CLINICIAN'S CAPSULE
What is known about the topic?
People who experience imprisonment have poor health status compared with the general population, and limited US data indicate high ED utilization.
What did this study ask?
What are the rates and acuity of ED utilization for men and women in Ontario in prison and after release?
What did this study find?
In prison and post-release, men and women had higher ED utilization rates than age- and sex-matched people, mostly for high-acuity conditions.
Why does this study matter to clinicians?
Providing excellent ED care and delivering interventions in prison and in the ED could improve health for this population.
INTRODUCTION
Internationally, people who experience imprisonment have worse health status than the general population.Reference Fazel and Baillargeon1,Reference Kouyoumdjian, Schuler and Matheson2 In Canada, where over 37,000 people are in prison at any given time,Reference Walmsley3 there is a paucity of data on access to healthcareReference Kouyoumdjian, Schuler and Hwang4 and on the specific challenges of providing effective emergency department (ED) care for this population.
U.S. studies have shown that a history of imprisonment is associated with increased ED utilization in prison and after prison release. A Rhode Island study showed that people released from prison had more ED visits compared with the general population, mostly due to mental health concerns, substance use disorders, and ambulatory care sensitive conditions,Reference Frank, Andrews and Green5 which are medical conditions for which ambulatory care should prevent or reduce hospital use.6 A longitudinal study of older adults in California identified high ED utilization rates in prison and post-release.Reference Humphreys, Ahalt and Stijacic-Cenzer7 A study of persons with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) at the time of release from prison in Connecticut found increased ED utilization that was driven largely by comorbid medical and psychiatric conditions.Reference Meyer, Qiu and Chen8 Another California study found that most ED utilization for people who experienced imprisonment was for mental health conditions, and this population had a higher proportion of frequent ED use than the general population.Reference McConville, Mooney and Williams9 Research on ED use in people who experience imprisonment is limited, however, by a focus on subpopulations,Reference Humphreys, Ahalt and Stijacic-Cenzer7–Reference McConville, Mooney and Williams9 examination of only the post-release period,Reference Frank, Andrews and Green5,Reference Meyer, Qiu and Chen8 and having been conducted only in the United States, in which there is a lack of universal health insurance.Reference Frank, Andrews and Green5,Reference Humphreys, Ahalt and Stijacic-Cenzer7–Reference McConville, Mooney and Williams9
Population-based data on ED utilization could offer valuable insights regarding the health status, healthcare needs, and access to care for this structurally vulnerable population. Building on initial research on healthcare utilization for this population across settings,Reference Kouyoumdjian, Cheng and Fung10 our objective was to describe the ED utilization of men and women in prison and after release, and to compare these data with data for the general population in Ontario, Canada. We explored ED utilization for high urgency and ambulatory care sensitive conditions.
METHODS
Study design and setting
We conducted a cohort study of people released from provincial prison in Ontario, Canada, in 2010 and age- and sex-matched people from the general population. Provincial correctional facilities in Canada hold people who are awaiting trial or sentencing, or who are sentenced to less than 2 years in prison.Reference Reitano11
In Ontario, provincial prisons are publicly funded and administered. For Ontario residents, hospitalizations and medically necessary physician services are paid for through the public health insurance system, the Ontario Health Insurance Plan (OHIP), including in provincial prison.
Participants
For all adults released from provincial prison in Ontario in 2010, the Ontario Ministry of Community Safety and Correctional Services transferred data to ICES, an independent, non-profit organization funded by the Ontario Ministry of Health and Long-Term Care, which holds health administrative data for Ontario residents. As described previously,Reference Kouyoumdjian, Cheng and Fung10 we linked these data with an encoded OHIP number in the Registered Persons Database, which is a database of people who are eligible for OHIP coverage. We linked using OHIP numbers when provided and valid, and otherwise with a validated deterministic or probabilistic linkage method using name and date of birth.Reference Chong12 We excluded apparently incorrect linkages and people not released to the community (Appendix).
For each person in the prison release group, we randomly selected four age- and sex-matched people from the Registered Persons Database who were registered for OHIP coverage on the date of release for the person released from prison. We matched for age and sex because these factors are strongly associated with healthcare utilization.Reference Blackwell, Martinez and Gentleman13,Reference Fitzpatrick, Rosella and Calzavara14 We used a matching ratio of 4:1 for statistical efficiency.Reference Morgenstern and Winn15
Measurements
Sociodemographic information
We defined neighbourhood income quintile and rural/small town residence using the postal code at the time of prison release. From correctional data, we used the self-reported race categories, Aboriginal, Black, and White, and we combined remaining categories and missing people into a Missing/Other category.
