The metabolic syndrome (MetS) is a pre-diabetic state, characterised by obesity, insulin resistance (IR) and dyslipidaemia(Reference Alberti, Zimmet and Shaw1). Lipid abnormalities of the MetS include low plasma HDL-cholesterol, increased LDL-cholesterol, abnormal apoB level and raised blood TAG (hypertriacylglycerolaemia)(Reference Alberti, Zimmet and Shaw1, Reference Grundy, Brewer and Cleeman2). Emerging evidence also suggests that postprandial TAG and chylomicron (CM) concentrations are strongly correlated with cardiovascular risk(Reference Alipour, Elte and van Zaanen3).
The long-term complications of the MetS include premature atherosclerosis and ischaemic myocardial lesion development(Reference Alberti, Zimmet and Shaw1, Reference Despres and Marette4), and are often characterised in stages of severity (i.e. stage 1 to stage 4(Reference Russell, Amy and Graham5–Reference Brindley and Russell7)) including early areas of cell lysis through to inflammatory cell infiltration and scarring.
n-3 PUFA, such as EPA (20 : 5) and DHA (22 : 6), have been reported to have beneficial effects in states of the MetS and cardiovascular complications(Reference Schwalfenberg8, Reference Carpentier, Portois and Malaisse9). Studies have reported that dietary fish oil (rich in n-3 PUFA) can reduce cardiovascular risk factors, including repression of plasma insulin, glucose and cholesterol levels(Reference Psota, Gebauer and Kris-Etherton10, Reference Von Schacky and Harris11). Evidence from human clinical trials suggests that n-3 PUFA reduce acute atherosclerotic infarction, and hence lower the risk of CHD(Reference Xiao, Sigg and Ujhelyi12, Reference Mozaffarian13). Furthermore, an investigation of the protective effect of n-3 PUFA on isoproterenol-induced myocardial infarction in rats has reported a marked reduction in the level of lipid components (cholesterol, TAG and NEFA) in the plasma and heart tissue(Reference Anandan, Mathew and Sankar14). In addition, a human trial conducted by Metcalf et al. (Reference Metcalf, James and Gibson15) has reported dietary n-3 PUFA to be readily incorporated into cardiomyocyte phospholipids, potentially exerting beneficial outcomes by consequent effects on myocardial membrane function. Despite this, there is no comprehensive histological evidence regarding the improvement of dietary n-3 PUFA on myocardial lesions and the long-term beneficial vascular effects.
Recently, our group has reported that acute (3-week) dietary n-3 PUFA supplementation can reduce weight gain, and improve postprandial lipid metabolism and associated pro-inflammatory response in the obese JCR:LA-cp rat, a model of the MetS(Reference Hassanali, Ametaj and Field16). The JCR:LA-cp rat, homozygous for the corpulent trait (cp/cp), exhibits symptoms of the MetS, enhanced hepatic VLDL and intestinal CM overproduction, as well as end-stage complications such as ischaemic myocardial lesions(Reference Russell, Amy and Graham5, Reference Russell, Graham and Richardson6, Reference Russell, Koeslag and Amy17–Reference Vine, Takechi and Russell22). Consequently, the aim of the present study was to (1) assess the long-term (chronic) effects of dietary n-3 PUFA supplementation on dyslipidaemia, IR and myocardial lesion development in the JCR:LA-cp rat and (2) investigate the putative mechanistic effects of dietary n-3 PUFA, specifically on intestinal enterocytes, in the obese JCR:LA-cp rat.
Materials and methods
Animal model and experimental procedures
Male obese (cp/cp) JCR:LA-cp rats were raised in our established breeding colony at the University of Alberta (Edmonton, AB, Canada), as described previously(Reference Russell, Amy and Graham5). Rats were weaned at 6 weeks, and allowed to age until 8 weeks of age. Obese rats (cp/cp) were randomly allocated to either a control hypercholesterolaemic isoenergetic lipid-balanced diet (LBD; n 8) (1 % (w/w) cholesterol; 15 % (w/w) total fat; polyunsaturated:saturated fat ratio 0·4) or a LBD supplemented with 5 % n-3 PUFA (of the total fat n 8; 1 % (w/w) cholesterol, 15 % (w/w) total fat; polyunsaturated:saturated fat ratio 0·4 and 5 % (w/w) fish oil-derived EPA/DHA) (Table 1), for 3 or 16 weeks, as indicated throughout. Note that the equivalent amount of n-3 PUFA from 5 % fish oil treatment in rats used in the present study equates to approximately 5 g fish oil/d for a 10 460 kJ/d (2500 kcal/d) human diet. Food consumption and body weight were recorded throughout the study. At 22 weeks of age, an oral fat challenge test was performed on all rats, as described previously(Reference Vine, Takechi and Russell22). At 24 weeks of age, rats were fasted overnight and killed under isoflurane anaesthesia. Plasma and serum were collected via cardiac puncture. Liver, heart and inguinal fat pads were weighed and snap-frozen in liquid N2 at − 80°C for subsequent analysis. Animal care and experimental procedure were conducted in accordance with the Canadian Council on Animal Care (Ottawa, ON, Canada) and approved by the University of Alberta Animal Care and Use Committee (ACUC-Livestock).
Table 1 Nutrient and lipid summaries for both dietary groups*

LBD, lipid-balanced control diet; P:S, polyunsaturated:saturated fat.
