Inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD), encompassing Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis, are chronic inflammatory disorders of the gastrointestinal tract(Reference Peyrin-Biroulet, Desreumaux and Sandborn1). As many as 1·4 million persons in the USA may suffer from IBD(Reference Loftus2). Current concepts of IBD pathogenesis suggest a complex interplay between genetic, nutritional and environmental factors, and the gut microbiota(Reference Peyrin-Biroulet, Desreumaux and Sandborn1, Reference Xavier and Podolsky3). Mild to moderate hyperhomocysteinaemia and gene variants of one-carbon metabolism are associated with IBD(Reference Peyrin-Biroulet, Gueant-Rodriguez and Chen4–Reference Mahmud, Molloy and McPartlin7). Markedly elevated concentrations of homocysteine were also found in the colonic mucosa of IBD patients(Reference Danese, Sgambato and Papa8, Reference Morgenstern, Raijmakers and Peters9). In the colon, a methyl-deficient diet (MDD) caused by folate and vitamin B12 deficiency and leading to increased homocysteine levels aggravated experimental colitis in rats by promoting oxidative stress, decreasing cell apoptosis and activating inter-related pro-inflammatory mechanisms(Reference Chen, Peyrin-Biroulet and George10). In the gastric mucosa of rats, a MDD affected cell organisation and function, with an alteration in mucin surface layer and a reduction in gastric gland layer(Reference Bossenmeyer-Pourie, Blaise and Pourie11).
Crohn's disease can involve the colon but also the small intestine. In one study, one-third of the patients had ileitis, colitis or ileocolitis at the time of diagnosis(Reference Peyrin-Biroulet, Loftus and Colombel12). Apoptosis of T cells has a key role in the pathophysiology of IBD(Reference Mudter and Neurath13). A disturbed ratio between pro-apoptotic and anti-apoptotic pathways mediated apoptosis resistance in patients with Crohn's disease(Reference Ina, Itoh and Fukushima14). By modulating apoptotic pathways(Reference Zhang, Cai and Adachi15), methyl donor status may contribute to intestinal homeostasis(Reference Peyrin-Biroulet, Rodriguez-Gueant and Chamaillard5). IBD are characterised by well-recognised defects in barrier and secretory function(Reference Henderson, van Limbergen and Schwarze16). The intestinal barrier, a complex system formed mostly by intestinal epithelial cells and the mucus layer, is a major element of intestinal homeostasis(Reference Roda, Sartini and Zambon17). Intestinal alkaline phosphatase is involved in the maintenance of gut microbial homeostasis(Reference Malo, Alam and Mostafa18). Disturbed antimicrobial defence provided by Paneth cells may be a critical factor in the pathogenesis of Crohn's disease(Reference Wehkamp, Koslowski and Wang19, Reference Peyrin-Biroulet, Beisner and Wang20). The Wnt/β-catenin pathway plays essential roles during development and adult homeostasis, including determination, proliferation, migration and differentiation of the intestine(Reference Clevers21).
The effects of a MDD on small-intestinal differentiation and barrier function are unknown. This experiment was carried out in pregnant animals and the in utero and postnatal effects of a MDD were investigated in rat pups. The aim of the present study was to examine the impact of a MDD (a diet deprived of folate, vitamin B12 and choline) on cell organisation, apoptosis, proliferation and differentiation in both segments of the small intestine in rats.
Materials and methods
Animal experiments
Adult female Wistar rats (Charles River) were maintained under standard laboratory conditions, on a 12 h light–12 h dark cycle, with food and water available ad libitum. At 1 month before pregnancy, adult females were fed with either a standard food (n 18, Maintenance diet M20; Scientific Animal Food and Engineering) or a diet without vitamin B12, folate and choline (n 19; Special Diet Service) according to Blaise et al. (Reference Blaise, Alberto and Nedelec22). Choline was eliminated from the diet because the alternative pathway for the methylation of homocysteine to form methionine is catalysed by betaine-homocysteine methyltransferase that uses betaine, a metabolite of choline, as the methyl group donor(Reference Selhub23). Within 24 h after delivery, litter size was reduced to ten pups for subsequent standardisation of the study, as described previously(Reference Blaise, Alberto and Nedelec22). The assigned diet was constantly maintained until the weaning of the offspring (i.e. postnatal day 21) and the pups were fed with the same diet as their mother until killing. The following two groups were considered: ten deprived pups from five dams subjected to methyl donor deficiency (two per dam) and eight control pups from four dams subjected to a normal diet (two per dam). The study was conducted in accordance with the National Institutes of Health Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. Animal experiments were performed in accredited establishments (Inserm U954) according to governmental guidelines no. 86/609/CEE.
Blood and small-intestinal tissue samples
The eighteen pups were killed at 26 d of age by excess halothane and weighed. Intracardiac blood samples were drawn from the weaning control (n 8) and MDD (n 10) pups for the measurement of plasma concentrations of vitamin B12, B9 and homocysteine. Plasma concentrations of vitamin B12 and folate were determined by radio-dilution isotope assay (simulTRAC-SNB; ICN). Homocysteine concentrations were measured by HPLC (Waters) coupled to MS (Api 4000 Qtrap; Applied Biosystems)(Reference Bossenmeyer-Pourie, Blaise and Pourie11). The intestine was then rapidly harvested.
