Refine search
Actions for selected content:
2 results
Convergence Rates in the Implicit Renewal Theorem on Trees
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Applied Probability / Volume 50 / Issue 4 / December 2013
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 January 2018, pp. 1077-1088
- Print publication:
- December 2013
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Implicit Renewal Theory and Power Tails on Trees
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Advances in Applied Probability / Volume 44 / Issue 2 / June 2012
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 January 2016, pp. 528-561
- Print publication:
- June 2012
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
 and similar recursions, where (
and similar recursions, where (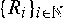 are independent and identically distributed copies of
are independent and identically distributed copies of 