* Fatty acid composition of the LBD and the diet supplemented with 5 % fish oil containing EPA and DHA; 5 % n-3 PUFA diet, as determined by GC as described previously(Reference Wang, Lu and Ruth56).
Assessment of postprandial lipidaemia
At 22 weeks of age and following a 16 h overnight fast, rats were subjected to an oral fat challenge test in order to assess non-fasting lipid metabolism(Reference Vine, Takechi and Russell22). In brief, all rats consumed a 5 g pellet prepared from 5001 laboratory chow, consisting of 49 % carbohydrate, 24 % crude protein, 10 % moisture, 6·5 % minerals, 6 % fibre and 4·5 % fat, and further supplemented with 25 % (w/w) dairy fat from double cream (raising the total fat content of the 5 g meal to approximately 30 % (w/w) of the total meal)(Reference Hassanali, Ametaj and Field16, Reference Vine, Takechi and Russell22). Blood samples were collected (from the tail) into tubes containing Na2EDTA at time intervals (0, 2, 4 and 6 h) following pellet consumption. Plasma and serum were separated by centrifugation (3901 g, 4°C, 10 min). Aliquots of plasma were immediately stored at − 80°C for biochemical analyses.
Mesenteric lymph duct cannulation and nascent lymph collection
To determine the effect of n-3 PUFA on the secretion of CM in mesenteric lymph, the superior mesenteric lymph duct of obese JCR:LA-cp rats was cannulated following consumption of a control LBD (n 5) or a 5 % n-3 PUFA diet (n 5) for 3 weeks(Reference Wang, Jacome-Sosa and Ruth23). Mesenteric lymph was collected into EDTA-coated vacutainers for 5 h following infusion of intralipid (Kabi Pharmacia, Uppsala, Sweden). The concentrations of TAG and total cholesterol were measured as described below for the plasma.
Isolation of primary jejunal enterocytes and quantification of apoB48 and Jun N-terminal kinase protein
Primary jejunal enterocytes were isolated from the intestine of obese rats fed either a control LBD or a 5 % n-3 PUFA diet for 3 weeks, as per the Weiser method(Reference Weiser24) of isolation and fractionation, as described previously(Reference Wang, Jacome-Sosa and Ruth23). The protein concentration of the isolated enterocyte fractions (no. 1–10) was determined, and immuno-Western blot analysis was used to probe the expression of apoB48 protein (as below) along the intestinal villus, from enterocyte fraction no. 1 (tip of the villus) to enterocyte fraction no. 10 (crypt of the villus). Pooled enterocyte fractions (no. 1–10) were assessed for Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) activity by Western blotting, to target phosphorylated (active) JNK (JNK-P) protein. Briefly, cell extracts were prepared in Triton lysis buffer and examined (50 μg protein) by immunoblot analysis, to target JNK-P (catalogue no. 9252; Cell Signalling, Beverly, MA, USA) and JNK (catalogue no. 558268; Pharmingen, San Diego, CA, USA).
Plasma biochemical determination
The biochemical lipid profile of obese rats fed either a control LBD or a 5 % n-3 PUFA diet was assessed using commercially enzymatic kits, as described previously(Reference Hassanali, Ametaj and Field16); including plasma TAG (catalogue no. 998-40 391/994-40 491; Wako Pure Chemicals, USA, Inc., Richmond, VA, USA), total cholesterol (catalogue no. 439-17 501; Wako), LDL-cholesterol (catalogue no. 993-00 404/999-00 504; Wako) and HDL-cholesterol (catalogue no. 258-20; Diagnostic Chemicals Limited, Charlottetown, PE, Canada). Plasma glucose levels were assessed as per the glucose oxidase method (catalogue no. 220-32; Diagnostic Chemicals Limited). Insulin was analysed by a solid-phase, two-site enzyme immunoassay (catalogue no. 10-1137-01; Mercodia AB, Uppsala, Sweden). Plasma adiponectin (catalogue no. 44-ADPR-0434; Alpco Diagnostics, Salem, NH, USA) and leptin (catalogue no. 22-LEP-E06; ALPCO) concentrations were determined using commercially available rodent-specific immunoassays.
The concentration of intestinally derived CM particles was determined by quantification of plasma apoB48, using an adapted immuno-Western blotting procedure, as described previously(Reference Vine, Glimm and Proctor25, Reference Smith, Proctor and Mamo26). Briefly, total plasma was separated by SDS-PAGE on a 3–8 % Tris-acetate polyacrylamide NuPage® gel (InVitrogen, Camarillo, CA, USA). Separated proteins were transferred to a polyvinylidene fluoride membrane (0·45 μm, ImmobilonP™; Millipore, Billerica, MA, USA). Membranes were incubated with a goat polyclonal antibody to apoB (1:100; catalogue no. sc-11 795; Santa-Cruz Biotechnology, Inc., Santa Cruz, CA, USA), which recognises both apoB100 and apoB48 isoforms. Detection was achieved using an anti-goat secondary antibody (catalogue no. sc-2304; Santa-Cruz Biotechnology, Inc.) and chemiluminescence (Enhanced Chemiluminescence (ECL) advance; Amersham Biosciences, Little Chalfont, Bucks, UK); intensity was quantified using linear densitometric comparison with a known mass of purified rodent apoB48 protein.