Morbidity
Using methods validated using ICES data,Reference Antoniou, Zagorski and Loutfy16–Reference Tu, Campbell and Chen21 we identified people with a diagnosis of diabetes, hypertension, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), asthma, congestive heart failure (CHF), and HIV. We applied definitions from the Ontario Mental Health and Addictions Scorecard and Evaluation Framework to identify people with a diagnosis in the past 2 years of any substance-related disorders, anxiety disorders, mood disorders, or schizophrenia.22 To describe morbidity burden, we used the Johns Hopkins Adjusted Clinical Group system,Reference Johns Hopkins23 based on diagnostic codes in OHIP for ambulatory care, the Canadian Institute for Health Information (CIHI) Discharge Abstract Database for hospitalizations, and the Same Day Surgery Database. For each person, we calculated the number of Aggregated Diagnosis Groups, which are 32 diagnosis clusters that indicate the burden of disease morbidity,Reference Austin, van Walraven and Wodchis24 using data for the 2 years prior to the initial release from provincial prison in 2010 or the corresponding date for matched people in the general population.
Outcomes
We used CIHI National Ambulatory Care Reporting System data for ED visits. We excluded planned or scheduled visits. We categorized ED visits as high urgency if the Canadian Triage Acuity Scale (CTAS) was 1 (resuscitation), 2 (emergent), or 3 (urgent), or if the patient was admitted to hospital, as done previously.Reference Khan, Glazier and Moineddin25,Reference Murray, Bullard and Grafstein26 To identify ambulatory care sensitive conditions, we applied International Classification of Disease (ICD) codes for seizures, COPD, asthma, heart failure and pulmonary edema, hypertension, angina, and diabetes.6,Reference Billings, Zeitel and Lukomnik27 Using the main diagnosis in National Ambulatory Care Reporting System data, we categorized ED visit reasons by ICD10-CA chapter.28
Analysis
We described characteristics of those in the prison release group and the general population.
We ended the follow-up period at the earliest of death, loss of OHIP eligibility, prison re-admission (for the prison release group), or 2 years post-release (or the corresponding date for the general population group). We calculated person-time as the number of days in each period under study. We calculated the ED utilization rate as the number of ED encounters divided by person-time at risk, and by period relative to the time in prison, that is, in prison during the admission prior to the initial release in 2010 and by period after the initial release in 2010. For each person in the general population, we used the admission and release dates for the matched person in the prison group. For example, if a person was admitted to prison on January 1, 2010, and released on February 1, 2010, we used those dates for those matched to that person as the time “in prison” and February 1, 2010, as the date of release. We considered rates as statistically significantly different if their 95% CIs did not overlap.Reference Knezevic29
We calculated rate ratios for ED utilization for the prison release group compared with the general population group. We used generalized estimating equations with a negative binomial model, in which we controlled for correlation due to matching. For each sex, we developed bivariate models to describe the unadjusted association between imprisonment status and ED utilization, and multivariable models adjusted for neighbourhood income quintile and rurality, to see if associations persisted after controlling for these potential confounders. We calculated rates of ED utilization overall, for high urgency visits, and for ambulatory care sensitive conditions.
We calculated the proportion of people in the prison release group and general population group who accessed ED care in each follow-up period, including high urgency visits and the number and proportion of visits in each follow-up period by reason for use.
We obtained study approval from the St. Michael's Hospital Research Ethics Board (study 15–296) and from the Hamilton Integrated Research Ethics Board (study 4422-C).
RESULTS
Characteristics of study participants
Of 53,955 people released from provincial prison in Ontario in 2010, we achieved valid linkage for 52,546 (97.4%) (Appendix). We excluded 3,685 people who were not released to the community in 2010. We matched the 48,861 people in the prison release group with 195,444 people in the general population. By the end of the 2-year follow-up period, 673 people (1.4%) in the prison release group and 581 people (0.3%) in the general population group had died.
Compared with the general population group, people in the prison release group were more likely to live in neighbourhoods with the lowest income quintile, to have a higher number of aggregated diagnosis groups, to have COPD, and to have a mood disorder, schizophrenia, an anxiety disorder, or a substance-related disorder (Table 1).
Table 1. Characteristics of people released from provincial prison in Ontario in 2010 and age- and sex-matched people in the general population

CHF = Congestive heart failure; COPD = chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; IQR = interquartile range. *Data on race were not available for the general population. †Diagnosis based on health administrative data.
