No CrossRef data available.
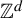 $\mathbb {Z}^{d}$-actions
$\mathbb {Z}^{d}$-actionsPublished online by Cambridge University Press: 04 October 2022
Let 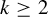 $k\geq 2$ and
$k\geq 2$ and 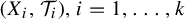 $(X_{i}, \mathcal {T}_{i}), i=1,\ldots ,k$, be
$(X_{i}, \mathcal {T}_{i}), i=1,\ldots ,k$, be 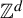 $\mathbb {Z}^{d}$-actions topological dynamical systems with
$\mathbb {Z}^{d}$-actions topological dynamical systems with 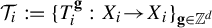 $\mathcal {T}_i:=\{T_i^{\textbf {g}}:X_i{\rightarrow } X_i\}_{\textbf {g}\in \mathbb {Z}^{d}}$, where
$\mathcal {T}_i:=\{T_i^{\textbf {g}}:X_i{\rightarrow } X_i\}_{\textbf {g}\in \mathbb {Z}^{d}}$, where 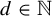 $d\in \mathbb {N}$ and
$d\in \mathbb {N}$ and 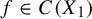 $f\in C(X_{1})$. Assume that for each
$f\in C(X_{1})$. Assume that for each 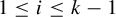 $1\leq i\leq k-1$,
$1\leq i\leq k-1$, 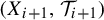 $(X_{i+1}, \mathcal {T}_{i+1})$ is a factor of
$(X_{i+1}, \mathcal {T}_{i+1})$ is a factor of 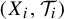 $(X_{i}, \mathcal {T}_{i})$. In this paper, we introduce the weighted topological pressure
$(X_{i}, \mathcal {T}_{i})$. In this paper, we introduce the weighted topological pressure 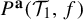 $P^{\textbf {a}}(\mathcal {T}_{1},f)$ and weighted measure-theoretic entropy
$P^{\textbf {a}}(\mathcal {T}_{1},f)$ and weighted measure-theoretic entropy 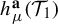 $h_{\mu }^{\textbf {a}}(\mathcal {T}_{1})$ for
$h_{\mu }^{\textbf {a}}(\mathcal {T}_{1})$ for 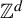 $\mathbb {Z}^{d}$-actions, and establish a weighted variational principle as
$\mathbb {Z}^{d}$-actions, and establish a weighted variational principle as  $$ \begin{align*} P^{\textbf{a}}(\mathcal{T}_{1},f)=\sup\bigg\{h_{\mu}^{\textbf{a}}(\mathcal{T}_{1})+\int_{X_{1}}f\,d\mu:\mu\in\mathcal{M}(X_{1}, \mathcal{T}_{1})\bigg\}. \end{align*} $$
$$ \begin{align*} P^{\textbf{a}}(\mathcal{T}_{1},f)=\sup\bigg\{h_{\mu}^{\textbf{a}}(\mathcal{T}_{1})+\int_{X_{1}}f\,d\mu:\mu\in\mathcal{M}(X_{1}, \mathcal{T}_{1})\bigg\}. \end{align*} $$
This result not only generalizes some well-known variational principles about topological pressure for compact or non-compact sets, but also improves the variational principle for weighted topological pressure in [16] from 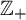 $\mathbb {Z}_{+}$-action topological dynamical systems to
$\mathbb {Z}_{+}$-action topological dynamical systems to 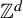 $\mathbb {Z}^{d}$-actions topological dynamical systems.
$\mathbb {Z}^{d}$-actions topological dynamical systems.