Measurement of lipogeneic gene targets
Total RNA was isolated from both hepatic and adipose tissue collected from obese (cp/cp) rats of both diet groups (TRIzol; InVitrogen) and reverse-transcribed into complementary DNA using MultiScribe™ Reverse transcriptase (High-Capacity cDNA Reverse Transcription Kit; Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA). The expression of acyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC), fatty acid synthase (FAS), PPARα, PPARγ and sterol regulatory element-binding protein-1 (SREBP-1) mRNA, relative to the housekeeping gene ACTB (β-actin), was measured by quantitative real-time PCR, using the StepOne™ Plus Real-Time PCR system (Applied Biosystems) and StepOne™ Software (version 2). PCR contained complementary DNA template, 100 nm of commercially available, pre-mixed target-specific primers and Taqman® FAM™-labelled probe (Applied Biosystems) for ACC (reference sequence NM _022193.1; catalogue no. Rn01456582_m1), ACTB (NM_031144.2; catalogue no. Rn00667869_m1), FAS (NM_017332.1; catalogue no. Rn01463550_m1), PPARα (NM_013196.1; catalogue no. Rn00566193_m1), PPARγ (NM_001145366.1, catalogue no. Rn00440945_m1) and SREBP-1 (XM_213329.5; catalogue no. Rn01495769). Thermal cycling conditions were as follows: 95°C for 20 s, followed by forty cycles of 95°C for 1 s and 60°C for 20 s. Gene quantification was assessed relative to ACTB mRNA, utilising the comparative 2− ΔC t method.
Measurement of lipogenic-related proteins
Proteins from liver and adipose homogenates were separated by SDS-PAGE electrophoresis on 3–8 % Tris-acetate polyacrylamide gels (InVitrogen), transferred to a polyvinylidene fluoride membrane (described previously) and incubated with antibodies for the following target proteins: anti-ACC goat polyclonal (1:20 000; catalogue no. sc-11 795; Santa-Cruz Biotechnology, Inc.); anti-FAS goat monoclonal (1:20 000; catalogue no. sc-55 580; New England BioLabs, Acton, MA, USA), anti-SREBP-1 mouse monoclonal (1:20 000; catalogue no. sc-13 551; Santa-Cruz Biotechnology, Inc.); anti-actin goat polyclonal (1:20 000; catalogue no. A5441; Sigma-Aldrich, St Louis, MO, USA); antibodies. Detection was achieved using anti-goat and anti-murine secondary antibodies and the ECL advance detection system (described previously; Amersham Biosciences). Results are expressed as a ratio of target protein:β-actin protein.
Heart histology and myocardial lesion analysis
Hearts were fixed in formalin, embedded in a single paraffin block, sectioned and then stained with haematoxylin and eosin as described previously(Reference Russell, Graham and Richardson6). Heart sections were examined blindly by an experienced observer, and the number of ischaemic lesions was identified in each of the sections. Myocardial lesions were categorised as stage 1 through to stage 4, as described previously(Reference Russell, Amy and Graham5–Reference Brindley and Russell7, Reference Russell, Koeslag and Dolphin27); stage 1, necrotic areas; stage 2, cell lysis with long-term inflammatory infiltration; stage 3, nodules of long-term inflammatory infiltration; stage 4, old scarred lesions. The number of lesions determined from sections of individual hearts was aggregated, and the mean incidence for each group was calculated.
Statistical analysis
Statistical analysis was performed using GraphPad Prism software, version 4.0. Data were tested for normal distribution, and significant differences between the obese (cp/cp) LBD and obese (cp/cp) 5 % n-3 PUFA groups were determined using Student's t test or repeated-measures ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post hoc tests, when appropriate. All results are expressed as means with their standard errors and the number of independent experiments as indicated in the figure legends. The level of significance was set at P < 0·05.
Results
Food intake, body fat and organ weight
Following a 16-week n-3 PUFA intervention, despite no reduction in food intake, 5 % n-3 PUFA-supplemented obese rats had significantly lower body weight (12–17 %; P < 0·05) compared with the obese control rats (Table 2; Fig. 1). Those rats supplemented with 5 % n-3 PUFA (16 weeks) had a reduced ratio of inguinal fat-pad weight:body weight compared with the obese control rats (P < 0·001) (Fig. 2). Furthermore, the weight of the liver isolated from obese rats supplemented with 5 % n-3 PUFA (16 weeks) was significantly decreased (P < 0·05) compared with the obese control rats (data not shown). The weight of the heart isolated from rats of both groups was unaltered by dietary n-3 PUFA (data not shown).
Table 2 Physical and fasting biochemical parameters of obese (cp/cp) male JCR:LA-cp rats fed a lipid-balanced control diet (LBD) or a 5 % n-3 PUFA diet
(Mean values with their standard errors, n 8)
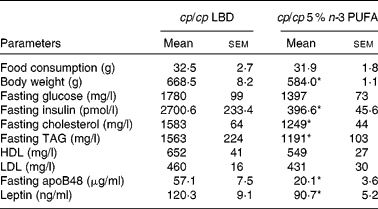
* Mean values were significantly different from those of the obese control (cp/cp) group (P < 0·05).

Fig. 1 Body weight of obese control (![]() , cp/cp) and 5 % n-3 PUFA-fed (
, cp/cp) and 5 % n-3 PUFA-fed (![]() , 16 weeks) obese JCR:LA-cp rats. Values are means, with standard errors represented by vertical bars (n 8). * Mean values were significantly different from those of the lipid-balanced diet cp/cp control group (P < 0·05).