Histology and staining procedures
The bowel was quickly removed and cut open longitudinally. Samples of the proximal (1 cm below the duodenum) and distal (three-quarters of the bowel length) bowel were harvested for each pup with the same protocol. Subsequently, bowel tissues were either fixed in 4 % buffered formalin, embedded in paraffin or snap-frozen in liquid N2, and stored at − 80°C until further use.
Light microscopic analysis
Light microscopic examination (Olympus BX60F microscope) was made on 5 μm-thick sections (stained with haematoxylin–eosin–safran). For each animal (controls, n 8; MDD animals, n 10), measurements of wall thickness, villous height, crypt length, submucosal thickness, muscular layer thickness, crypt density, villous density, villous width and enterocyte size were made for the proximal and distal small intestine.
Goblet cells were identified by standard staining with Alcian blue pH 2·5 (for acidic sialomucins), Alcian blue pH 1·0 (for acidic sulfomucins) and periodic acid–Schiff for neutral and acidic mucins. From each group, three animals (controls, n 3; MDD animals, n 3) were used with a sample of the proximal bowel and a sample of the distal bowel for each animal.
Intestinal alkaline phosphatase was detected according to the useful protocol(Reference Cox and Singer24) by using specific chromogen: 5-bromo-4-chloro-3-indoyl phosphatase (Roche) and nitro blue tetrazolium (Roche). From each group, three animals of each group (controls, n 3; MDD animals, n 3) were used with a sample of the proximal bowel and a sample of the distal bowel for each animal.
Immunohistochemical analysis
Sections were processed for peroxidase immunostaining using the Dako Laboratories system following the manufacturer's recommendations. Immunohistochemistry was performed on formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissue sections using the streptavidin–biotin–peroxidase method in a Dakocytomation AutoStainer (Dako). The sections were first deparaffinised and rehydrated. Antigen retrieval was performed by incubating the slides in Tris–citrate buffer (pH 6·0) for 20 min at 97°C (PT Link; Dakocytomation). For lysosyme antibody use, pretreatment with trypsin was performed. Endogenous peroxidase activity was blocked by incubation with 3 % H2O2 for 10 min. Primary antibodies used were as follows: rabbit anti-Ki-67 (1:100; Thermo Scientific), rabbit anti-mucin-2 (MUC-2, 1:200; Santa Cruz Biotechnology), rabbit anti-lysosyme (1:1000; Dakocytomation), rabbit anti-cleaved caspase-3 (1:400; Cell Signaling), rabbit anti-proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA, 1:800; Abcam), rabbit myeloperoxidase (1:4000; Dakocytomation), rabbit anti-phospho-histone H3 (1:2000; Medical and Biological Laboratories) and goat anti-minichromosome maintenance (MCM) protein 6 (1:400; Santa Cruz Biotechnology). Primary antibodies were incubated on slides for 30 min at room temperature. Biotinylated secondary antibodies were polyclonal swine anti-rabbit (1:150; Dakocytomation), polyclonal rabbit anti-goat (1:150; Dakocytomation) or polyclonal goat anti-mouse (1:150; Dakocytomation).
Sections were incubated with 3,3′-diaminobenzidine substrate (Dakocytomation) for 1 min before the reaction was stopped in distilled water, and counterstained with haematoxylin. Withdrawal of the primary antibody and replacement with a non-specific antibody were used as negative controls.
Cell proliferation was evaluated by MCM-6, Ki-67, PCNA and phospho-histone H3 antibody immunostaining: the number of positive cells in the crypt and villus was counted microscopically for a total of 500 cells in control (n 4) and MDD animals (n 4) and the index of proliferation for each marker was determined (for a total of 100 cells).
Apoptosis was investigated using cleaved caspase-3 antibody: the labelling index was determined by counting microscopically positive cells in control (n 8) and MDD animals (n 10).
Paneth cells were evaluated by the labelling index using lysosyme antibody: positive cells in the crypt were counted microscopically in control (n 3) and MDD animals (n 3).
Goblets cells were secondary evaluated by determining the labelling index using MUC-2 antibody: positive cells were counted microscopically in the crypt and villus in control (n 3) and MDD animals (n 3). Mucus production was investigated by examination of the mucus layer.
Apostain labelling (anti-single-stranded DNA)
Apoptosis was also investigated using the Apostain method according to the manufacturer's recommendations (Bender MedSystems)(Reference Verzola, Gandolfo and Ferrario25). The labelling index was determined by counting microscopically the number of crypt positive cells in control (n 3) and MDD animals (n 3) in both proximal and distal small bowels.
