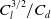Camber morphing is an effective way to control the lift generated by any aerofoil and potentially improve the range (as measured by the lift-to-drag ratio) and endurance (as measured by 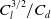 $C_l^{3/2}/C_d$
). This can be especially useful for fixed-wing Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) undergoing different flying manoeuvres and flight phases. This work investigates the aerodynamic characteristics of the NACA0012 aerofoil morphed using a Single Corrugated Variable-Camber (SCVC) morphing approach. Structural analysis and morphed shapes are obtained based on small-deformation beam theory using chain calculations and validated using finite-element software. The aerofoil is then reconstructed from the camber line using a Radial Basis Function (RBF)-based interpolation method (J.H.S. Fincham and M.I. Friswell, “Aerodynamic optimisation of a camber morphing aerofoil,” Aerosp. Sci. Technol., 2015). The aerodynamic analysis is done by employing two different finite-volume solvers (OpenFOAM and ANSYS-Fluent) and a panel method code (XFoil). Results reveal that the aerodynamic coefficients predicted by the two finite-volume solvers using a fully turbulent flow assumption are similar but differ from those predicted by XFoil. The aerodynamic efficiency and endurance factor of morphed aerofoils indicate that morphing is beneficial at moderate to high lift requirements. Further, the optimal morphing angle increases with an increase in the required lift. Finally, it is observed for a fixed angle-of-attack that an optimum morphing angle exists for which the aerodynamic efficiency becomes maximum.
$C_l^{3/2}/C_d$
). This can be especially useful for fixed-wing Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) undergoing different flying manoeuvres and flight phases. This work investigates the aerodynamic characteristics of the NACA0012 aerofoil morphed using a Single Corrugated Variable-Camber (SCVC) morphing approach. Structural analysis and morphed shapes are obtained based on small-deformation beam theory using chain calculations and validated using finite-element software. The aerofoil is then reconstructed from the camber line using a Radial Basis Function (RBF)-based interpolation method (J.H.S. Fincham and M.I. Friswell, “Aerodynamic optimisation of a camber morphing aerofoil,” Aerosp. Sci. Technol., 2015). The aerodynamic analysis is done by employing two different finite-volume solvers (OpenFOAM and ANSYS-Fluent) and a panel method code (XFoil). Results reveal that the aerodynamic coefficients predicted by the two finite-volume solvers using a fully turbulent flow assumption are similar but differ from those predicted by XFoil. The aerodynamic efficiency and endurance factor of morphed aerofoils indicate that morphing is beneficial at moderate to high lift requirements. Further, the optimal morphing angle increases with an increase in the required lift. Finally, it is observed for a fixed angle-of-attack that an optimum morphing angle exists for which the aerodynamic efficiency becomes maximum.