, 16 weeks) obese JCR:LA-cp rats. Values are means, with standard errors represented by vertical bars (n 8). * Mean values were significantly different from those of the lipid-balanced diet cp/cp control group (P < 0·05).

Fig. 2 Ratio of the weight of inguinal fat pads:body weight of either obese (cp/cp) control JCR:LA-cp rats or JCR:LA-cp rats fed a 5 % n-3 PUFA diet (16 weeks). Values are means, with standard errors represented by vertical bars (n 8). *** Mean value was significantly different from that of the lipid-balanced diet cp/cp control group (P < 0·001).
Fasting biochemical profile
Treatment with 5 % n-3 PUFA for 16 weeks significantly lowered fasting plasma leptin and insulin concentrations (P < 0·05; Table 2). In addition, treatment with 5 % n-3 PUFA increased (improved) fasting plasma adiponectin concentration (P < 0·05; Fig. 3), but did not significantly reduce fasting glucose concentration (Table 2). Furthermore, fasting plasma cholesterol and TAG concentrations were reduced in rats fed the 5 % n-3 PUFA diet (16 weeks), compared with the obese control rats (P < 0·05) (Table 2).

Fig. 3 Fasting plasma adiponectin concentration of either obese (cp/cp) or 5 % n-3 PUFA (16 weeks)-fed JCR:LA-cp rats. Values are means with standard errors represented by vertical bars (n 8). * Mean value was significantly different from that of the lipid-balanced diet cp/cp control group (P < 0·005).
Non-fasting (postprandial) lipid response
Consistent with previous results from acute dietary n-3 PUFA supplementation in JCR:LA-cp rats, the postprandial lipid response (measured as area under the curve) for TAG was significantly lower in obese rats fed a 5 % n-3 PUFA diet chronically for 16 weeks compared with the obese control rats (54 %; P < 0·05; Fig. 4(a)), apoB48 (69 %; P < 0·01; Fig. 4(b)); and total cholesterol (38 %; P < 0·001; Fig. 4(c)).

Fig. 4 Postprandial response of plasma TAG (a), apoB48 (b) and total cholesterol (c) (area under the curve) of control (![]() , cp/cp) and 5 % n-3 PUFA-fed (
, cp/cp) and 5 % n-3 PUFA-fed (![]() ), (16 weeks) JCR:LA-cp rats, following an oral fat challenge. Values are means with standard errors represented by vertical bars (n 8). Mean values were significantly different from those of the lipid-balanced diet cp/cp control group: *P < 0·05, **P < 0·01, ***P < 0·001.
), (16 weeks) JCR:LA-cp rats, following an oral fat challenge. Values are means with standard errors represented by vertical bars (n 8). Mean values were significantly different from those of the lipid-balanced diet cp/cp control group: *P < 0·05, **P < 0·01, ***P < 0·001.
Expression of enterocytic apoB48 protein and secretion of chylomicron lymphatic cholesterol and TAG
The abundance of enterocyte-specific apoB48 (number of CM particles) was significantly lower (43·8 %; P < 0·05) in obese JCR:LA-cp rats fed a 5 % n-3 PUFA diet for 3 weeks, compared with the obese control rats (Fig. 5). Obese JCR:LA-cp rats fed a 5 % n-3 PUFA diet (3 weeks) also secreted 30 % less CM-associated cholesterol (P < 0·05) into mesenteric lymph compared with rats fed the control diet (Fig. 6(a)). Interestingly, by comparison, the secretion of CM-TAG, into mesenteric lymph, was increased (1·7-fold; P < 0·05) in those rats fed a 5 % n-3 PUFA diet (Fig. 6(b)).

Fig. 5 Enterocyte-specific apoB48 protein expression in obese (![]() , cp/cp) JCR:LA-cp rats fed either a control lipid-balanced diet or a 5 % n-3 PUFA (
, cp/cp) JCR:LA-cp rats fed either a control lipid-balanced diet or a 5 % n-3 PUFA (![]() )-enriched diet for 3 weeks. Primary jejunal enterocytes were isolated as per the Weiser method of isolation and fractionation, as described previously(Reference Wang, Jacome-Sosa and Ruth23). Immuno-Western blot analysis probed the expression of apoB48 protein (as per Methods) along the intestinal villus from enterocyte fraction 1 (tip of the villus) to enterocyte fraction 10 (crypt of the villus). Values are means, with standard errors represented by vertical bars (n 5). * Mean values were significantly different between total enterocyte and apoB48 mass of 5 % n-3 PUFA cp/cp v. lipid-balanced diet (LBD) cp/cp control (P < 0·05). † Mean values were significantly different in enterocyte fraction 5-specific apoB48 protein of 5 % n-3 PUFA cp/cp v. LBD cp/cp control (P < 0·05).
)-enriched diet for 3 weeks. Primary jejunal enterocytes were isolated as per the Weiser method of isolation and fractionation, as described previously(Reference Wang, Jacome-Sosa and Ruth23). Immuno-Western blot analysis probed the expression of apoB48 protein (as per Methods) along the intestinal villus from enterocyte fraction 1 (tip of the villus) to enterocyte fraction 10 (crypt of the villus). Values are means, with standard errors represented by vertical bars (n 5). * Mean values were significantly different between total enterocyte and apoB48 mass of 5 % n-3 PUFA cp/cp v. lipid-balanced diet (LBD) cp/cp control (P < 0·05). † Mean values were significantly different in enterocyte fraction 5-specific apoB48 protein of 5 % n-3 PUFA cp/cp v. LBD cp/cp control (P < 0·05).

