Spectral variability offers a new technique to identify small scale structures from scintillation, as well as determining the absorption mechanism for peaked-spectrum (PS) radio sources. In this paper, we present very long baseline interferometry (VLBI) imaging using the long baseline array (LBA) of two PS sources, MRC 0225–065 and PMN J0322–4820, identified as spectrally variable from observations with the Murchison Widefield Array (MWA). We compare expected milliarcsecond structures based on the detected spectral variability with direct LBA imaging. We find MRC 0225–065 is resolved into three components, a bright core and two fainter lobes, roughly 430 pc projected separation. A comprehensive analysis of the magnetic field, host galaxy properties, and spectral analysis implies that MRC 0225–065 is a young radio source with recent jet activity over the last 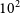 $10^2$–
$10^2$–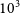 $10^3$ yr. We find PMN J0322–4820 is unresolved on milliarcsecond scales. We conclude PMN J0322–4820 is a blazar with flaring activity detected in 2014 with the MWA. We use spectral variability to predict morphology and find these predictions consistent with the structures revealed by our LBA images.
$10^3$ yr. We find PMN J0322–4820 is unresolved on milliarcsecond scales. We conclude PMN J0322–4820 is a blazar with flaring activity detected in 2014 with the MWA. We use spectral variability to predict morphology and find these predictions consistent with the structures revealed by our LBA images.