It is well documented that numerous stresses such as weaning, infection and inflammation can result in gut mucosal injury(Reference Touchette, Carroll, Allee, Matteri, Dyer, Beausang and Zannelli1–Reference Blikslager, Moeser, Gookin, Jones and Odle4), and consequently result in diarrhoea and poor growth of pigs.
One emerging view is that pro-inflammatory cytokines play a critical role in gut injury(Reference Pié, Lallès, Blazy, Laffitte, Sève and Oswald2). Overproduction of pro-inflammatory cytokines can have a strongly adverse influence on gut integrity and epithelial function(Reference Mckay and Baird5). Therefore, controlling the release of intestinal pro-inflammatory cytokines may have potential benefits in alleviating these gut disorders.
Arginine (Arg) is a dibasic amino acid. Traditionally, it is thought of as a non-essential amino acid. However, in the last two decades, Arg has attracted major interest because it plays an important role in many physiological and biological processes including physiology of the gastrointestinal tract(Reference Anggard6). Arg has been shown to be effective in a number of gut injury models(Reference Sukhotnik, Helou, Mogilner, Lurie, Bernsteyn, Coran and Shiloni7, Reference Fu, Zhang, Zhang, Wang, Gao and Xu8). However, little research has been conducted to investigate these effects in weaned piglets.
Several studies show that Arg exerts its protective action through NO-dependent effects and NO-independent effects(Reference Duggan, Gannon and Walker9). However, little research has been conducted to investigate the anti-inflammatory action of Arg in the gut.
In the present experiment, Escherichia coli lipopolysaccharide (LPS) was administered as an inflammatory agent to establish the model of gut injury following the model of Mercer et al. (Reference Mercer, Smith, Cross, Russell, Chang and Cacioppo10). The objective was to evaluate whether Arg supplementation could attenuate the gut injury through an anti-inflammatory role and to examine the mechanism(s) of action of Arg in weaned pigs.
Materials and methods
Animal care and diets
The animal protocol for this research was approved by the Animal Care and Use Committee of Hubei Province. Seventy-two crossbred pigs (Duroc × Large White × Landrace) weaned at age 21 ± 1 d (5·78 ± 0·26 kg), were balanced for initial body weight and ancestry across four treatment groups. Pigs were housed in 2·50 × 1·80 m2 pens with six replicate pens (three pens of females and three pens of males) per treatment and three pigs per pen. Each pen was equipped with a feeder and a nipple waterer to allow pigs access ad libitum to feed and water. The basal diet (Table 1) was formulated according to National Research Council(11) requirements for all nutrients. All feed was pelleted. Crude protein, calcium and phosphorus of diets were analysed according to the procedures of the Association of Official Analytical Chemists(12). Room temperature was maintained at 25–27°C. Lighting was natural.
Table 1 Ingredient composition of the basal diet (as-fed basis)

* A rumen-stable fat powder (purchased from Berg+Schmidt, Germany).
† In the 0·5 % Arg diet, 0·86 % glycine and 0·14 % maize starch were replaced by 0·5 % Arg, 0·43 % glycine and 0·07 % maize starch. In the 1·0 % Arg diet, 0·86 % glycine and 0·14 % maize starch were replaced by 1·0 % Arg. All diets were isonitrogenous.
‡ A compound acidifier including lactic acid and phosphoric acid (provided by Wuhan Fanhua Biotechnology Company, Wuhan, China).
§ The vitamin and mineral premix (defatted rice bran as carrier) provided the following amounts per kg complete diet: retinol acetate, 2700 μg; cholecalciferol, 62·5 μg; dl-α-tocopheryl acetate, 20 mg; menadione, 3 mg; vitamin B12, 18 μg; riboflavin, 4 mg; niacin, 40 mg; pantothenic acid, 15 mg; choline chloride, 400 mg; folic acid, 700 μg; thiamin, 1·5 mg; pyridoxine, 3 mg; biotin, 100 μg; Zn, 80 mg (ZnSO4.7H2O); Mn, 20 mg (MnSO4.5H2O); Fe, 83 mg (FeSO4.H2O); Cu, 25 mg (CuSO4.5H2O); I, 0·48 mg (KI); Se, 0·36 mg (Na2SeO3.5H2O).
¶ Based on diets containing maize starch.