ED utilization in prison
In prison, men used the ED 0.6 times per person-year and women used the ED 1.3 times per person-year (Table 2), and 6.6% of people in the prison release group used the ED (Appendix). For men, 64.2% of visits were high urgency, and 73.0% of visits were high urgency for women. Ambulatory care sensitive conditions accounted for 3.2% of ED visits for men and 5.1% for women. By ICD-10-CA chapter, the main diagnosis was injury, poisoning, and certain other consequences of external causes for 34.7% of visits, symptoms, signs, and abnormal clinical and laboratory findings not otherwise classified for 17.4% of visits, and mental and behavioural disorders for 11.9% of visits (Table 3).
Table 2. Emergency department utilization for N = 48,861 people released from provincial prison in Ontario in 2010, by period relative to time in prison and gender
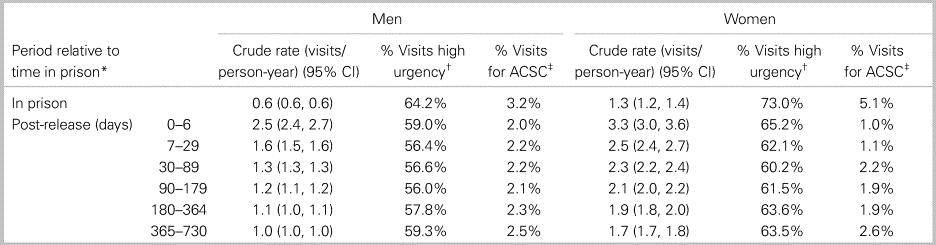
*In prison refers to the time in prison during the admission prior to the initial release in 2010, and post-release refers to the time after the initial release in 2010. †High urgency includes visits with a Canadian Triage Acuity Scale (CTAS) of 1 (resuscitation), 2 (emergent), or 3 (urgent) or if the patient was admitted to hospital. ‡ACSC are ambulatory care sensitive conditions.
Table 3. Reasons for emergency department utilization for 48,861 people released from provincial prison in Ontario in 2010, by ICD-10-CA chapter and in prison or post-release* (% of N visits)

* In prison refers to the time in prison during the admission prior to the initial release in 2010, and post-release refers to the 2 years after the initial release in 2010.
Compared with the general population in the corresponding time period, rates of use and the proportion of people with ED use were higher for men and women while in prison (Table 4, Figure 1, and Appendix). Rate ratios did not change substantially after adjusting for neighbourhood income quintile and rurality, at 3.2 for men and 6.4 for women (see Table 4).
Table 4. Rate ratios of emergency department utilization for 48,861 people released from provincial prison in Ontario in 2010 and 195,444 age- and sex-matched people in the general population, by period relative to time in prison* and gender

* In prison refers to the time in prison during the admission prior to the initial release in 2010, and post-release refers to the time after the initial release in 2010 or the corresponding period for matched people in the general population.

Figure 1. Rate ratios of high urgency* emergency department utilization for people released from provincial prison in Ontario in 2010 compared with age- and sex-matched people in the general population, by the period relative to time in prison† and gender. *High urgency includes visits with a Canadian Triage Acuity Scale (CTAS) of 1 (resuscitation), 2 (emergent), or 3 (urgent) or if the patient was admitted to hospital. †In prison refers to the time in prison during the admission prior to the initial release in 2010, and post-release refers to the time after the initial release in 2010, or the corresponding period for matched people in the general population.
ED utilization post-release
For the prison release group in the week after release, the ED utilization rate increased compared with the rate in prison (see Table 2) and 4.0% of people accessed ED care (Appendix). Over the 2 years post-release, the ED utilization rate decreased, and the majority of visits were high urgency (see Table 2). Ambulatory care sensitive conditions accounted for 1.0% to 2.6% of visits for men and women over the 2-year period (see Table 2).
By ICD-10-CA chapter, the main reasons for ED use in the 2 years post-release were similar to those in prison, with 23.6% for injury, poisoning and certain other consequences of external causes, 17.2% for mental and behavioural disorders, 15.5% for symptoms, signs and abnormal clinical and laboratory findings not elsewhere classified, and 10.7% for factors influencing health status and contact with health services (see Table 3).
During all periods post-release, the overall and high urgency ED utilization rates were significantly increased for men and women in the prison release group compared with the general population (see Table 4 and Figure 1), and a higher proportion of people in the prison release group accessed care compared with the general population group (Appendix).
