In order to study the structure and temperature distribution within high-mass star-forming clumps, we employed the Australia Telescope Compact Array to image the 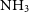 $\mathrm{NH}_3$ (J,K) = (1,1) through (6,6) and the (2,1) inversion transitions, the
$\mathrm{NH}_3$ (J,K) = (1,1) through (6,6) and the (2,1) inversion transitions, the 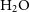 $\mathrm{H}_2\mathrm{O}$
$\mathrm{H}_2\mathrm{O}$ 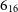 $6_{16}$-
$6_{16}$-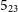 $5_{23}$ maser line at 22.23508 GHz, several
$5_{23}$ maser line at 22.23508 GHz, several 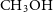 $\mathrm{CH}_3\mathrm{OH}$ lines and hydrogen and helium recombination lines. In addition, 22- and 24-GHz radio continuum emission was also imaged.
$\mathrm{CH}_3\mathrm{OH}$ lines and hydrogen and helium recombination lines. In addition, 22- and 24-GHz radio continuum emission was also imaged.
The 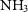 $\mathrm{NH}_3$ lines probe the optical depth and gas temperature of compact structures within the clumps. The
$\mathrm{NH}_3$ lines probe the optical depth and gas temperature of compact structures within the clumps. The 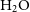 $\mathrm{H}_2\mathrm{O}$ maser pinpoints the location of shocked gas associated with star formation. The recombination lines and the continuum emission trace the ionised gas associated with hot OB stars. The paper describes the data and presents sample images and spectra towards select clumps. The technique for estimating gas temperature from
$\mathrm{H}_2\mathrm{O}$ maser pinpoints the location of shocked gas associated with star formation. The recombination lines and the continuum emission trace the ionised gas associated with hot OB stars. The paper describes the data and presents sample images and spectra towards select clumps. The technique for estimating gas temperature from 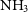 $\mathrm{NH}_3$ line ratios is described. The data show widespread hyperfine intensity anomalies in the
$\mathrm{NH}_3$ line ratios is described. The data show widespread hyperfine intensity anomalies in the 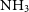 $\mathrm{NH}_3$ (1,1) images, an indicator of non-LTE
$\mathrm{NH}_3$ (1,1) images, an indicator of non-LTE 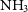 $\mathrm{NH}_3$ excitation. We also identify several new
$\mathrm{NH}_3$ excitation. We also identify several new 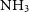 $\mathrm{NH}_3$ (3,3) masers associated with shocked gas. Towards AGAL328.809+00.632, the
$\mathrm{NH}_3$ (3,3) masers associated with shocked gas. Towards AGAL328.809+00.632, the 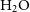 $\mathrm{H}_2\mathrm{O}$
$\mathrm{H}_2\mathrm{O}$ 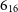 $6_{16}$-
$6_{16}$-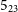 $5_{23}$ line, normally seen as a maser, is instead seen as a thermally excited absorption feature against a strong background continuum. The data products are described in detail.
$5_{23}$ line, normally seen as a maser, is instead seen as a thermally excited absorption feature against a strong background continuum. The data products are described in detail.