Let 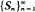 be the sequence of partial sums of independent N(μ, 1) random variables. The boundary in the {(n, Sn)} plane which minimizes the expected number of times n that Sn will be below a boundary when μ = θ > 0 subject to a given expected number of visits that Sn will be above the same boundary when μ = 0 is shown to be linear and is also characterized. Similar results are shown for Brownian motion.
be the sequence of partial sums of independent N(μ, 1) random variables. The boundary in the {(n, Sn)} plane which minimizes the expected number of times n that Sn will be below a boundary when μ = θ > 0 subject to a given expected number of visits that Sn will be above the same boundary when μ = 0 is shown to be linear and is also characterized. Similar results are shown for Brownian motion.