Published online by Cambridge University Press: 26 January 2023
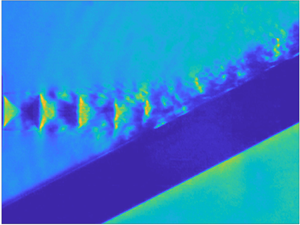
In this paper, the acoustic resonance mechanism for different axisymmetric screech modes of the underexpanded jets that impinge on an inclined plate is investigated experimentally. The ideally expanded Mach number of jets ( $M_j$) ranges from 1.05 to 1.56. The nozzle-to-plate distance at the jet axis and the impingement angle are respectively set as 5.0
$M_j$) ranges from 1.05 to 1.56. The nozzle-to-plate distance at the jet axis and the impingement angle are respectively set as 5.0 $D$ and
$D$ and  $30^{\circ }$, where
$30^{\circ }$, where  $D$ is the nozzle exit diameter. The acoustic results show that the
$D$ is the nozzle exit diameter. The acoustic results show that the  $M_j$ range for the A2 screech mode of impinging jets is broader than that of underexpanded free jets, and a new axisymmetric screech mode A3 appears. With the increase of
$M_j$ range for the A2 screech mode of impinging jets is broader than that of underexpanded free jets, and a new axisymmetric screech mode A3 appears. With the increase of  $M_j$, the effect of the impinging plate on the shock cell structures of jets becomes obvious gradually, and the second suboptimal peaks are evident in the axial wavenumber spectra of mean shock structures. The coherent flow structures at screech frequencies are extracted from time-resolved schlieren images via the spectral proper orthogonal decomposition (SPOD). The axial wavenumber spectra of the selected SPOD modes suggest that the A1, A2 and A3 screech modes are respectively closed by the guided jet modes that are energized by the interactions between the Kelvin–Helmholtz wavepacket and the first three shock wavenumber peaks. The upstream- and downstream-propagating waves that constitute the screech feedback loop are analysed by applying wavenumber filters to the wavenumber spectra of SPOD modes. The frequencies of these three screech modes can be predicted by the phase constraints between the nozzle exit and the rear edge of the third shock cell. For the A3 mode, the inclined plate invades the third shock cell with the increase of
$M_j$, the effect of the impinging plate on the shock cell structures of jets becomes obvious gradually, and the second suboptimal peaks are evident in the axial wavenumber spectra of mean shock structures. The coherent flow structures at screech frequencies are extracted from time-resolved schlieren images via the spectral proper orthogonal decomposition (SPOD). The axial wavenumber spectra of the selected SPOD modes suggest that the A1, A2 and A3 screech modes are respectively closed by the guided jet modes that are energized by the interactions between the Kelvin–Helmholtz wavepacket and the first three shock wavenumber peaks. The upstream- and downstream-propagating waves that constitute the screech feedback loop are analysed by applying wavenumber filters to the wavenumber spectra of SPOD modes. The frequencies of these three screech modes can be predicted by the phase constraints between the nozzle exit and the rear edge of the third shock cell. For the A3 mode, the inclined plate invades the third shock cell with the increase of  $M_j$, and the phase constraint cannot be satisfied at the lower side of the jets, which leads the A3 mode to fade away. The present results suggest that external boundaries can modulate the frequency and mode of jet screech by changing the axial spacings of shock cells.
$M_j$, and the phase constraint cannot be satisfied at the lower side of the jets, which leads the A3 mode to fade away. The present results suggest that external boundaries can modulate the frequency and mode of jet screech by changing the axial spacings of shock cells.