Experimental design
Treatments included: (1) non-challenged control (CONTR; pigs fed a control diet and injected with sterile saline); (2) LPS-challenged control (LPS; pigs fed the same control diet and challenged by injection with Escherichia coli LPS); (3) LPS+0·5 % Arg treatment (pigs fed a 0·5 % Arg diet and challenged with LPS); and (4) LPS+1·0 % Arg treatment (pigs fed a 1·0 % Arg diet and challenged with LPS). The doses of Arg (l-Arg; purity >99 %; Ajinomoto, Japan) were chosen because our preliminary study showed them to reduce weight loss in LPS-challenged pigs. We supplemented 0·86, 0·43 and 0 % glycine (purity >99 %; Ajinomoto) to the control, 0·5 % Arg and 1·0 % Arg diets, respectively, to obtain isonitrogenous diets according to Gurbuz et al. (Reference Gurbuz, Kunzelman and Ratzer13). At 08.00 hours of day 16, pigs were injected intraperitoneally with either 100 μg E. coli LPS/kg body weight or the same amount of 0·9 % (w/v) NaCl solution. The LPS (E. coli serotype 055: B5; Sigma Chemical Inc., St Louis, MO, USA) was dissolved in sterile 0·9 % NaCl solution (500 mg LPS/l saline). At 14.00 hours of day 16 (6 h post-challenge), one pig per pen was killed for evaluation of intestinal morphology and gene expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines and PPARγ. To exclude the possible effects of LPS-induced food intake reduction on gastrointestinal characteristics of the slaughtered pigs, the pigs selected for slaughtering were individually transferred to an adjacent cage at 20.00 hours of day 15, and were deprived of feed until slaughter. The remaining two pigs per pen were provided feed until 08.00 hours of day 18. Body weight and feed intake were measured at 08.00 hours of days 0, 16 and 18.
Sample collection
Three castrated males and three females from each group were humanely killed by intravenous injection of sodium pentobarbital (40 mg/kg body weight) 6 h following injection with LPS or saline. A midline laparotomy was performed. The abdomen was incised, and the small intestine was dissected free of the mesentery and arranged in measured lengths on a chilled stainless steel tray. The 2 × 3, 10 and 0·5 cm segments were cut at every point 25, 50 and 75 % of the total intestinal length to represent samples for duodenum, jejunum and ileum, respectively.
The 2 × 3 cm intestinal segments were processed, embedded and stained according to the procedures of Luna(Reference Luna14). The segments were flushed gently with ice-cold PBS (pH 7·4) and then fixed in 10 % fresh, chilled formalin solution. The 10 cm intestinal segments were opened longitudinally and the contents were flushed with ice-cold PBS. The mucosa was scraped with a glass slide, snap-frozen in liquid nitrogen and then stored at − 80°C for further analysis of protein and DNA. The 0·5 cm intestinal segments were gently rinsed in ice-cold PBS and immediately frozen in liquid nitrogen, and then stored at − 80°C for pro-inflammatory cytokines and PPARγ mRNA analysis.
Mucosal protein and DNA
The mucosa samples were homogenized with a tissue homogenizer in ice-cold PBS EDTA (0·05 m-Na3PO4, 2·0 m-NaCl, 2 × 10− 3 m-EDTA, pH 7·4) using a 1:10 (w/v) ratio. Protein concentration of mucosal homogenates was measured by the method of Lowry et al. (Reference Lowry, Rosebrough, Farr and Randall15) using a detergent-compatible protein assay (Bio-Rad Laboratories, Hercules, CA, USA) and bovine serum albumin as standards. Mucosal DNA content was evaluated by a fluorometric assay(Reference Labarca and Paigen16).
Intestinal morphology
After a 24 h fixation, the intestinal segments were taken out, and dehydrated using increasing concentrations of ethanol (70–100 %) and chloroform. After dehydration, the segments were embedded in paraffin, and then placed in a refrigerator to make the paraffin sufficiently hard. Cross-sections of the segments were cut approximately 5 μm thick with a microtome (American Optical Co., Scientific Instrument Division, Buffalo, NY, USA), and stained with haematoxylin and eosin. The method was according to Nabuurs et al. (Reference Nabuurs, Hoogendoorn, van der Molen and van Osta17). In each section, ten fields were examined using a light microscope with a computer-assisted morphometric system (BioScan Optimetric; BioScan Inc., Edmonds, WA, USA). The villus height and the associated crypt depth were measured. Villus height is defined as the distance from the villus tip to crypt mouth and crypt depth from crypt mouth to base.