Fig. 6 Secretion of chylomicron-associated (a) cholesterol and (b) TAG into mesenteric lymph. Mesenteric lymph cannulation procedures were carried out as described previously(Reference Wang, Jacome-Sosa and Ruth23). Cholesterol and TAG secretion (μg/ml) into mesenteric lymph was compared in obese (cp/cp) JCR:LA-cp rats fed a 5 % n-3 PUFA diet v. those fed a control lipid-balanced diet (LBD) for 3 weeks. Values are means, with standard errors represented by vertical bars (n 5). * Mean value was significantly different from that of the LBD cp/cp control group in all cases (P < 0·05).
Expression of genes involved in lipogenesis and fatty acid oxidation
The expression of both hepatic and adipose ACC, FAS, SREBP-1, PPARα and PPARγ mRNA is reported in Fig. 7(a) (hepatic) and Fig. 8(a) (adipose). Hepatic specific ACC (25 %; P < 0·05) and SREBP-1 (61·3 %; P < 0·01) mRNA levels were significantly reduced in obese rats fed a 5 % n-3 PUFA diet (16 weeks) compared with the control rats (Fig. 7(a)). Similarly, adipose-specific expression of SREBP-1 mRNA was also significantly lower (37 %; P < 0·05) in those obese rats fed a 5 % n-3 PUFA diet (16 weeks) (Fig. 8(a)). The gene expression of PPARα/γ and ACC was unaltered in the adipose tissue of obese rats fed a 5 % n-3 PUFA diet, while FAS mRNA was significantly up-regulated (1·9-fold; P < 0·05) compared with the obese control rats (Fig. 8(a)).

Fig. 7 Hepatic gene and protein expression of lipogenic enzymes in JCR:LA-cp rats in response to long-term feeding (16 weeks) of 5 % n-3 PUFA (▨). (a) The expression of ACC, FAS, SREBP-1, PPARα and PPARγ mRNA, relative to the housekeeping gene β-actin, in the livers of both obese (□, cp/cp) and 5 % n-3 PUFA-fed groups. ((b) and (c)) Protein abundance of ACC, FAS, precursor SREBP-1 (approximately 125 kDa) and mature SREBP-1 (approximately 68 kDa) protein, relative to β-actin protein expression, in the livers of the obese (cp/cp) control and 5 % n-3 PUFA diet groups. Values are means, with standard errors represented by vertical bars (n 8). Mean values were significantly different from those of the lipid-balanced diet cp/cp control group: * P < 0·05, ** P < 0·01.

Fig. 8 Adipose-specific gene and protein expression of lipogenic enzymes in JCR:LA-cp rats in response to long-term feeding (16 weeks) of 5 % n-3 PUFA (▨). (a) Expression of ACC, FAS, SREBP-1, PPARα and PPARγ mRNA, relative to the housekeeping gene β-actin, in the adipose tissue of obese (□, cp/cp) and 5 % n-3 PUFA-fed JCR:LA-cp rats. ((b) and (c)) Protein abundance of ACC, FAS and precursor SREBP-1 (approximately 125 kDa) protein, relative to β-actin protein expression, in the adipose tissue of the obese (cp/cp) control and 5 % n-3 PUFA diet groups. Values are means, with standard errors represented by vertical bars (n 8). Mean values were significantly different from those of the lipid-balanced diet cp/cp control group: * P < 0·05, ** P < 0·01.
Protein expression of lipogenic enzymes
The abundance of hepatic ACC, FAS and SREBP-1 proteins is reported in Fig. 7(b) and (c). The abundance of hepatic FAS protein was significantly lower in rats fed a 5 % n-3 PUFA diet for 16 weeks (P < 0·01; Fig. 7(b) and (c)), relative to the obese control rats. However, ACC protein was not significantly altered in livers from 5 % n-3 PUFA-fed rats, relative to the obese control rats (Fig. 7(b) and (c)). Both precursor (125 kDa) and mature (68 kDa) hepatic SREBP-1 proteins were reduced in the 5 % n-3 PUFA diet group (16 weeks) compared with the obese control group (P < 0·01) (Fig. 7(b) and (c)). Adipose tissue-specific expression of ACC and SREBP-1 protein (125 kDa) was not significantly altered in rats fed a 5 % n-3 PUFA diet (Fig. 8(b) and (c)). Furthermore, treatment with 5 % n-3 PUFA significantly reduced FAS protein expression in the adipose (P < 0·05) compared with the obese control rats (Fig. 8(b) and (c)).
Enterocytic phosphorylated Jun N-terminal kinase protein
The protein expression of phosphorylated JNK (active) protein was significantly reduced (72·6 %; P < 0·01) in the enterocytes of obese JCR:LA-cp rats fed a 5 % n-3 PUFA diet for 3 weeks compared with the obese control group (Fig. 9).