ED utilization by women who experienced imprisonment
In prison and post-release, the ED utilization rate was significantly higher for women than men in the prison release group, and over 60% of visits were high urgency (see Table 2). For women, ED visits for ambulatory care sensitive conditions made up 5.1% of visits while in prison and 1.0% of ED visits during the week after release.
DISCUSSION
We found that rates of ED utilization were markedly higher for people in prison and after release compared with age- and sex-matched people in the general population. Rates of ED utilization were highest in the week after prison release. The majority of ED visits were high urgency, and a small proportion of visits were for ambulatory care sensitive conditions. The most common reasons for ED visits were related to injury and mental health disorders. In the prison-release group, women had significantly higher ED utilization than men and had a large proportion of high urgency visits.
Strengths of this study include that we comprehensively assessed ED utilization in prison and on release for a large and population-based sample, including for high urgency visits and for ambulatory care sensitive conditions. Instead of relying on self-reported healthcare use, we accessed health administrative data, which are comprehensive for Ontario residents in the setting of universal healthcare. We compared rates of use with several age- and sex-matched people in the general population for each person in the prison-release group.
This study also has several limitations. Indigenous people are overrepresented in provincial prisons, and healthcare utilization on First Nations is not included in provincial health administrative data. Healthcare utilization rates post-release may therefore underestimate use, which would lead to a conservative bias. Reasons for ED use are provided only by ICD-10-CA chapter, each of which includes multiple conditions or diseases. Our main study objective was to describe ED utilization in people who experience imprisonment, and we did not develop explanatory models to understand the causal impact of imprisonment on ED utilization. In prison, healthcare providers and correctional staff decide whether to send a patient to the ED, which could lead to fewer visits and proportionately greater use for high urgency reasons. The study results may not be generalizable to other jurisdictions, for example, those with different healthcare systems.
Consistent with prior research,Reference Kouyoumdjian, Schuler and Matheson2,Reference Frank, Andrews and Green5,Reference Humphreys, Ahalt and Stijacic-Cenzer7–Reference McConville, Mooney and Williams9,Reference Frank, Linder and Becker30,Reference Winkelman, Genao and Wildeman31 our study demonstrates that people who experience imprisonment are high users of EDs in comparison with the general population, and that a high proportion of visits was for injury and mental health issues. The majority of ED visits were for acute problems that were not ambulatory-care sensitive, suggesting that these patients may be using the ED more because they need the ED more for high-acuity care. For this population, therefore, efforts should focus on reducing the risk of emergency health issues, rather than on reducing unnecessary ED visits, recognizing that the same interventions such as discharge planning, case management, and primary care referral may be effective at achieving either goal.Reference Krieg, Hudon and Chouinard32,Reference Moe, Kirkland and Rawe33
This study has implications for ED care and research. Given the high ED use rate for people who experience imprisonment, ED clinicians and administrators might work towards ensuring appropriate and nondiscriminatory care in the ED for people in custody,Reference Fahmy, Kouyoumdjian and Berkowitz34–Reference Nolan and Ackery37 supporting effective transitions of care to and from prison, and developing mechanisms to identify patients who were recently released from prison and facilitating access to primary care. To better define prevention opportunities and treatment needs, future research should focus on the pathways leading to ED use for this population, including from the patient perspective, as well as on implementing and evaluating ED- and community-based strategies to reduce the risk of emergency health issues.
CONCLUSION
In conclusion, people who experience imprisonment have a high rate of ED utilization in prison and after prison release. Improved prison discharge planning, connecting patients who experience imprisonment with appropriate services, and attention to the health of women experiencing imprisonment are important foci, particularly at the time of prison release.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by ICES, which is funded by an annual grant from the Ontario Ministry of Health and Long-Term Care (MOHLTC). We acknowledge the Ontario Ministry of Community Safety and Correctional Services (MCSCS), which supported the study, and we appreciate the contributions of Mr. Michael Kirk to the study.
Parts of this material are based on data and/or information compiled and provided by CIHI. However, the analyses, conclusions, opinions, and statements expressed in the material are those of the authors and not necessarily those of CIHI. The analyses, opinions, results, and conclusions reported in this paper are also independent from the other sources that provided data and funding. No endorsement by ICES, the MOHLTC, or the MCSCS is intended or should be inferred.
Financial support
This study was funded by grants from the Physicians’ Services Incorporated Foundation (15–22) and the Foundation for Advancing Family Medicine of the College of Family Physicians of Canada.
Competing interests
None declared.
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL
The supplementary material for this article can be found at https://doi.org/10.1017/cem.2019.401