Crypt cell proliferation and villus cell apoptosis
Crypt cell proliferation was determined using 5-bromodeoxyuridine (Roche Diagnostic Corporation, IN, USA). At 2 h before slaughter, 5-bromodeoxyuridine was injected intraperitoneally at 25 mg/kg body weight. Tissue slices (5 μm) were deparaffinized, rehydrated and stained for bromodeoxyuridine labelling (Cell Proliferation Kit from Amersham Life Science, Amersham, UK). For each slide, the number of stained cells was counted in at least ten crypts. The proliferation index was measured as the ratio of the number of crypt cells staining positively for 5-bromodeoxyuridine and total cell number.
Villus cell apoptosis was assessed by the terminal deoxyuridine nick-end labelling immunohistochemical assay using the In Situ Cell Death Detection Kit (Boehringer Mannheim GmbH, Mannheim, Germany). Tissue slides (5 μm) were deparaffinized, rehydrated and microwave-pretreated in 10 mm-citrate buffer (pH 6·0) to retrieve antigen. After washing, the slides were incubated in buffer containing a nucleotide mixture with fluorescein-labelled deoxy-UTP and terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase at 37°C for 1 h. After washing, the slides were incubated with blocking solution (3 % H2O2 in methanol) for 10 min and stained with anti-fluorescein antibody, Fab fragment from sheep, conjugated with horseradish peroxidase (converter-peroxidase) at 37°C for 30 min. AES substrate (Zymed Laboratories Inc., San Francisco, CA, USA) was applied for colour development. For each slide, the number of stained cells was counted in at least ten villi. The apoptotic index was defined as the ratio of the number of apoptotic terminal deoxyuridine nick-end labelling-positive cells and total cell number.
IL-6, TNF-α and PPARγ mRNA
RNA was extracted from 0·5 cm intestinal segments using the TRIzol Reagent (Invitrogen Life Technologies, Carlsbad, CA, USA) according to manufacturer's guidelines. Each extracted RNA (6 μl) was used as templates in cDNA synthesis. Reverse transcription was performed in a mixture of 1 μl Oligo-dT18 (Invitrogen Life Technologies), 0·5 μl RNasin inhibitor (Promega, Madison, WI, USA), 2 μl dNTP (Promega), 1 μl M-MLV transcriptase (Promega), 4 μl M-MLV RT reaction buffer (Promega) and 5·5 μl RNase-free water. The reaction was carried out for 5 min at 70°C, 1 h at 37°C, 5 min at 95°C and 5 min at 4°C.
To amplify IL-6, TNF-α, PPARγ (target gene) and β-actin cDNA fragments, the following sequences of PCR primer pairs were used: forward 5′-GGCTGCTTCTGGTGATGGCTA-3′, reverse 5′-TTGCCTCAGGGTCTGGATCAG-T-3′ for IL-6 (419 bp); forward 5′-CCACGTTGTAGCCAATGTCA-3′, reverse 5′-CAGCAAAGTCCAGATAGTCG-3′ for TNF-α (375 bp); forward 5′-TCCCGCTGACCAAAGCAAAGGC-3′, reverse 5′-CCACGGAGCGAAACTGACACCC-3′ for PPARγ (195 bp); forward 5′-CGTCCACCGCAAATGCTTCTAG-3′, reverse 5′-TGCTGTCACCTTCACCGTTCC-3′ for β-actin (210 bp). The oligonucleotide primers of IL-6, TNF-α, PPARγ and β-actin genes were designed from pig gene sequences in GenBank (M80258, X57321, AJ006757, AY550069). To minimize amplification of potentially contaminating genomic DNA, the primers were designed to span introns and intron–exon boundaries. Of the RT reaction, 1 μl of the produced cDNA was used in SYBR Green PCR Master Mix (Promega) and 0·8 μl of each 20 pm primer. The total volume of PCR reaction system was 50 μl. Cycling parameters were 94°C × 3 min, followed by fifty cycles of 94°C × 15 s, 57°C × 30 s, 72°C × 30 s. Amplification products were verified by melting curves, agarose gel electrophoresis and direct sequencing. Results were analysed by the comparative cycle threshold (C T) method (2− ΔΔCT)(Reference Livak and Schmittgen18), where C T is the number of cycles required to reach an arbitrary threshold. The validation of ΔΔC T calculation was confirmed by the following procedures. Briefly, a cDNA preparation was diluted over a 100-fold range. For each dilution sample, amplifications were performed using target and β-actin primers. The average C T was calculated for both target and β-actin gene and the ΔC T (C T,target − C T,β-actin) was determined. A plot of the log cDNA dilution versus ΔC T was made. The absolute value of the slope is close to zero, indicating the amplification efficiencies of the target and β-actin genes are similar. So, ΔΔC T calculation for the relative quantification of target genes could be used. The C T for target gene of each sample was corrected by subtracting the C T for β-actin (ΔC T). The ileal segments of the CONTR group were chosen as reference samples, and the ΔC T for all experimental samples was subtracted by the average ΔC T for the reference samples (ΔΔC T). Finally, experimental mRNA abundance relative to control mRNA abundance was calculated with use of the formula 2− ΔΔCT.
