The growing number of black hole binary (BHB) mergers detected by the Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory have the potential to enable an unprecedented characterisation of the physical processes and astrophysical conditions that govern the formation of compact binaries. In this paper, we focus on investigating the dynamical formation of BHBs in dense star clusters through a state-of-the-art set of 58 direct N-body simulations with N 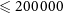 $\leqslant200\,000$ particles which include stellar evolution, gravitational braking, orbital decay through gravitational radiation, and galactic tidal interactions. The simulations encompass a range of initial conditions representing typical young globular clusters, including the presence of primordial binaries. The systems are simulated for
$\leqslant200\,000$ particles which include stellar evolution, gravitational braking, orbital decay through gravitational radiation, and galactic tidal interactions. The simulations encompass a range of initial conditions representing typical young globular clusters, including the presence of primordial binaries. The systems are simulated for 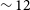 $\sim 12$ Gyr. The dataset yields 117 BHB gravitational wave (GW) events, with 97 binaries merging within their host cluster and 20 merging after having been ejected. Only 8% of all ejected BHBs merge within the age of the Universe. Systems in this merging subset tend to have smaller separations and larger eccentricities, as this combination of parameters results in greater emission of gravitational radiation. We confirm known trends from Monte Carlo simulations, such as the anti-correlation between the mass of the binary and age of the cluster. In addition, we highlight for the first time a difference at low values of the mass ratio distribution between in-cluster and ejected mergers. However, the results depend on assumptions on the strength of GW recoils, thus in-cluster mergers cannot be ruled out at a significant level of confidence. A more substantial catalogue of BHB mergers and a more extensive library of N-body simulations are needed to constrain the origin of the observed events.
$\sim 12$ Gyr. The dataset yields 117 BHB gravitational wave (GW) events, with 97 binaries merging within their host cluster and 20 merging after having been ejected. Only 8% of all ejected BHBs merge within the age of the Universe. Systems in this merging subset tend to have smaller separations and larger eccentricities, as this combination of parameters results in greater emission of gravitational radiation. We confirm known trends from Monte Carlo simulations, such as the anti-correlation between the mass of the binary and age of the cluster. In addition, we highlight for the first time a difference at low values of the mass ratio distribution between in-cluster and ejected mergers. However, the results depend on assumptions on the strength of GW recoils, thus in-cluster mergers cannot be ruled out at a significant level of confidence. A more substantial catalogue of BHB mergers and a more extensive library of N-body simulations are needed to constrain the origin of the observed events.