Published online by Cambridge University Press: 06 November 2023
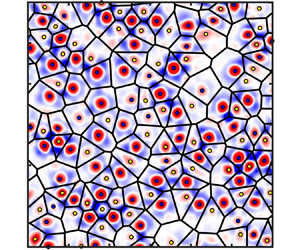
We investigate the spatial distribution and dynamics of the vortices in rotating Rayleigh–Bénard convection in a reduced Rayleigh number range  $1.3\le Ra/Ra_{c}\le 83.1$. Under slow rotations (
$1.3\le Ra/Ra_{c}\le 83.1$. Under slow rotations ( $Ra\approx 80\,Ra_{c}$), the vortices are distributed randomly, which is manifested by the size distribution of the Voronoi cells of the vortex centres being a standard
$Ra\approx 80\,Ra_{c}$), the vortices are distributed randomly, which is manifested by the size distribution of the Voronoi cells of the vortex centres being a standard  $\varGamma$ distribution. The vortices exhibit Brownian-type horizontal motion in the parameter range
$\varGamma$ distribution. The vortices exhibit Brownian-type horizontal motion in the parameter range  $Ra\gtrsim 10\,Ra_{c}$. The probability density functions of the vortex displacements are, however, non-Gaussian at short time scales. At modest rotating rates (
$Ra\gtrsim 10\,Ra_{c}$. The probability density functions of the vortex displacements are, however, non-Gaussian at short time scales. At modest rotating rates ( $4\,Ra_{c}\le Ra\lesssim 10\,Ra_{c}$), the centrifugal force leads to radial vortex motions, i.e. warm cyclones (cold anticyclones) moving towards (outwards from) the rotation axis. The horizontal scale of the vortices decreases with decreasing
$4\,Ra_{c}\le Ra\lesssim 10\,Ra_{c}$), the centrifugal force leads to radial vortex motions, i.e. warm cyclones (cold anticyclones) moving towards (outwards from) the rotation axis. The horizontal scale of the vortices decreases with decreasing  $Ra/Ra_c$, and the size distribution of their Voronoi cells deviates from the
$Ra/Ra_c$, and the size distribution of their Voronoi cells deviates from the  $\varGamma$ distribution. In the rapidly rotating regime (
$\varGamma$ distribution. In the rapidly rotating regime ( $1.6\,Ra_{c}\le Ra\le 4\,Ra_{c}$), the vortices are densely distributed. The hydrodynamic interaction of neighbouring vortices results in the formation of vortex clusters. Within clusters, cyclones exhibit inverse-centrifugal motion as they submit to the outward motion of the strong anticyclones, and the radial velocity of the anticyclones is enhanced. The radial mobility of isolated vortices, scaled by their vorticity strength, is shown to be a simple power function of the Froude number. For all flow regimes studied, we show that the number of vortices with a lifespan greater than
$1.6\,Ra_{c}\le Ra\le 4\,Ra_{c}$), the vortices are densely distributed. The hydrodynamic interaction of neighbouring vortices results in the formation of vortex clusters. Within clusters, cyclones exhibit inverse-centrifugal motion as they submit to the outward motion of the strong anticyclones, and the radial velocity of the anticyclones is enhanced. The radial mobility of isolated vortices, scaled by their vorticity strength, is shown to be a simple power function of the Froude number. For all flow regimes studied, we show that the number of vortices with a lifespan greater than  $t$ decreases exponentially as
$t$ decreases exponentially as  $\exp ({-t/{\tau }})$ for large time, where
$\exp ({-t/{\tau }})$ for large time, where  $\tau$ represents the characteristic lifetime of long-lived vortices.
$\tau$ represents the characteristic lifetime of long-lived vortices.