Statistical analysis
All data were subjected to ANOVA appropriate for randomized complete block design by using the GLM procedure of SAS (SAS Institute, Cary, NC, USA). LPS pigs were compared by preplanned contrasts with either CONTR pigs to determine the effect of LPS challenge, or to LPS+0·5 % or 1·0 % Arg pigs to determine the effect of Arg supplementation within challenged pigs. Significance of differences was calculated using the LSMEANS statement, and results are presented as least-square means and pooled standard errors of the means. Differences were considered as significant when P < 0·05. Instances in which P < 0·10 are discussed as trends.
Results
Performance
The growth performance data are presented in Table 2. There was no difference in initial body weight among treatments. During days 0–16 (pre-challenge), there was no difference in body weight, average daily gain, average daily feed intake and gain:feed ratio among treatments. During days 16–18 (post-challenge), LPS challenge resulted in a 175 % reduction of average daily gain (P < 0·001) and a 65 % reduction of average daily feed intake (P < 0·001) compared to the CONTR pigs. Dietary supplementation of 0·5 % Arg significantly alleviated the weight loss compared to the LPS pigs (P = 0·025). Supplementation of 1·0 % Arg also showed a similar pattern numerically, however, this effect did not achieve statistical significance (P = 0·149). Dietary supplementation of 0·5 or 1·0 % Arg did not affect average daily feed intake compared to the LPS pigs. All pigs subjected to the LPS challenge lost weight, so we did not calculate gain:feed ratio for these groups.
Table 2 Effects of arginine (Arg) supplementation on the growth performance of weaned pigs during pre- and post-challenge periods*
(Least-square mean values for six pens)

ADFI, average daily feed intake; ADG, average daily gain; NC, not calculated.
* CONTR (non-challenged control): pigs fed a control diet and injected with sterile saline; LPS (lipopolysaccharide-challenged control): pigs fed the same control diet and challenged with Escherichia coli LPS; LPS+0·5 % Arg:pig fed a 0·5 % Arg diet and challenged with LPS; LPS+1·0 % Arg:pig fed a 1·0 % Arg diet and challenged with LPS.
† Contrast: (1) CONTR v. LPS; (2) LPS v. LPS+0·5 % Arg; (3) LPS v. LPS+1·0 % Arg.
During the 18 d study, there were no differences among treatments in overall average daily gain and average daily feed intake. The LPS pigs had a 19 % lower gain:feed ratio (P = 0·070) compared to the CONTR pigs. Arg supplementation did not affect gain:feed ratio compared to the LPS pigs.
Mucosal protein and DNA
The data for intestinal mucosal protein and DNA contents are presented in Table 3. The LPS pigs had decreased mucosal protein content in duodenum (26 % lower, P = 0·002) and jejunum (30 % lower, P = 0·015) compared to the CONTR pigs. In addition, the LPS pigs also showed a significant decrease in DNA content in jejunum (36 % lower, P = 0·006) and ileum (36 % lower, P < 0·001) compared to the CONTR pigs. Compared to the LPS pigs, the LPS+0·5 % Arg pigs had increased protein content in duodenum (23 % higher, P = 0·034) and jejunum (31 % higher, P = 0·071), and increased DNA content in jejunum (33 % higher, P = 0·089). Compared to the LPS pigs, the LPS+1·0 % Arg pigs had increased protein content in duodenum (19 % higher, P = 0·076) and jejunum (31 % higher, P = 0·071), and increased DNA content in ileum (34 % higher, P = 0·005).
Table 3 Effects of arginine (Arg) supplementation on intestinal mucosal protein and DNA contents (expressed as mg/g mucosa) of weaned pigs after 6 h Escherichia coli lipopolysaccharide (LPS) challenge*
(Least-square mean values for six pigs)

* CONTR (non-challenged control): pigs fed a control diet and injected with sterile saline; LPS (LPS-challenged control): pigs fed the same control diet and challenged with Escherichia coli LPS; LPS+0·5 % Arg:pig fed a 0·5 % Arg diet and challenged with LPS; LPS+1·0 % Arg:pig fed a 1·0 % Arg diet and challenged with LPS.
