harmanus and Dohmen 2 . Recently, C. difficile RT 078 has been reported from both hospitalized patients (ages unknown) and environmental surfaces in eastern China.Reference Jin, Ni and Wei 3 In our study, we identified 6 C. difficile isolates of RT 078 from elderly patients (average age, 85 years) in a tertiary hospital in Beijing, China, from April 2015 to December 2015. A total of 50 C. difficile isolates, including RT 078, were obtained from 642 feces samples. Toxin genes tcdA, tcdB, cdtA, and cdtB, were identified using polymerase chain reaction (PCR) ribotyping, sequencing of tcdC, and multilocus sequence typing (MLST) for all isolates. In addition, C. difficile isolates of 6 RT 078 were tested for susceptibility to rifampin, moxifloxacin, vancomycin, clindamycin, levofloxacin, tetracycline, and erythromycin using Etest strips (bioMèrieux, Marcy-l'Étoile, France). The interpretation of minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) results followed the Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI) M100-S23 guideline recommendations published in 2013 4 and other previous studies.Reference Bourgault, Lamothe and Loo 5 – Reference Jin, Luo and Huang 7
In total, 12 nontoxingenic isolates were identified; the rest were positive for tcdA/tcdB. A total of 20 strain types (STs), distributed in clades 1 (38 isolates), 3 (1 isolate), 4 (3 isolates), and 5 (8 isolates) were identified (Figure 1A). The most frequent STs were ST2 (9 isolates), ST3 (8 isolates), and ST11 (8 isolates). Overall, 19 PCR RTs were found after comparing with the reference strains from European Centers for Disease Control (ECDC)-Brazier Collection and the American Tissue Culture Collection (ATCC) by capillary electrophoresis (Figure 1B). Of 8 ST11 isolates, 6 displayed the same band with ECDC 078 and ATCC 1875 (Figure 1C). In addition, all 6 isolates were also confirmed as RT078, with a mutation point at position 184 and Δ39-bp deletion. Our results resemble previous findings: a single ST11 was associated with several PCR RTs, including RTs 033, 045, 066, 078, 126, and 193,Reference Knetsch, Terveer and Lauber 8 suggesting that PCR ribotyping is essential for the subtyping of ST11 and ST1 (including RTs 016, 027, 036, and 176). The 6 RT 078 isolates were all sensitive to rifampin and vancomycin; only 1 of the 6 isolates (ie, 25053-2) was resistant to moxifloxacin and levofloxacin. Almost all RT 078 isolates were intermediately resistant or resistant to clindamycin, except for 25053-2. Antibiotic misuse in a large aging population is an area of concern in China; increased reports of C. difficile infection and the emergence of hypervirulent RT 027 and RT 078 CDI strains might represent a threat to the public health in the near future. Thus, we are seeking to develop standardized methods to diagnosis, treat, and prevent CDI and to identify and characterize the isolates by molecular typing through a nationwide surveillance network in China.
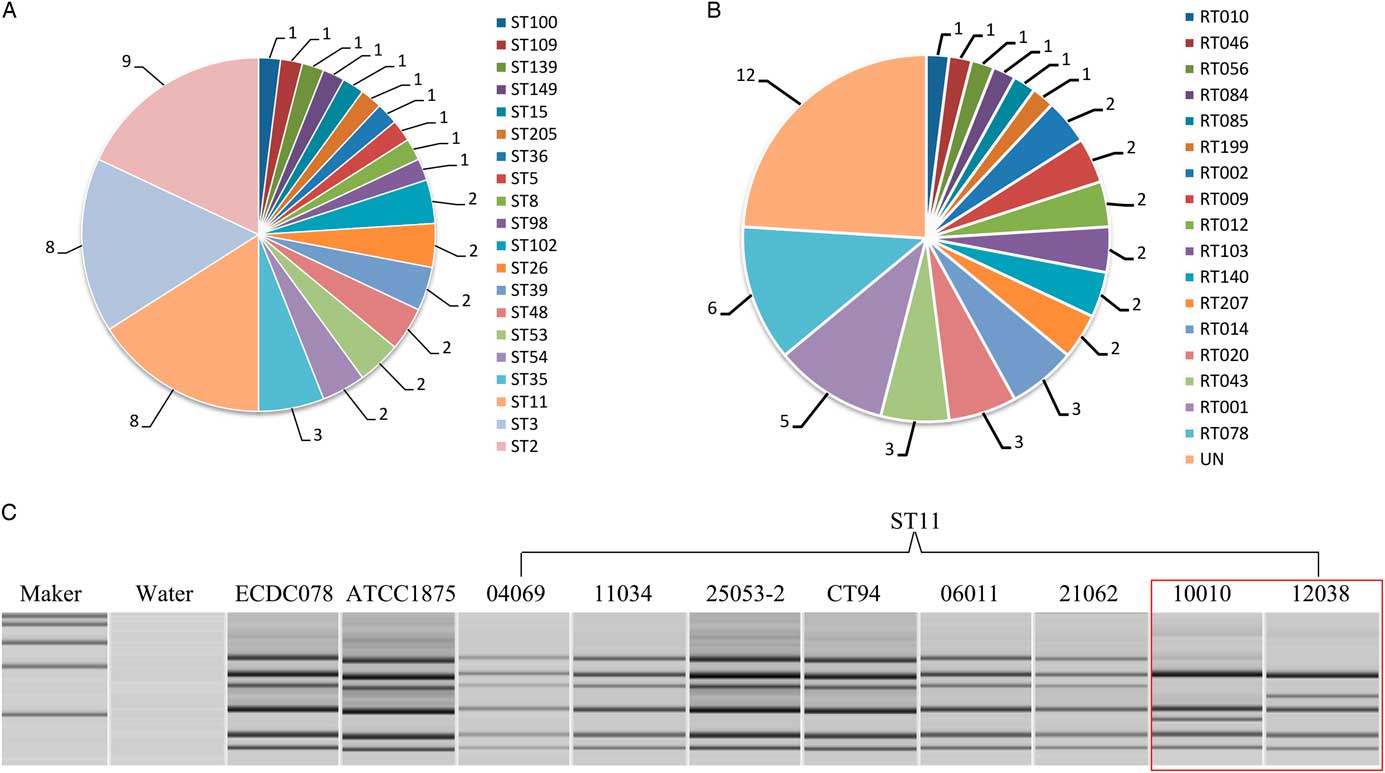
FIGURE 1 Strain types (STs) and PCR riboypes (RTs) identified in this study, and the capillary electrophoresis bands of 8 isolates with ST 11. A. Proportion of STs in this study. B. Proportion of RTs in this study. C. The capillary electrophoresis bands of 8 ST 11 isolates, of which 6 strains are RT 078 after comparing with references from the European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control and the American Type Culture Collection. The isolates in the red square are not RT 078, although they are ST11.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
Financial support: This study was supported by a grant from the State Key Laboratory of Infectious Disease Prevention and Control in China (grant no. 2017SKLD304), by a China–United Kingdom collaborative grant (grant no. 70029), and by a China–Australia collaborative grant (grant no. 70033).
Potential conflicts of interest: All authors report no conflicts of interest relevant to this article.