Immunoblot
Soluble extracts (20 μg/lane) were separated by 5–10 % SDS–PAGE under reducing conditions and transferred to Immobilon membranes (Millipore Corporation). Blots were blocked in 5 % non-fat milk in Tris-buffered saline Tween-20 (10 mm-Tris–HCl, 150 mm-NaCl, pH 7·6, containing 0·1 % Tween-20) for 1 h at 37°C and then incubated with primary antibodies overnight at 4°C. The membranes were extensively washed with Tris-buffered saline Tween-20 and then incubated for 1 h at room temperature with an appropriate secondary antibody. After future washings, blots were developed using enhanced chemiluminescence (Amersham Biosciences). Primary antibodies for β-actin (1:1000; US Biological), caudal type homeobox 2 (CDX-2) (1:1000; BioGenex), β-catenin (1:1000; Cell Signaling Technology), cyclin-dependent kinase 2 (cdk2, 1:1000; Santa Cruz Biotechnology Inc.), cyclin E (1:1000; Millipore) and protein phosphatase 2Ac (PP2Ac) subunit (1:1000; Cell Signaling Technology) were used. Appropriate secondary antibodies conjugated to horseradish peroxidase were used for detection with enhanced chemiluminescence. Soluble extracts were obtained from the distal small intestine of three control animals and three MDD animals.
Protein interactions: Duolink
The ‘proximity ligation’ assay (Duolink®in situ PLA™ reagents; Olink Bioscience, Eurogentec) was used according to the manufacturer's instructions to visualise and quantify, in mucosal sections, the β-catenin–E-cadherin interaction and the serine phosphorylation of β-catenin. Regular immunostaining antibodies were used combined with a generic Duolink™ kit (Eurogentec). Primary antibodies were β-catenin (1:200; Cell Signaling Technology), E-cadherin (1:200; Zymed Invitrogen Laboratories) and phosphor-serine (1:100; Cell Signaling Technology). This analysis was performed in the distal small intestine of three control and three MDD animals. A pair of oligonucleotide-labelled secondary antibodies (PLA probes) binds to the primary antibodies, and generates a signal only when the two probes are in close proximity. After amplification, the signal from each detected pair is visualised as an individual fluorescent dot. The PLA signals were counted and assigned to a specific subcellular location based on microscopic images (Olympus BX51WI microscope with BlobFinder freeware from the Centre for Image Analysis, Uppsala University).
Statistical analysis
Mann–Whitney U tests were used to determine statistical significance, with a limit set to P< 0·05 using Statview 5.0 software (JMP).
Results
All control dams (n 18) had a successful gestation and kept their litter until the end of the suckling period. Among the MDD females (n 19), three of them did not deliver and one of them killed all its pups on postnatal day 12. There was no difference in litter size between the control and MDD dams, with a median of eleven pups per litter for both groups.
Confirmation of methyl donor deficiency
Levels of vitamin B12, folate and homocysteine were measured in blood samples of rats to evaluate the influence of the MDD on these parameters (Table 1). As expected, at 26 d of age, compared with the standard diet, the deficient diet significantly decreased the plasma concentration of both vitamin B12 and folate and was accompanied by an increase in the plasma concentration of homocysteine. Tissue levels of vitamin B12 and folate were not measured.
Table 1 Plasma levels of homocysteine, vitamin B12 and vitamin B9 (folate) in methyl-deficient diet (MDD) and control rat pups (Mean values with their standard errors)
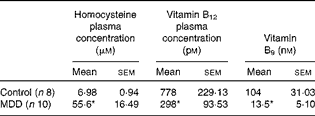
* Mean values were significantly different from those of the controls (P< 0·01; Mann–Whitney U test).
Methyl-deficient diet effects on body weight and small-bowel structure
At weaning, the MDD pups (n 10) weighed significantly less than the control pups (n 8) (controls 31·57 (sem 6·84) g v. MDD animals 21·41 (sem 0·96) g; P< 0·001).
The distal intestine of MDD pups (Fig. 1(d)) showed global hypotrophy compared with that of control pups (Fig. 1(b)). By contrast, there was no difference regarding the proximal small-bowel structure between the control and MDD animals (Fig. 1(a) and (c), respectively).

Fig. 1 Microscopic views of (a, c) the proximal and (b, d) distal small bowel in (a, b) control and (c, d) methyl-deficient diet (MDD) rat pups (haematoxylin–eosin–safran × 200). There was shows a global hypotrophy of the distal small intestine in (d) MDD animals.
As described in Table 2, the major changes were observed in the distal small bowel of MDD animals, with a decrease in distal bowel thickness in MDD pups compared with the controls, whereas no difference was noted regarding the proximal small-bowel thickness of MDD and control pups. The distal bowel of MDD pups showed a global wall hypotrophy with smaller villous height, smaller crypt length, smaller submucosal thickness and smaller muscular layer thickness. In the distal small intestine, villous width was significantly smaller in MDD animals with a decrease in enterocyte size.
Table 2 Morphological changes in proximal and distal small-bowel walls in methyl-deficient diet (MDD) and control rat pups (Mean values with their standard errors)

Mean values were significantly different from those of the controls: * P< 0·05; ** P< 0·01 (Mann–Whitney U test).
In the proximal bowel, minor changes were found in MDD animals with smaller crypt width, smaller villous width and smaller villous axis width. The MDD did not affect the other parameters studied (villous height, crypt length, submucosal thickness, muscular layer thickness, crypt density, villous density, enterocyte size and ratio of villous height:crypt length) in the proximal small bowel of rats.