† Contrast: (1) CONTR v. LPS; (2) LPS v. LPS+0·5 % Arg; (3) LPS v. LPS+1·0 % Arg.
Intestinal morphology
Data for small intestinal morphology are shown in Table 4. Compared to CONTR pigs, LPS pigs showed a decrease in villus height in duodenum (30 % lower, P < 0·001), jejunum (29 % lower, P < 0·001) and ileum (17 % lower, P = 0·003), and also an increase in crypt depth in duodenum (13 % higher, P = 0·080), jejunum (22 % higher, P = 0·066) and ileum (40 % higher, P = 0·001). Relative to LPS pigs, dietary supplementation of 0·5 % Arg significantly increased villus height in duodenum (29 % higher, P = 0·001), jejunum (21 % higher, P < 0·001) and ileum (27 % higher, P < 0·001), and also significantly decreased crypt depth in duodenum (25 % lower, P < 0·001), jejunum (25 % lower, P = 0·013) and ileum (16 % lower, P = 0·043). Supplementation of 1·0 % Arg also exerted similar effects on villus height and crypt depth.
Table 4 Effects of arginine (Arg) supplementation on villus height and crypt depth of weaned pigs after 6 h Escherichia coli lipopolysaccharide (LPS) challenge*
(Least-square mean values for six pigs)

* CONTR (non-challenged control): pigs fed a control diet and injected with sterile saline; LPS (LPS-challenged control): pigs fed the same control diet and challenged with Escherichia coli LPS; LPS+0·5 % Arg:pig fed a 0·5 % Arg diet and challenged with LPS; LPS+1·0 % Arg:pig fed a 1·0 % Arg diet and challenged with LPS.
† Contrast: (1) CONTR v. LPS; (2) LPS v. LPS+0·5 % Arg; (3) LPS v. LPS+1·0 % Arg.
Enterocyte proliferation and apoptosis
The data for enterocyte proliferation and apoptosis are presented in Table 5. A significant decrease in crypt cell proliferation index was observed in duodenum (34 % lower, P < 0·001), jejunum (36 % lower, P < 0·001) and ileum (36 % lower, P < 0·001) in LPS pigs compared to CONTR pigs. Supplementation with 0·5 % Arg resulted in a significant increase in crypt cell proliferation index in duodenum (29 % higher, P = 0·005), jejunum (39 % higher, P = 0·002) and ileum (52 % higher, P < 0·001) compared to LPS pigs. Supplementation with 1·0 % Arg also exerted similar effects on crypt cell proliferation.
Table 5 Effects of arginine (Arg) supplementation on enterocyte proliferation and apoptosis of weaned pigs after 6 h Escherichia coli lipopolysaccharide (LPS) challenge*
(Least-square mean values for six pigs)
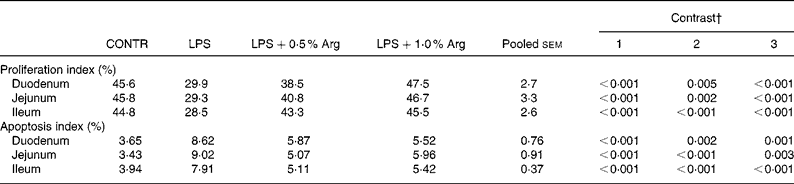
* CONTR (non-challenged control): pigs fed a control diet and injected with sterile saline; LPS (LPS-challenged control): pigs fed the same control diet and challenged with Escherichia coli LPS; LPS+0·5 % Arg:pig fed a 0·5 % Arg diet and challenged with LPS; LPS+1·0 % Arg:pig fed a 1·0 % Arg diet and challenged with LPS.
† Contrast: (1) CONTR v. LPS; (2) LPS v. LPS+0·5 % Arg; (3) LPS v. LPS+1·0 % Arg.
Following LPS injection, a significant increase in villus cell apoptosis index was seen in duodenum (136 % higher, P < 0·001), jejunum (163 % higher, P < 0·001) and ileum (101 % higher, P < 0·001) compared to CONTR pigs. Dietary supplementation of 0·5 % Arg decreased villus cell apoptosis index in duodenum (32 % lower, P = 0·002), jejunum (44 % lower, P < 0·001) and ileum (35 % lower, P < 0·001) compared to LPS pigs. Supplementation with 1·0 % Arg also exerted similar effects on villus cell apoptosis.
mRNA expression of intestinal pro-inflammatory cytokines and PPARγ
The data for mRNA expression of IL-6, TNF-α and PPARγ are shown in Table 6. LPS challenge increased IL-6 mRNA abundance in duodenum (81 % higher, P = 0·080) and jejunum (3·52-fold higher, P < 0·001) compared to CONTR pigs. Compared to LPS pigs, exposure to 0·5 and 1·0 % Arg decreased IL-6 mRNA abundance in jejunum by 36 % (P = 0·082) and 41 % (P = 0·053), respectively.