Fig. 9 Activity of Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) was assessed via Western blot to target phosphorylated JNK (JNK-P) protein. Enterocyte extracts (50 μg protein) were examined by immunoblot analysis, utilising antibodies from Cell Signalling (JNK-P) and Pharmingen (JNK). JNK-P protein was measured in obese (cp/cp) JCR:LA-cp rats fed either a 5 % n-3 PUFA diet or a control lipid-balanced diet (LBD) for 3 weeks; a representative blot and graph, presented as a measure of arbitrary density units, are shown. Values are means, with standard errors represented by vertical bars (n 5). ** Mean value was significantly different from that of the LBD cp/cp control group in all cases (P < 0·01).
Frequency of myocardial lesions
Representative images of the stages (stages 1–4) of myocardial lesions assessed are shown in Fig. 10. The frequency of stages of myocardial lesion development (stages 1–4) for all four treatment groups is reported in Fig. 11. Supplementation with n-3 PUFA for 16 weeks in the obese JCR:LA-cp rat had no effect on the frequency of early stage 1 lesions (Fig. 11). Most notably, the 5 % n-3 PUFA diet significantly reduced the number of late stage 3 (areas of chronic inflammatory infiltration) lesions (83·3 %; P < 0·05) in obese rats compared with the control group (Fig. 11). Additionally, in the hearts of rats supplemented with a 5 % n-3 PUFA diet, no stage 4 lesions were detected (Fig. 11).

Fig. 10 Representative micrographs of ischaemic lesions in the hearts of obese JCR:LA-cp rats (age 24 weeks). (a) Stage 1: area of necrosis with no long-term inflammatory cell infiltration in the left ventricle. (b) Stage 2: area of long-term inflammatory cell infiltration, without visible cell lysis, in the trabecular muscle. (c) Stage 3: area of active inflammatory cell activity and cell lysis in the lower trabecular muscle. (d) Stage 4: early scarred lesion with a small number of inflammatory cells or fibroblasts in the upper penvalvular region of the heart. All images were captured at a magnification of 2 × after haematoxylin and eosin staining of heart sections.
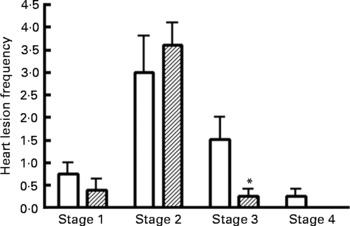
Fig. 11 Frequency of myocardial lesions in the hearts of JCR:LA-cp rats from obese control (□, cp/cp) and 5 % n-3 PUFA (▨) diet groups (16 weeks). (a) Stage 1 lesions; (b) stage 2 lesions; (c) stage 3 lesions; (d) stage 4 lesions. Values are means, with standard errors represented by vertical bars (n 8). * Mean values were significantly different from those of the lipid-balanced diet cp/cp control group in all cases (P < 0·05).
Discussion
The main objective of the present study was to investigate the impact of chronic (16 weeks) dietary intervention with n-3 PUFA on pre-existing hyperinsulinaemia, dyslipidaemia and ischaemic lesion development, in the JCR:LA-cp rat model. Our findings show that chronic feeding of a diet with increased n-3 PUFA can improve both metabolic parameters and vascular complications associated with the MetS.
The chronic effect of n-3 PUFA on body weight and fat deposition
While obesity is known to increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular complications, the long-term effect of dietary fat consumption in the process of development of diabetes, IR and dyslipidaemia remains controversial. Thorsdottir et al. (Reference Thorsdottir, Tomasson and Gunnarsdottir28) demonstrated in a study of overweight men that the inclusion of fish oil (n-3 PUFA) in the diet induced a greater weight loss (1 kg) over 4 weeks, than those on a diet without fish oil(Reference Thorsdottir, Tomasson and Gunnarsdottir28). An additional study in overweight hypertensive subjects, which showed a weight-loss programme incorporating fish meals rich in n-3 PUFA, was more effective in reducing weight loss, serum lipids and glucose–insulin metabolism, than either treatment alone(Reference Mori, Bao and Burke29). Interestingly, and consistent with our previous finding in this rat model(Reference Hassanali, Ametaj and Field16), we observed that increased dietary n-3 PUFA reduced body-weight gain in the absence of any alteration in food intake.
Clinical data also suggest that type 2 diabetic patients subjected to a diet rich in n-3 PUFA have reduced abdominal subcutaneous fat, in addition to improved IR(Reference Summers, Fielding and Bradshaw30). Consistent with this, inguinal fat (intra-abdominal) depots were significantly lower in n-3 PUFA dietary groups in the present study. Additional animal studies have also shown that dietary supplementation with fish oil (n-3 PUFA) can make an impact upon fatty acid proportions and distribution in subcutaneous and visceral fat(Reference Bilby, Jenkins and Staples31, Reference Soriguer, Moreno and Rojo-Martínez32). Indeed, it has been suggested previously that n-3 PUFA may not be as readily deposited, but more freely oxidised within the adipose tissue, implying that n-3 PUFA may at least have a partial protective effect against weight gain per se (Reference Storlien, Kriketos and Jenkins33–Reference Feskens, Loeber and Kromhout35).
The chronic effect of n-3 PUFA on glucose, insulin resistance and adipokines
Studies have indicated that dietary fish oil (n-3 PUFA) may act to normalise and/or improve the storage of lipids and glucose oxidation within skeletal muscle. Evidence supports the notion that hypolipidaemic effects of n-3 PUFA act to reduce lipid utilisation within skeletal muscle, restore glucose oxidation and normalise insulin sensitivity(Reference Lombardo, Hein and Chicco36). In the present study, JCR:LA-cp rats from the n-3 PUFA diet groups had significantly improved fasting plasma insulin (but only a trend towards improved glucose levels), implying improved IR, consistent with previous data(Reference Russell, Amy and Dolphin37).