Overall, these findings indicate that the MDD affects differently the distal and proximal small bowel, with major changes producing a global hypotrophy of the intestinal wall in the distal small bowel.
Methyl-deficient diet effects on cell apoptosis and proliferation in small-bowel mucosa
Cleaved caspase-3 and Apostain-positive cells in crypts are shown in Fig. 2. In control rats (Fig. 2(a) and (c)), the number of positive cleaved caspase-3 cells was significantly lower than that in MDD animals in crypts of both proximal (MDD animals 3·5 (sd 0·40) % v. controls 1·4 (sd 1·02) %, P= 0·018; Fig. 2(b) and (e)) and distal small bowel (MDD animals 3·37 (sd 2·27) % v. controls 0·4 (sd 0·4) %, P< 0·001; Fig. 2(d) and (e))). The Apostain labelling index confirmed an increase in apoptotic cell number in crypts of MDD animals in both proximal (MDD animals 12·93 (sd 1·98) % v. controls 3·22 (sd 0·37) %, P< 0·001) and distal small bowels (MDD animals 9·28 (sd 2·14) % v. controls 4·35 (sd 0·64) %; P= 0·005) (Fig. 2(f)).

Fig. 2 Cleaved caspase-3 immunostaining in the proximal small intestine of (a) control and (b) methyl-deficient diet (MDD) animals shows an increase in labelling cells in the crypt of MDD pups. The same observation was made for the distal small intestine in both (c) control and (d) MDD animals ( × 400). (e) Results of the cleaved caspase-3 index. Values are means, with standard deviations represented by vertical bars. * Mean value for MDD animals (n 10, ![]() ) was significantly different from that of the controls (n 8,
) was significantly different from that of the controls (n 8, ![]() ) (P< 0·05; Mann–Whitney U test). (f) Results of the Apostain labelling index. Values are means, with standard deviations represented by vertical bars. * Mean value for MDD animals (n 3,
) (P< 0·05; Mann–Whitney U test). (f) Results of the Apostain labelling index. Values are means, with standard deviations represented by vertical bars. * Mean value for MDD animals (n 3, ![]() ) was significantly different from that of the controls (n 3,
) was significantly different from that of the controls (n 3, ![]() ) (P< 0·05; Mann–Whitney U test).
) (P< 0·05; Mann–Whitney U test).
Proliferation was assessed by immunohistochemical analysis using four markers: phospho-histone H3, a marker of cells in late G2 and M phase(Reference Scott, Morris and Bird26); Ki-67, a protein present during all active phases of the cell cycle (G1, S, G2 and mitosis)(Reference Giaginis, Vgenopoulou and Vielh27); PCNA, a polymerase-associated protein that is synthesised in early G1 and S phases of the cell cycle(Reference Giaginis, Vgenopoulou and Vielh27); MCM-6 (MCM protein-6), a marker of proliferation (present in the active phase of the cell cycle G1, S, G2 and mitosis) and immaturity(Reference Stoeber, Tlsty and Happerfield28). The results are shown in Fig. 3. There was no difference regarding the proliferation index obtained with phospho-histone H3 immunostaining between the control and MDD animals (proximal bowel (Fig. 3(e)): MDD animals 4·1 (sd 0·70) % v. controls 4·18 (sd 1·3) %, P= 0·81; distal bowel (Fig. 3(f)): MDD animals 4·40 (sd 0·77) % v. controls 4·47 (sd 1·3) %, P= 0·69). The Ki-67 staining index in the crypts and villus of the distal and proximal small-intestinal mucosa in MDD and control animals was broadly similar (Fig. 3(e) and (f)). The number of MCM-6-positive cells was significantly higher in MDD pups in the villus of the distal bowel when compared with the controls (MDD animals 55·8 (sd 13·38) % v. controls 3 (sd 1·73) %, P= 0·046; Fig. 3(c), (d) and (f)). By contrast, the number of crypt cells staining MCM-6-positive did not differ between the MDD and control animals in the distal small bowel (84 (sd 5·57) % v. 83·83 (sd 5·57) %, respectively, P= 0·82). Conversely, in the proximal small bowel (Fig. 3(a), (b) and (e)), similar expression levels of MCM-6 protein were noted in the villus of control and MDD animals (MDD animals 2·67 (sd 0·58) % v. controls 3 (sd 1) %, P= 0·64), whereas a decrease in positive MCM-6 cells was observed in the crypts of MDD animals (MDD animals 52·83 (sd 10·77) % v. controls 83·17 (sd 2·57) %, P= 0·048). A decreased number of PCNA-positive cells was noted in the crypts of the proximal small bowel of MDD animals compared with the controls (46·25 (sd 9·21) % v. 59 (sd 6·39) %, respectively, P= 0·05; Fig. 3(e)), whereas the number of PCNA-positive cells did not differ between the MDD and control animals in the distal small bowel (47·5 (sd 9·21) % v. 59 (sd 6·39) %, respectively, P= 0·47; Fig. 3(f)).

