The bright radio source, GLEAM J091734 $-$001243 (hereafter GLEAM J0917
$-$001243 (hereafter GLEAM J0917 $-$0012), was previously selected as a candidate ultra-high redshift (
$-$0012), was previously selected as a candidate ultra-high redshift ( $z \gt 5$) radio galaxy due to its compact radio size and faint magnitude (
$z \gt 5$) radio galaxy due to its compact radio size and faint magnitude (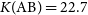 $K(\mathrm{AB})=22.7$). Its redshift was not conclusively determined from follow-up millimetre and near-infrared spectroscopy. Here we present new HST WFC3 G141 grism observations which reveal several emission lines including [NeIII]
$K(\mathrm{AB})=22.7$). Its redshift was not conclusively determined from follow-up millimetre and near-infrared spectroscopy. Here we present new HST WFC3 G141 grism observations which reveal several emission lines including [NeIII] $\lambda$3867, [NeV]
$\lambda$3867, [NeV] $\lambda$3426 and an extended (
$\lambda$3426 and an extended (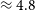 $\approx 4.8\,$kpc), [OII]
$\approx 4.8\,$kpc), [OII] $\lambda$3727 line which confirm a redshift of
$\lambda$3727 line which confirm a redshift of 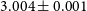 $3.004\pm0.001$. The extended component of the [OII]
$3.004\pm0.001$. The extended component of the [OII]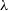 $\lambda$3727 line is co-spatial with one of two components seen at 2.276 GHz in high resolution (
$\lambda$3727 line is co-spatial with one of two components seen at 2.276 GHz in high resolution ( $60\times 20\,$mas) Long Baseline Array data, reminiscent of the alignments seen in local compact radio galaxies. The BEAGLE stellar mass (
$60\times 20\,$mas) Long Baseline Array data, reminiscent of the alignments seen in local compact radio galaxies. The BEAGLE stellar mass (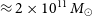 $\approx 2\times 10^{11}\,\textit{M}_\odot$) and radio luminosity (
$\approx 2\times 10^{11}\,\textit{M}_\odot$) and radio luminosity (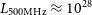 $L_{\mathrm{500MHz}}\approx 10^{28}\,$W Hz
$L_{\mathrm{500MHz}}\approx 10^{28}\,$W Hz $^{-1}$) put GLEAM J0917
$^{-1}$) put GLEAM J0917 $-$0012 within the distribution of the brightest high-redshift radio galaxies at similar redshifts. However, it is more compact than all of them. Modelling of the radio jet demonstrates that this is a young,
$-$0012 within the distribution of the brightest high-redshift radio galaxies at similar redshifts. However, it is more compact than all of them. Modelling of the radio jet demonstrates that this is a young, 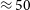 $\approx 50\,$kyr old, but powerful,
$\approx 50\,$kyr old, but powerful, 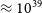 $\approx 10^{39}\,$W, compact steep spectrum radio source. The weak constraint on the active galactic nucleus bolometric luminosity from the [NeV]
$\approx 10^{39}\,$W, compact steep spectrum radio source. The weak constraint on the active galactic nucleus bolometric luminosity from the [NeV]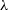 $\lambda$3426 line combined with the modelled jet power tentatively implies a large black hole mass,
$\lambda$3426 line combined with the modelled jet power tentatively implies a large black hole mass, 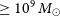 $\ge 10^9\,\textit{M}_\odot$, and a low, advection-dominated accretion rate, i.e. an Eddington ratio
$\ge 10^9\,\textit{M}_\odot$, and a low, advection-dominated accretion rate, i.e. an Eddington ratio 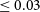 $\le 0.03$. The [NeV]
$\le 0.03$. The [NeV]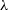 $\lambda$3426/[NeIII]
$\lambda$3426/[NeIII]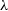 $\lambda$3867 vs [OII]
$\lambda$3867 vs [OII]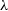 $\lambda$3727/[NeIII]
$\lambda$3727/[NeIII]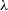 $\lambda$3867 line ratios are most easily explained by radiative shock models with precursor photoionisation. Hence, we infer that the line emission is directly caused by the shocks from the jet and that this radio source is one of the youngest and most powerful known at cosmic noon. We speculate that the star-formation in GLEAM J0917
$\lambda$3867 line ratios are most easily explained by radiative shock models with precursor photoionisation. Hence, we infer that the line emission is directly caused by the shocks from the jet and that this radio source is one of the youngest and most powerful known at cosmic noon. We speculate that the star-formation in GLEAM J0917 $-$0012 could be on its way to becoming quenched by the jet.
$-$0012 could be on its way to becoming quenched by the jet.