Furthermore, n-3 PUFA supplementation significantly decreased plasma leptin levels. Existing evidence suggests leptin to be a contributor to the hypolipidaemic benefits of n-3 PUFA, reducing TAG biosynthesis and enhancing β-oxidation(Reference Ukropec, Reseland and Gasperikova38). While the effects of n-3 PUFA on plasma and tissue leptin levels remain controversial(Reference Ukropec, Reseland and Gasperikova38), studies have shown that n-3 PUFA supplementation may reduce leptin mRNA expression(Reference Ukropec, Reseland and Gasperikova38). Plasma leptin levels have also been shown to be reduced in rodents supplemented with dietary n-3 PUFA (fish oil), with corresponding decreases in visceral adipose tissue(Reference Higuchi, Shirai and Saito39). The ability of n-3 PUFA to reduce plasma leptin levels in our IR rodent model may occur directly via suppression of leptin mRNA expression (not measured in the present study). Alternatively, it may be possible that plasma leptin could be modulated indirectly via the parallel reductions in plasma insulin, inguinal (intra-abdominal) fat weight and body weight.
It is well established that there is a negative correlation between the concentration of plasma adiponectin (an adipokine with anti-diabetic properties) and BMI(Reference Matsuzawa, Funahashi and Shimomura40). Consistent with this, fasting adiponectin concentration was significantly enhanced in rats supplemented with 5 % n-3 PUFA, while body weight was profoundly reduced. It may be that n-3 PUFA influence the expression of adipokines (such as leptin and adiponectin) via direct interaction with transcription factors, or indirectly via mechanisms that control fatty acid oxidation, synthesis and/or storage(Reference Lombardo and Chicco41); but this remains to be defined.
Potential mechanisms of n-3 PUFA via regulation of lipogenic enzymes
SREBP are sterol-responsive transcription factors. SREBP are synthesised in their precursor form (approximately 125 kDa) in the endoplasmic reticulum, before cleavage to their active (nuclear) form (approximately 68 kDa), in response to low cellular sterol levels, regulating the expression of lipid-related genes, including lipogenic enzymes (FAS and ACC)(Reference Davidson42). In particular, the SREBP-1 isoform is selective for genes involved in fatty acid synthesis: ACC, FAS; stearoyl-CoA desaturase-1(Reference Weber, Boll and Stampfl43). In the present study, chronic dietary n-3 PUFA reduced both gene and protein expression of hepatic precursor and mature SREBP-1, also down-regulating lipogenic enzyme expression of hepatic ACC mRNA and FAS protein, consistent with the expression of SREBP-1(Reference Gallardo, Bonzon-Kulichenko and Fernandez-Agullo44). Studies have shown that PUFA can act as a competitive antagonist for the liver X receptor, a nuclear receptor responsive to endogenous oxysterols, in vitro (Reference Yoshikawa, Shimano and Yahagi45). We also know that inhibition of the binding of the liver X receptor/retinoid X receptor heterodimer to the liver X receptor response element, in the promoter region of SREBP-1c, can suppress the expression of SREBP-1c(Reference Yoshikawa, Shimano and Yahagi45). More recently, the same group has reported that the primary mechanism underlying PUFA-induced SREBP-1c suppression, in fact, occurs at the proteolytic processing level in vivo (Reference Takeuchi, Yahagi and Izumida46). The ability of PUFA to suppress SREBP-1 may also be dependent on the level of the incorporation of PUFA into cellular lipids, as recently suggested by Di Nunzio et al. (Reference Di Nunzio, van Deursen and Verhoeven47).
The hypolipidaemic effect of n-3 PUFA may arise either via the reduced expression of SREBP-1, reducing lipogenesis and cholesterol biosynthesis, as discussed above, or via activation of the common PUFA-activated transcription factor, PPARα(Reference Davidson42, Reference Kliewer, Sundseth and Jones48, Reference Kim, Takahashi and Ezaki49), promoting fatty acid oxidation. However, in the present study, we found that hepatic- and adipose-specific expression of PPAR (α/γ) mRNA was not significantly regulated in response to chronic dietary n-3 PUFA.
Furthermore, while dietary n-3 PUFA induced a marked reduction in hepatic SREBP-1 gene and protein abundance, only a modest suppression of adipose-specific SREBP-1 mRNA was observed. The differential PUFA-mediated regulation of SREBP-1 between tissue types in the JCR:LA-cp model is consistent with that observed in other rodent models(Reference Mater, Thelen and Pan50, Reference Price, Nelson and Clarke51). In the present study, we observed a greater abundance of hepatic SREBP-1 mRNA compared with adipose-specific SREBP-1. By contrast, we report greater PPARγ mRNA in adipose compared with hepatic tissue. As reviewed by Kersten(Reference Kersten52), data suggest that SREBP-1 regulates lipogenic genes in the liver, while PPARγ is essential for the regulation of lipogenesis in the adipose. Thus, PUFA-induced regulation of lipogenesis may exhibit tissue specificity, via hepatic SREBP-1 and PPARγ in the adipose tissue.