Fig. 3 Minichromosome maintenance 6 (MCM-6) immunostaining in the proximal small intestine of (a) control and (b) methyl-deficient diet (MDD) animals shows a decrease in labelling cells in the crypt of MDD pups. In the distal small bowel, the number of labelling cells in crypts is broadly similar in (c) controls and (d) MDD animals, while there was an increase in labelling cells in the villus (d) ( × 400). (e and f) Results of the labelling index after immunostaining for phospho-histone H3 (PHH3), Ki-67 and MCM-6. Values are means, with standard deviations represented by vertical bars in (e) the proximal and (f) distal small bowel. * Mean value for MDD animals (n 4, ![]() ) was significantly different from that of the controls (n 4,
) was significantly different from that of the controls (n 4, ![]() ) (P< 0·05; Mann–Whitney U test). PHH3c, crypt PHH3 index; MCM-6c, crypt MCM-6 index; MCM-6v, villous MCM-6 index; Ki-67c, crypt Ki-67 index; Ki-67v, villous Ki-67 index; PCNAc, crypt proliferating cell nuclear antigen index.
) (P< 0·05; Mann–Whitney U test). PHH3c, crypt PHH3 index; MCM-6c, crypt MCM-6 index; MCM-6v, villous MCM-6 index; Ki-67c, crypt Ki-67 index; Ki-67v, villous Ki-67 index; PCNAc, crypt proliferating cell nuclear antigen index.
Taken together, these data show that the MDD increases cell apoptosis in the crypts of both proximal and distal small bowels. Proliferation is also affected by the MDD with an increased positive MCM-6 cell number in the villus of the distal small intestine and a decreased positive MCM-6 and PCNA cell number in proximal small-bowel mucosa.
Methyl-deficient diet affects enterocyte differentiation in distal small bowel
In enterocytes from the control animals (Fig. 4(a), (c), (e) and (g)), a gradual histomorphological change was noted as the cells progressed from the villus base to the villus tip and was characterised by increasing cytoplasmic eosinophilia, and rounding and more basal position of the nucleus. By contrast, in MDD animals, enterocytes maintained the same morphology along the length of the villus and enterocytes situated in the tip of the villus had the same aspect as those situated in crypts, characterised by a darker, more amphophilic cytoplasm, and more elongated and centrally positioned nuclei. The morphology of enterocytes (absorptive epithelial cells) in the distal small intestine appeared abnormal on haematoxylin–eosin–safran-stained histological sections in MDD pups (Fig. 4(d) and (h)) compared with control pups (Fig. 4(c) and (g)). In the proximal small intestine, the morphology of enterocytes in controls (Fig. 4(a) and (e)) and MDD pups (Fig. 4(b) and (f)) indicated normal maturation of absorptive epithelial cells.

Fig. 4 Haematoxylin–eosin-safran staining comparing (e, f, g, h) crypts and (a, b, c, d) the top of the villus of enterocytes shows a normal morphological maturation of enterocytes in the proximal bowel of (a, e) controls and (b, f) methyl-deficient diet (MDD) animals. In the distal small bowel, the absence of morphological enterocyte changes in MDD animals when comparing (h) crypt and (d) the top of the villus indicates an absence of enterocyte maturation ( × 1000). (i, j, k, l) Intestinal alkaline phosphatase labelling shows a normal staining of the villus in the proximal small bowel of (i) control and (j) MDD pups, whereas a decrease in intestinal alkaline phosphatase staining was noted in the distal small intestine of (l) MDD pups compared with (k) control animals ( × 400; three controls and three MDD animals).
To further characterise this phenotype, we examined the expression of a well-established marker of enterocyte maturation, namely intestinal alkaline phosphatase(Reference Lalles29). In the proximal small intestine, an appropriate expression of intestinal alkaline phosphatase was observed in controls (Fig. 4(i)) and MDD animals (Fig. 4(j)). By contrast, very weak expression of intestinal alkaline phosphatase was observed in MDD animals (Fig. 4(l)) compared with the controls (Fig. 4(k)) in the distal small intestine. Furthermore, as shown in Fig. 3(d), inappropriate persistent expression of MCM-6, a marker of villus epithelial immaturity, along the entire villus axis was observed in the distal small intestine of MDD animals associated with decreased size of enterocytes.
Collectively, these results indicate a lack of enterocyte differentiation in the distal small bowel of MDD pups.
Methyl-deficient diet alters β-catenin expression in the distal small bowel
The Wnt/β-catenin signalling pathway is involved in virtually every aspect of embryonic development and also controls homeostatic self-renewal in a number of adult tissues, including the intestine(Reference Clevers21). Immunostaining showed a loss of expression of β-catenin in the tip of the villus in the distal small bowel of MDD rat pups compared with the control animals. By contrast, the MDD did not affect β-catenin expression in the proximal small bowel of rat pups (data not shown).
Park et al. (Reference Park, Kim and Lee30) demonstrated that cdk2 in association with cyclin E directly binds to β-catenin and promotes the rapid degradation of cytosolic β-catenin. We previously showed that cellular deficiency in vitamin B12 was associated with a reduced expression of cdk2–cyclin E level in neuroblastoma cells(Reference Battaglia-Hsu, Akchiche and Noel31). In line with these previous reports, Western blot analysis showed that β-catenin, cdk2 and cyclin E expression levels were lower in MDD rat pups compared with the control animals (Fig. 5(c)). Low levels of cyclin E and cdk2 may reflect a mechanism whereby the intestine limits β-catenin degradation in the case of the MDD.