Table 6 Effects of arginine (Arg) supplementation on intestinal IL-6, TNF-α and PPARγ mRNA abundance of weaned pigs after 6 h Escherichia coli lipopolysaccharide (LPS) challenge*
(Least-square mean values for six pigs)

* CONTR (non-challenged control): pigs fed a control diet and injected with sterile saline; LPS (LPS-challenged control): pigs fed the same control diet and challenged with Escherichia coli LPS; LPS+0·5 % Arg:pig fed a 0·5 % Arg diet and challenged with LPS; LPS+1·0 % Arg:pig fed a 1·0 % Arg diet and challenged with LPS.
† Contrast: (1) CONTR v. LPS; (2) LPS v. LPS+0·5 % Arg; (3) LPS v. LPS+1·0 % Arg.
LPS administration resulted in a significant increase in TNF-α mRNA abundance in duodenum (2·35-fold higher, P = 0·003), jejunum (4·55-fold higher, P < 0·001) and ileum (4·24-fold higher, P < 0·001) compared to CONTR pigs. Relative to LPS pigs, dietary supplementation of 0·5 % Arg decreased TNF-α mRNA abundance in jejunum (35 % lower, P = 0·030) and ileum (31 % lower, P = 0·039), and 1·0 % Arg supplementation decreased TNF-α mRNA abundance in jejunum (50 % lower, P = 0·003).
LPS injection increased PPARγ mRNA abundance by 194 % in jejunum (P = 0·003). Compared to the LPS pigs, 0·5 % Arg supplementation increased PPARγ mRNA abundance in duodenum (49 % higher, P = 0·075), jejunum (60 % higher, P = 0·006) and ileum (102 % higher, P = 0·063), and 1·0 % Arg supplementation increased PPARγ mRNA abundance by 46 % in duodenum (P = 0·094).
Discussion
In the present study, to evaluate whether Arg supplementation could attenuate gut injury through an anti-inflammatory role in weaned pigs, we took advantage of a model for inducing gut injury in pigs by injecting Escherichia coli LPS(Reference Mercer, Smith, Cross, Russell, Chang and Cacioppo10). LPS is a molecule found in the membrane of all gram-negative bacteria. LPS induces symptoms of acute bacterial infection including anorexia, hypersomnia and fever. In addition, LPS results in a variety of morphological alterations in the digestive tract, such as submucosal oedema, epithelial lifting at the tips of villi, frank haemorrhage and necrosis(Reference Mercer, Smith, Cross, Russell, Chang and Cacioppo10), ileal mucosal acidosis(Reference VanderMeer, Wang and Fink19), and results in an increase in mucosal permeability(Reference Fink, Antonsson, Wang and Rothschild20). Besides the direct effect of LPS on gut, LPS may induce indirectly intestinal injury via reduced feed intake. It has been shown that feed intake is correlated with intestinal morphology(Reference Verdonk, Spreeuwenberg, Bakker, Verstegen, Lindberg and Ogle21). In the current study, the pigs were deprived of feed after 6 h LPS challenge (i.e. before slaughter), which excludes the possible effects of feed intake on gastrointestinal characteristics.
In the present study, LPS challenge severely decreased performance of weaned pigs during 48 h post-challenge, which is consistent with the findings of Johnson(Reference Johnson22) and Liu et al. (Reference Liu, Li, Gong, Yi, Gaines and Carroll23). Prior to LPS challenge, Arg supplementation had no effect on growth performance of weaned pigs. In contrast to the present findings, Kim et al. (Reference Kim, McPherson and Wu24) reported that dietary supplementation with 0·2 and 0·4 % Arg to milk-fed piglets improved growth performance. Additionally, Takahashi et al. (Reference Takahashi, Orihashi and Yukio25) reported that Arg supplementation improved body weight gain and feed efficiency in male broiler chickens. The reason for the discrepancy might be that the Arg level of the basal diet (1·28 %) in the current study was adequate for maintaining growth of weaned pigs in normal physiological condition. During 48 h post-challenge, 0·5 % Arg supplementation alleviated the weight loss compared to the LPS pigs, which indicates the importance of exogenous Arg supply under stress, infection and diseases. Similarly, Kohli et al. (Reference Kohli, Meininger, Haynes, Yan, Self and Wu26) reported that daily oral administration of l-Arg-HCl reduced body weight loss in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. It has been reported that Arg may act as a metabolic regulator to increase protein synthesis and decrease protein catabolism under infection and stress situations(Reference Frank, Escobar, Nguyen, Jobgen, Jobgen, Davis and Wu27) by stimulating the secretion of insulin, growth hormone and glucagon(Reference Wu, Meininger, Knabe, Bazer and Rhoads28). Therefore, it is possible that 0·5 % Arg supplementation alleviated growth suppression associated with the LPS challenge partially by decreasing protein catabolism and maintaining the protein deposition rate of skeletal muscle.