The acute effect of n-3 PUFA on intestinal enterocytes
We have shown that both acute(Reference Hassanali, Ametaj and Field16) and long-term n-3 PUFA intervention clearly exert beneficial effects specifically in our model to improve postprandial lipids, therefore suggesting that the ability of n-3 PUFA to improve postprandial metabolism, during conditions of IR, may occur via the direct action of n-3 PUFA on intestinal CM secretion (Figs. 5 and 6). For this reason, we initiated a subsequent acute (3-week) n-3 PUFA intervention to assess potential mechanistic effects of n-3 PUFA, directly on intestinal enterocyte CM production, associated lymphatic lipid secretion and JNK-associated insulin signalling. We observed that 3 weeks (short-term) of dietary intervention with n-3 PUFA was sufficient to reduce the intestinal production of apoB48 (CM) (Fig. 5), but also suppressed the subsequent lymphatic cholesterol secretion (Fig. 6). This is complementary to the observed improvement (reduction) to both fasting and postprandial plasma apoB48 (both acute and chronic) and cholesterol (chronic) reported in our previous acute study(Reference Hassanali, Ametaj and Field16) and the present long-term (chronic) study. Consistent with clinical observations, neither long-term nor acute(Reference Hassanali, Ametaj and Field16) intervention with n-3 PUFA lowered fasting plasma LDL concentrations, suggestive of preferential n-3 PUFA-induced improvement to intestinally derived lipoprotein fractions. Interestingly, while the n-3 PUFA diet lowered fasting and postprandial plasma TAG, we observed an increase in lymphatic TAG secretion from the intestine following acute n-3 PUFA supplementation (Fig. 6). We hypothesise that there may be an increase in CM particle size and/or enhanced clearance of TAG, although this remains to be elucidated.
Most recently, n-3 PUFA have been reported to exert potent anti-inflammatory effects that improve IR and other symptoms of the MetS in mice, via binding to G protein-coupled receptor 120(Reference Oh da, Talukdar and Bae53). This study reported n-3 PUFA (DHA specifically) to block both NF-κB and JNK pathways, reversing IR induced by a high-fat diet(Reference Oh da, Talukdar and Bae53). Supportive of this notion, in the present study, n-3 PUFA appear to improve associated insulin signalling pathways in the intestine by reducing the activity of enterocyte-specific JNK (Fig. 9). Collectively, these data support the hypothesis that n-3 PUFA may act directly on the intestine to improve insulin signalling and lower non-fasting lipid contribution following a lipid excursion.
The chronic effect of n-3 PUFA on myocardial lesion development
Development of ischaemic lesions, secondary to vascular damage or dysfunction, is a major endpoint of CVD(Reference Baldassarre, Amato and Eligini54). JCR:LA-cp rats develop lesions spontaneously, as a result of the hyperinsulinaemic and hyperlipidaemic status of these rodents(Reference Russell, Graham and Richardson6, Reference Russell, Ewart and Kelly55). Rats from the present study were killed at a relatively early age, and may explain the low frequency of stage 4 (advanced scarred lesions) heart lesions compared with previous studies(Reference Russell, Amy and Graham5, Reference Russell, Koeslag and Dolphin27). However, rats from the present study presented with a large number of early stage 2 lesions, probably due to the high lipid and cholesterol load, in the control diet. Dietary n-3 PUFA (5 %) in the JCR:LA-cp rats resulted in fewer stage 3 myocardial lesions, consistent with the complete absence of stage 4 lesions in these animals, as well as an amelioration of myocardial histology; evidence that n-3 PUFA may inhibit CVD progression. It may be reasonable to suggest that the vascular improvement observed, in response to dietary n-3 PUFA, is due to chronic improvement to metabolic status, including non-fasting lipids, visceral fat, insulin sensitivity, or potentially via a direct effect of n-3 PUFA on the heart.
Concluding remarks
In conclusion, the present study provides evidence that chronic increased dietary n-3 PUFA has beneficial effects on both hepatic and intestinal lipid metabolism, IR, body weight and myocardial ischaemic lesion frequency in the obese JCR:LA-cp rat. Dietary n-3 PUFA may confer additional therapeutic potential to lower the risk of atherosclerotic progression in patients with metabolic disorders over the long term. Future directions should focus on additional animal and clinical studies to help verify a beneficial target dose for human therapy and to further define the mechanistic pathways behind the action of n-3 PUFA.
Acknowledgements
The present study was supported in part by a pilot grant from the Alberta Diabetes Institute (S. D. P.), a NSERC Discovery grant (S. D. P. and D. F. V.) and a HSFC Grant-in-aid (S. D. P.). S. D. P. is a HSFC New Investigator. The authors wish to declare no conflict of interest. We wish to thank Kristina MacNaughton and Sharon Sokolik for their excellent technical assistance throughout the present study. We also wish to acknowledge Anja Jaeschke (University of Cincinnati, Cincinnati, OH, USA) for her contribution to the JNK activity studies. S. D. P., J. L., D. F. V. and C. J. F. conceived and designed the experiments. J. L., Z. H., Y. W., R. M., M. R., D. S., F. B. and J. C. R. performed the experiments. J. L., S. D. P., J. C. R., F. B. and D. F. V. analysed the data. F. B., S. D. P. and J. L. prepared the manuscript.















