We have used integral field spectroscopy of a sample of six nearby (z ~ 0.01–0.04) high star-formation rate ( $\text{SFR} \sim 10\hbox{--}40$
$\text{SFR} \sim 10\hbox{--}40$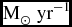 $\text{M}_\odot \text{ yr$^{-1}$}$) galaxies to investigate the relationship between local velocity dispersion and star-formation rate on sub-galactic scales. The low-redshift mitigates, to some extent, the effect of beam smearing which artificially inflates the measured dispersion as it combines regions with different line-of-sight velocities into a single spatial pixel. We compare the parametric maps of the velocity dispersion with the Hα flux (a proxy for local star-formation rate), and the velocity gradient (a proxy for the local effect of beam smearing). We find, even for these very nearby galaxies, the Hα velocity dispersion correlates more strongly with velocity gradient than with Hα flux—implying that beam smearing is still having a significant effect on the velocity dispersion measurements. We obtain a first-order non parametric correction for the unweighted and flux weighted mean velocity dispersion by fitting a 2D linear regression model to the spaxel-by-spaxel data where the velocity gradient and the Hα flux are the independent variables and the velocity dispersion is the dependent variable; and then extrapolating to zero velocity gradient. The corrected velocity dispersions are a factor of ~ 1.3–4.5 and ~ 1.3–2.7 lower than the uncorrected flux-weighted and unweighted mean line-of-sight velocity dispersion values, respectively. These corrections are larger than has been previously cited using disc models of the velocity and velocity dispersion field to correct for beam smearing. The corrected flux-weighted velocity dispersion values are σm ~ 20–50 km s−1.
$\text{M}_\odot \text{ yr$^{-1}$}$) galaxies to investigate the relationship between local velocity dispersion and star-formation rate on sub-galactic scales. The low-redshift mitigates, to some extent, the effect of beam smearing which artificially inflates the measured dispersion as it combines regions with different line-of-sight velocities into a single spatial pixel. We compare the parametric maps of the velocity dispersion with the Hα flux (a proxy for local star-formation rate), and the velocity gradient (a proxy for the local effect of beam smearing). We find, even for these very nearby galaxies, the Hα velocity dispersion correlates more strongly with velocity gradient than with Hα flux—implying that beam smearing is still having a significant effect on the velocity dispersion measurements. We obtain a first-order non parametric correction for the unweighted and flux weighted mean velocity dispersion by fitting a 2D linear regression model to the spaxel-by-spaxel data where the velocity gradient and the Hα flux are the independent variables and the velocity dispersion is the dependent variable; and then extrapolating to zero velocity gradient. The corrected velocity dispersions are a factor of ~ 1.3–4.5 and ~ 1.3–2.7 lower than the uncorrected flux-weighted and unweighted mean line-of-sight velocity dispersion values, respectively. These corrections are larger than has been previously cited using disc models of the velocity and velocity dispersion field to correct for beam smearing. The corrected flux-weighted velocity dispersion values are σm ~ 20–50 km s−1.