Machines and mechanisms realize processes, from the shaping process of a milling machine and the motion process of an automotive system to the trajectory realization of a robot. The dynamics of a machine generated by a properly chosen set of constraints in combination with an appropriate drive system is designed to meet the prescribed requirements of the process, which is done by projecting the machine equations of motion on the process dynamics. We get a set of nonlinear relations, which represent the machine motion in terms of the required process motion. A well-known example is the projection of arbitrary many robot degrees of freedom (DOFs) on a given path resulting in a set of nonlinear equations with one DOF only, the path coordinate s. Application of this idea can be used to construct a mobility space 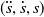 $(\ddot{s}, \dot{s}, s)$ for any combination of coordinates and constraints. The paper presents a corresponding approach for n-link robots by applying multibody system theory. Method might be interesting for layout of machines and mechanisms. Practical aspects are discussed, and an example is given.
$(\ddot{s}, \dot{s}, s)$ for any combination of coordinates and constraints. The paper presents a corresponding approach for n-link robots by applying multibody system theory. Method might be interesting for layout of machines and mechanisms. Practical aspects are discussed, and an example is given.