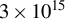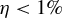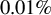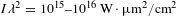Refine search
Actions for selected content:
4 results
Multibeam laser–plasma interaction at the Gekko XII laser facility in conditions relevant for direct-drive inertial confinement fusion
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 11 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 February 2023, e24
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Collective absorption of laser radiation in plasma at sub-relativistic intensities
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 7 / 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 July 2019, e39
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Raman–Brillouin interplay for inertial confinement fusion relevant laser–plasma interaction
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 4 / 2016
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 July 2016, e23
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Temperature dependence of parametric instabilities in the context of the shock-ignition approach to inertial confinement fusion
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 3 / 2015
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 February 2015, e6
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation