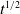The aim of this paper is to determine the effects of forces exerted on the cantilever probe tip of an atomic force microscope (AFM). These forces vary according to the separation distance between the probe tip and the surface of the sample being examined. Hence, at a distance away from the surface (farther than don), these forces have an attractive nature and are of Van der Waals type, and when the probe tip is situated in the range of a0≤dts≤don, the capillary force is added to the Van der Waals force. At a distance of dts≤a0, the Van der Waals and capillary forces remain constant at intermolecular distances, and the contact repulsive force repels the probe tip from the surface of sample. The capillary force emerges due to the contact of thin water films with a thickness of hc which have accumulated on the sample and probe. Under environmental conditions a layer of water or hydrocarbon often forms between the probe tip and sample. The capillary meniscus can grow until the rate of evaporation equals the rate of condensation. For each of the above forces, different models are presented. The smoothness or roughness of the surfaces and the geometry of the cantilever tip have a significant effect on the modeling of forces applied on the probe tip. Van der Waals and the repulsive forces are considered to be the same in all the simulations, and only the capillary force is altered in order to evaluate the role of this force in the AFM-based modeling. Therefore, in view of the remarkable advantages of the piezoelectric microcantilever and also the extensive applications of the tapping mode, we investigate vibrational motion of the piezoelectric microcantilever in the tapping mode. The cantilever mentioned is entirely covered by two piezoelectric layers that carry out both the actuation of the probe tip and the measuringof its position.