Ion-exchange sites with very high selectivity for Cs (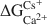 = 40 kJ/eq) similar to illite were generated in a controlled way in montmorillonites b. (1) repeated wetting-drying cycles and b. (2) charge reduction using the Hofmann-Klemen effect. An almost continuous range of sites with selectivities varying from ln
= 40 kJ/eq) similar to illite were generated in a controlled way in montmorillonites b. (1) repeated wetting-drying cycles and b. (2) charge reduction using the Hofmann-Klemen effect. An almost continuous range of sites with selectivities varying from ln 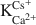 = 33 to 5 was observed.
= 33 to 5 was observed.