Fig. 5 (a) Results of the Duolink™ assay showing a decreased β-catenin–E-cadherin interaction in the distal small bowel of methyl-deficient diet (MDD) rat pups (a) (the study was made on fifty-four epithelial cells in control animals and fifty-seven epithelial cells in MDD animals). Values are means, with standard deviations represented by vertical bars. * Mean value was significantly different from the controls (P< 0·0001). β-Catenin phosphorylation on serine residues was increased in the distal small bowel of MDD animals (b) (the study was made on fifty-two epithelial cells in control animals and fifty-seven epithelial cells in MDD animals). Values are means, with standard deviations represented by vertical bars. * Mean value was significantly different from the controls (P< 0·0001). (c) Western blot of protein phosphatase 2Ac (PP2Ac), caudal type homeobox 2 (CDX-2), cyclin E, cdk2 and β-catenin using β-actin as the control in the distal small bowel (controls (n 3) and MDD animals (n 3)).
Protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A) comprises a family of serine/threonine phosphatases(Reference Janssens and Goris32). At the plasma membrane, PP2A forms a complex with E-cadherin and β-catenin, two components of the Wnt signalling cascade(Reference Janssens and Goris32). In PP2A− / − embryos, both E-cadherin and β-catenin are redistributed to the cytoplasm, resulting in the degradation of β-catenin in both the presence and absence of a Wnt signal(Reference Janssens and Goris32). Consistently, Western blot analysis of protein extracts from the distal small bowel revealed decreased PP2Ac levels (Fig. 5(c)), and Duolink™ results in the distal small bowel showed a decreased interaction between β-catenin and E-cadherin in MDD animals compared with the controls (MDD animals 22·7 (sd 15·3) v. controls 64·4 (sd 29·7), respectively; P< 0·001; Fig. 5(a)). Impaired β-catenin expression was accompanied by an increased phosphorylation of β-catenin on serine residues in MDD animals compared with the controls (MDD animals 22·17 (sd 12·62) v. controls 10·86 (sd 8·10), respectively, P< 0·001; Fig. 5(b)).
We previously demonstrated that deprivation of methyl group donors down-regulated CDX-2 protein(Reference Lu, Freund and Muller33), a master regulator of intestinal differentiation(Reference Coskun, Troelsen and Nielsen34). CDX-2 expression levels were similar in MDD and control animals (Fig. 5(c)), indicating that the MDD impairs enterocyte differentiation in the distal small bowel by altering the β-catenin pathway and not CDX-2 expression.
Methyl-deficient diet impairs goblet cell and Paneth cell lineages in the proximal small bowel
Intestinal homeostasis in healthy subjects is ensured by a complex system called the ‘intestinal barrier’, composed mainly of a thick mucus layer containing antimicrobial products(Reference Roda, Sartini and Zambon17). A global defect of mucosal immune response (barrier function, innate and adaptative responses) is observed in IBD(Reference Roda, Sartini and Zambon17). MUC-2 is the major macromolecular constituent of intestinal mucus(Reference Heazlewood, Cook and Eri35). Paneth cells are secretory epithelial cells of small-intestinal crypts, known to synthesise and secrete several antimicrobial peptides, including lysozyme, secretory phospho-lipase A2 and human defensins(Reference Wehkamp, Salzman and Porter36).
Lysozyme antibody was thus used to stain Paneth cells. As depicted in Fig. 6, the number of lysozyme-stained cells was decreased in crypts of the proximal bowel of MDD pups (Fig. 6(b)) and the Paneth cell staining index was significantly lower in MDD pups (Fig. 6(e)) (MDD animals 8·66 (sd 3·7) % v. controls 21·66 (sd 3·61) %). In the distal bowel, the MDD did not affect the number of Paneth cells (Fig. 6(c), (d) and (e)).

Fig. 6 Lysosyme immunostaining in the proximal small intestine shows a decrease in labelling cells in crypts of (b) methyl-deficient diet (MDD) pups compared with (a) control animals. In the distal small intestine, no difference was noted between (c) control and (d) MDD animals ( × 400). (e) Results of the labelling index obtained after lysosyme immunostaining. Values are means (controls, n 3; MDD animals, n 3), with standard deviations represented by vertical bars. Paneth cells were evaluated by the labelling index using lysosyme antibody: positive cells in the crypt were counted microscopically for a total of 100 cells. * Mean value for MDD animals (![]() ) was significantly different from that of the controls (
) was significantly different from that of the controls (![]() ) (P< 0·05; Mann–Whitney U test).
) (P< 0·05; Mann–Whitney U test).