Mucosal protein and DNA contents are important indicators for cell metabolism. Villus height and crypt depth can be regarded as a criterion to reflect intestinal morphology. In the present study, compared to the LPS pigs, 0·5 or 1·0 % Arg supplementation increased mucosal protein and DNA contents, and increased villus height and decreased crypt depth following Arg supplementation, which indicates that Arg supplementation protected the intestinal mucosa from damage caused by the LPS challenge. In agreement with the present findings, Sukhotnik et al. (Reference Sukhotnik, Helou, Mogilner, Lurie, Bernsteyn, Coran and Shiloni7) reported that oral Arg improved intestinal recovery following ischaemia–reperfusion injury in rats. In addition, dietary Arg supplementation accelerated ulcer healing in experimental ulcerative ileitis(Reference Sukumar, Loo, Magur, Nandi, Oler and Levine29) and stimulated small intestinal mucosal recovery following experimental radiation enteritis(Reference Gurbuz, Kunzelman and Ratzer13). In the current experiment, improvement of intestinal mucosa is concurrent with alleviation of growth suppression induced by LPS challenge following 0·5 % Arg supplementation. Therefore, it is possible that feeding Arg in the diet to the LPS-challenged pigs attenuated growth depression partially by alleviating the intestinal mucosa injury. However, in contrast to 0·5 % Arg supplementation, 1·0 % Arg supplementation alleviated intestinal mucosa injury, but did not alleviate growth suppression significantly. The reason for the discrepancy might be that over-supplementation of Arg resulted in Arg–lysine antagonism, and lowered the absorption of lysine(Reference Baker30), or resulted in a general amino acid imbalance(Reference Anderson, Lewis, Peo and Crenshaw31), and consequently counteracted the advantage of 1·0 % Arg supplementation on growth performance of the challenged pigs.
The dynamic process of epithelial cell turnover is a function of the rates of crypt cell proliferation, migration along the small intestine crypt–villus axis, differentiation and cell death via apoptosis(Reference Sukhotnik, Helou, Mogilner, Lurie, Bernsteyn, Coran and Shiloni7). To some degree, normal intestinal morphology depends on the balance of epithelial cell turnover(Reference Sukhotnik, Helou, Mogilner, Lurie, Bernsteyn, Coran and Shiloni7). Decreased cell proliferation and increased apoptosis may be the main mechanisms responsible for intestinal mucosal injury(Reference Sukhotnik, Helou, Mogilner, Lurie, Bernsteyn, Coran and Shiloni7). In the present study, dietary supplementation of Arg attenuated the decrease of crypt cell proliferation and the increase of villus cell apoptosis caused by the LPS challenge. The present findings are consistent with the results of Sukhotnik et al. (Reference Sukhotnik, Helou, Mogilner, Lurie, Bernsteyn, Coran and Shiloni7) who reported that Arg increased mucosal cell proliferation in functioning intestine and decreased the cell apoptosis in ileum in rats suffering from ischaemia–reperfusion injury. Additionally, some research has shown that Arg stimulated intestinal epithelial cell migration(Reference Rhoads, Chen and Gookin32, Reference Rhoads, Niu, Odle and Graves33). In the current study, feeding Arg in the diet to the LPS-challenged pigs may alleviate the intestinal mucosa injury via maintaining the balance of epithelial cell turnover.
