We examine the long-term stability (on decade-like timescales) of optical ‘high polarisation’ (HP) state with 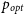 ${p_{opt}}$
${p_{opt}}$ 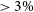 ${> 3\%}$, which commonly occurs in flat-spectrum (i.e., beamed) radio quasars (FSRQs) and is a prominent marker of blazar state. Using this clue, roughly a quarter of the FSRQ population has been reported to undergo HP
${> 3\%}$, which commonly occurs in flat-spectrum (i.e., beamed) radio quasars (FSRQs) and is a prominent marker of blazar state. Using this clue, roughly a quarter of the FSRQ population has been reported to undergo HP 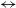 $\leftrightarrow$ non-HP state transition on year-like timescales. This work examines the extent to which HP (i.e., blazar) state can endure in a FSRQ, despite these ‘frequent’ state transitions. This is the first attempt to verify, using purely opto-polarimetric data for a much enlarged sample of blazars, the recent curious finding that blazar state in individual quasars persists for at least a few decades, despite its changing/swinging observed fairly commonly on year-like timescales. The present analysis is based on a well-defined sample of 83 radio quasars, extracted from the opto-polarimetric survey RoboPol (2013–2017), for which old opto-polarimetric data taken prior to 1990 could be found in the literature. By a source-wise comparison of these two datasets of the same observable (
$\leftrightarrow$ non-HP state transition on year-like timescales. This work examines the extent to which HP (i.e., blazar) state can endure in a FSRQ, despite these ‘frequent’ state transitions. This is the first attempt to verify, using purely opto-polarimetric data for a much enlarged sample of blazars, the recent curious finding that blazar state in individual quasars persists for at least a few decades, despite its changing/swinging observed fairly commonly on year-like timescales. The present analysis is based on a well-defined sample of 83 radio quasars, extracted from the opto-polarimetric survey RoboPol (2013–2017), for which old opto-polarimetric data taken prior to 1990 could be found in the literature. By a source-wise comparison of these two datasets of the same observable (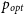 $p_{opt}$), we find that
$p_{opt}$), we find that 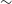 $\sim$90% of the 63 quasars found in blazar state in our RoboPol sample, were also observed to be in that state about three decades before. On the other hand, within the RoboPol survey itself, we find that roughly a quarter of the blazars in our sample migrated to the other polarisation state on year-like timescales, by crossing the customary
$\sim$90% of the 63 quasars found in blazar state in our RoboPol sample, were also observed to be in that state about three decades before. On the other hand, within the RoboPol survey itself, we find that roughly a quarter of the blazars in our sample migrated to the other polarisation state on year-like timescales, by crossing the customary 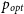 $p_{opt}$ = 3% threshold. Evidently, these relatively frequent transitions (in either direction) do not curtail the propensity of a radio quasar to retain its blazar (i.e., HP) state for at least a few decades. The observed transitions/swings of polarisation state are probably manifestation of transient processes, like ejections of synchrotron plasma blobs (VLBI radio knots) from the active nucleus.
$p_{opt}$ = 3% threshold. Evidently, these relatively frequent transitions (in either direction) do not curtail the propensity of a radio quasar to retain its blazar (i.e., HP) state for at least a few decades. The observed transitions/swings of polarisation state are probably manifestation of transient processes, like ejections of synchrotron plasma blobs (VLBI radio knots) from the active nucleus.