Goblet cells were evaluated by MUC-2 immunostaining and standard staining (Alcian blue pH 2·5, Alcian blue pH 1·0 and periodic acid–Schiff). A decrease in mucus layer thickness was observed in MDD rats (Fig. 7(b) and (d)). In the proximal small intestine, the goblet cell index obtained with MUC-2 immunostaining in the crypt and villus was significantly lower in MDD animals (Fig. 7(b) and (i)) compared with the controls (Fig. 7(a)) (crypts: MDD animals 8·66 (sd 1·52) % v. controls 15·33 (sd 1·52) %; villus: MDD animals 7 (sd 1) % v. controls 17 (sd 2·64) %). Furthermore, standard stainings (periodic acid–Schiff; Fig. 7(c), (d), (g) and (h)) confirmed a decrease in neutral and acidic mucin production by goblet cells (Fig. 7(d) and (i)). In the distal small bowel, the MDD did not influence goblet cell number and mucin production (Fig. 7(e), (g), (f), (h) and (j)).

Fig. 7 Mucin-2 (MUC-2) immunostaining in the proximal small intestine shows a decrease in labelling cells in both crypts and villus of methyl-deficient diet (MDD) animals (b), with decreased mucus layer thickness compared with the control animals (a). In the distal small intestine, no difference was noted between the (e) control and (f) MDD animals ( × 200). The same results were obtained with periodic acid–Schiff (PAS) staining (c, d, g, h) ( × 400). (i, j) Results of the goblet cell index obtained in the crypt and villus after MUC-2 immunostaining and standard staining (Alcian blue pH 2·5, Alcian blue pH 1·0 and PAS). Values are means (controls, n 3; MDD animals, n 3), with standard deviations represented by vertical bars. * Mean value for MDD animals (![]() ) was significantly different from that of the controls (
) was significantly different from that of the controls (![]() ) (P< 0·05; Mann–Whitney U test). MUC-2c, crypt MUC-2 index; MUC-2v, villous MUC-2 index; BA-1c, crypt Alcian blue pH 1·0 index; BA-1v, villous Alcian blue pH 1·0 index; BA-2·5c, crypt Alcian blue pH 2·5 index; BA-2·5v, villous Alcian blue pH 2·5 index; PASc, crypt PAS index; PASv, villous PAS index.
) (P< 0·05; Mann–Whitney U test). MUC-2c, crypt MUC-2 index; MUC-2v, villous MUC-2 index; BA-1c, crypt Alcian blue pH 1·0 index; BA-1v, villous Alcian blue pH 1·0 index; BA-2·5c, crypt Alcian blue pH 2·5 index; BA-2·5v, villous Alcian blue pH 2·5 index; PASc, crypt PAS index; PASv, villous PAS index.
Taken as a whole, these findings show that the MDD impairs goblet cell and Paneth cell lineages in the proximal small bowel.
Discussion
We evaluated for the first time the effects of a MDD on the structure and functions of the distal and proximal small intestine in rats.
The distal small intestine was markedly affected by the MDD as illustrated by marked decreased wall thickness in MDD animals and overall hypotrophy. By contrast, wall thickness of the proximal small intestine was not affected by the MDD. This finding indicates that distal small bowel growing is particularly sensitive to the MDD.
Intestinal homeostasis is physiologically maintained through the balance between apoptosis and cell proliferation. An increased number of apoptotic cells were observed in the crypt of the proximal and distal small-bowel mucosa. We reported similar effects of the MDD on gastric mucosa(Reference Bossenmeyer-Pourie, Blaise and Pourie11) and hippocampus(Reference Blaise, Nédélec and Schroeder37), but not in the colon(Reference Chen, Peyrin-Biroulet and George10). Homocysteine treatment has been shown to induce apoptosis of different cell types in vitro (Reference Zhang, Cai and Adachi15, Reference Blaise, Alberto and Nedelec22). In the hippocampus of MDD rats, increased apoptosis was found in cells containing homocysteine(Reference Blaise, Nédélec and Schroeder37), whereas vitamin restriction did not influence cryptic apoptotic rates in rat intestinal epithelial cells(Reference Vijayalakshhmi, Sesikeran and Udaykumar38). Apoptotic cell death in the intestinal crypt can also be induced by hyperhomocysteinaemia that is known to cause DNA damage and altered DNA repair(Reference Mattson and Shea39).
According to previous reports, homocysteine has been shown to elicit cellular proliferation in vascular smooth muscle cells(Reference Zou, Yang and Hou40), microglia(Reference Zou, Zhao and Gao41) or gastric mucosa in MDD rats(Reference Bossenmeyer-Pourie, Blaise and Pourie11). The pro-mitogenic effects are associated with the generation of reactive oxygen species(Reference Zhang, Zeng and Guo42). Other studies have demonstrated that homocysteinaemia induced cell-cycle arrest in hepatocytes(Reference Liu, Zhao and Gao43) or venous endothelial cells(Reference Zhang, Cao and Qin44) by the reduction of cyclin pathway induction(Reference Zhang, Cao and Qin44). In the present study, the MDD effects on cell proliferation differed between the proximal and distal small-intestinal mucosa, as a decreased number of MCM-6- and PCNA-positive crypt cells was noted in the proximal small intestine, whereas the number of Ki-67 and phospho-histone H3 crypt labelling cells was not disturbed by the MDD.