In the current study, we hypothesized that Arg exerted its protective effect on the gut through attenuating intestinal inflammatory response. Consistent with mucosal injury caused by the LPS challenge, increased expression of IL-6 in duodenum and jejunum, and TNF-α in all three intestinal segments was observed. In agreement with the present observations, many studies have reported the up-regulated expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines in the intestine of man and animals during enteric infection and intestinal inflammatory diseases(Reference Oswald, Dozois, Barlagne, Fournout, Johansen and Bogh34) and in newly weaned pigs(Reference Pié, Lallès, Blazy, Laffitte, Sève and Oswald2). Over-production of pro-inflammatory cytokines can have a negative influence on gut integrity and epithelial function(Reference Mckay and Baird5). In the present study, the LPS pigs fed the 0·5 % Arg diet exhibited decreased jejunal IL-6, jejunal and ileal TNF-α mRNA, and those fed the 1·0 % Arg diet exhibited decreased jejunal TNF-α mRNA compared to the LPS pigs. Currently, there are very few studies on the regulation of intestinal pro-inflammatory cytokines through dietary Arg supplementation. Marion et al. (Reference Marion, Coëffier, Lemoulan, Gargala, Ducrotté and Déchelotte35) reported that Arg reduced CXC chemokines (e.g. IL-8 and Mig) in the human intestinal epithelial cell line HCT-8 under inflammatory conditions, which suggests that Arg exerted beneficial influence on intestinal inflammatory response. In addition, Arg exerted an inhibitory effect on pro-inflammatory cytokine production in many other stress models(Reference Fu, Zhang, Zhang, Wang, Gao and Xu8, Reference Cui, Iwasa, Iwasa and Ogoshi36, Reference Yeh, Yeh, Lin and Chen37). Arg down-regulated pro-inflammatory cytokine expression or production in spleen, thymus, lung and liver of burned rats(Reference Cui, Iwasa, Iwasa and Ogoshi36), in serum and lung of immature rats after gut ischaemia–reperfusion(Reference Fu, Zhang, Zhang, Wang, Gao and Xu8), and in peritoneal lavage fluid of septic rat(Reference Yeh, Yeh, Lin and Chen37), thus preventing the development of inflammation. In the current study, it is possible that feeding pigs dietary Arg reduced gut mucosal injury partially by suppressing pro-inflammatory cytokine production.
To explore the molecular mechanism by which Arg attenuated intestinal inflammatory response, we examined the role of PPARγ. PPARγ, a member of the superfamily of nuclear hormone receptors, has recently been recognized as an endogenous regulator of intestinal inflammation(Reference Nakajima, Wada and Miki38, Reference Cuzzocrea, Pisano and Dugo39). PPARγ ligands have been shown to be effective in a number of intestinal inflammatory models(Reference Katayama, Wada and Nakajima40, Reference Sato, Kozar, Zou, Weatherall, Attuwaybi, Moore-Olufemi, Weisbrodt and Moore41). The protective effects of PPARγ and its ligands is associated with the inhibition of a wide variety of inflammatory indices such as pro-inflammatory cytokines(Reference Moraes, Piqueras and Bishop-Bailey42). The mechanism of action of PPARγ in inflammation is in the trans-suppression of pro-inflammatory cytokine gene activation by negatively interfering with the NF-κB, STAT-1 and AP-1 signalling pathways(Reference Moraes, Piqueras and Bishop-Bailey42).
In the present study, we have observed for the first time that intestinal PPARγ expression is up-regulated and the synthesis of intestinal IL-6 and TNF-α were decreased simultaneously in Arg-supplemented pigs after LPS challenge. So, it is possible that the protective effects of Arg on intestinal mucosal injury were associated with decreasing the expression of intestinal pro-inflammatory cytokines through activating PPARγ expression. The inhibitory effect of PPARγ on pro-inflammatory cytokines could be mediated through the inhibition of NF-κB. Indeed, in a rat model of LPS-induced injury(Reference Calkins, Bensard, Heimbach, Meng, Shames, Pulido and McIntyre43), Arg inhibited the NF-κB DNA binding and stabilized I-κB complex, which both may account for the decreased pro-inflammatory cytokines. Additionally, a study has shown that activation of PPARγ in the colon inhibits mucosal production of IL-1β and TNF-α by down-regulation of the NF-κB and mitogen-activated protein kinase signal pathways(Reference Desreumaux, Dubuquoy and Nutten44). Regretfully, in the current study, no categorical evidence demonstrated that Arg was working directly through PPARγ. Further studies are needed to accomplish it either by including a PPARγ antagonist or by knocking out or down the expression of PPARγ in the experimental designs.
In conclusion, dietary supplementation of Arg exerts beneficial effects in alleviating gut mucosal injury of LPS-challenged pigs. It is possible that the protective effects of Arg on the intestine are associated with decreasing the expression of intestinal pro-inflammatory cytokines through activating PPARγ expression.
Acknowledgements
The authors express their gratitude to the National Basic Research Program of China (2004CB117504), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (30500362) and the Hubei Provincial Department of Education (D200718003) for financial support. There is no conflict of interest that should be disclosed.








