In various stochastic models the random equation 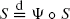 of implicit renewal theory appears where the real random variable S and the stochastic process Ψ with index space and state space R are independent. By use of stochastic approximation the distribution function of S is recursively estimated on the basis of independent or ergodic copies of Ψ. Under integrability assumptions almost sure L1-convergence is proved. The choice of gains in the recursion is discussed. Applications are given to insurance mathematics (perpetuities) and queueing theory (stationary waiting and queueing times).
of implicit renewal theory appears where the real random variable S and the stochastic process Ψ with index space and state space R are independent. By use of stochastic approximation the distribution function of S is recursively estimated on the basis of independent or ergodic copies of Ψ. Under integrability assumptions almost sure L1-convergence is proved. The choice of gains in the recursion is discussed. Applications are given to insurance mathematics (perpetuities) and queueing theory (stationary waiting and queueing times).