Taken together, these results suggest that crypt cell-cycle arrest induced by the MDD may be linked to a reduced number of crypt cells in the early G1 phase, probably by decreasing cyclin-dependent kinase activity. Indeed, MCM proteins are known to be expressed in abundance during all phases of the cell cycle (early phase of G1, G2, M and S) and degraded in quiescence, senescence and differentiation steps(Reference Stoeber, Tlsty and Happerfield28). The MCM protein complex is associated with the origins of DNA replication to form part of the pre-replicative complex. Activation of the MCM complex by cyclin-dependent kinases leads to the initiation of DNA synthesis(Reference Maiorano, Cuvier and Danis45). In the distal bowel, mucosal deficiency was associated with an increased MCM-6 labelling of cells in the villus, whereas the number of Ki-67-labelled cells was not affected by the MDD and no effects on cell proliferation were observed in crypts. Furthermore, the absence of the degradation of MCM-6 protein in the villus was associated with the morphological absence of the maturation of enterocytes and reduced intestinal alkaline phosphatase expression, a known marker of enterocyte differentiation(Reference Lalles29), underscoring the potent effects of the MDD on enterocyte maturation.
Intestinal alkaline phosphatase has been shown to play a key role in the maintenance of normal gut microbial homeostasis(Reference Malo, Alam and Mostafa18). It has been shown to limit the access of toxins and microbes to underlying tissues(Reference McGuckin, Eri and Simms46). Tuin et al. (Reference Tuin, Poelstra and de Jager-Krikken47) found a reduced expression of epithelial intestinal alkaline phosphatase mRNA in patients with IBD. The MDD could also predispose to the development of IBD by decreasing the production of intestinal alkaline phosphatase in the distal small intestine, the main site of small-bowel Crohn's disease(Reference Hendrickson, Gokhale and Cho48). A reduced expression of β-catenin and a decreased interaction between β-catenin and E-cadherin may provide a clue to impaired enterocyte differentiation in the distal small bowel of MDD rat pups(Reference Clevers21). Low expression levels of PP2Ac in MDD animals may trigger increased degradation of β-catenin(Reference Park, Kim and Lee30, Reference Takahashi-Yanaga and Sasaguri49).
Interestingly, the MDD also affected the proximal small bowel as indicated by a reduction of Paneth and goblet cells that was associated with decreased mucin secretion. MUC-2 is known to be a major component of the intestinal barrier(Reference Zhang, Cao and Qin44). Although mice with reduced lineage cells (both goblet cells and Paneth cells) have not been reported to develop spontaneous inflammation(Reference Yang, Bermingham and Finegold50, Reference Shroyer, Wallis and Venken51), knockout of the intestinal mucin gene, Muc 2, leads to spontaneous colitis in mice, confirming that MUC-2 is critical for the maintenance of intestinal homeostasis(Reference Van der Sluis, De Koning and De Bruijn52–Reference Heller, Florian and Bojarski55). Regarding Paneth cells, the key role of small-intestinal antimicrobial peptides in the intestinal barrier has been highlighted in both human subjects and mice(Reference Karlsson, Putsep and Chu56). Accordingly, a reduction of Paneth cell α-defensins has been shown to be a key contributor to the pathogenesis of Crohn's ileitis(Reference Heazlewood, Cook and Eri35). The effects of the MDD on the small-intestinal barrier will require further investigation. Finally, epigenetic changes caused by the MDD may allow for a better understanding of intestinal carcinogenesis in IBD patients(Reference Janssens and Goris32).
Several studies have explored the influence of nutritional determinants on hyperhomocysteinaemia in IBD patients and most of them have reported low levels of circulating vitamin B12 and folate in IBD patients(Reference Peyrin-Biroulet, Rodriguez-Gueant and Chamaillard5). The present findings provide a rationale for a role of vitamin B12 and folate deficiency in the pathogenesis of Crohn's disease.
Lastly, the differential effects of the MDD observed in the proximal and distal small-bowel segments of MDD rats could be explained by differences in folate and vitamin B12 absorption along the small bowel. Indeed, proteins involved in intestinal folate absorption are mainly expressed in the proximal small bowel(Reference Said57), whereas vitamin B12 absorption mainly occurs in the distal small bowel(Reference Quadros58). Hence, susceptibility to the MDD may differ between the proximal and distal small bowel.
In conclusion, the present results show that the MDD during pregnancy and the suckling period affects differently the proliferation and differentiation of intestinal cells in the proximal and distal small bowel. The effects of the MDD on enterocyte differentiation in the small bowel may be linked to the alteration of the β-catenin signalling pathway. The MDD might be used as an experimental model for small-bowel Crohn's disease. This remains to be investigated in depth.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by institutional grants obtained from the Lorraine region and from Inserm, France. J.-L. G. and L. P.-B. designed the research; A. B., S. P., C. B.-P., G. G., A. G., J.-B. C. and F. C. conducted the research; A. B. analysed the data; A. B., L. P.-B., C. B.-P. and J.-L. G. wrote the paper; L. P.-B. had primary responsibility for the final content. All authors read and approved the final manuscript. The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.











