Introduction
Gay, bisexual and other men who have sex with men (MSM) appear to be disproportionately affected by a variety of psychological problems, including depression, distress, generalised anxiety disorder, substance use and suicide (Batchelder et al., Reference Batchelder, Safren, Mitchell, Ivardic and O'Cleirigh2017; King et al., Reference King, Semlyen, Tai, Killaspy, Osborn, Popelyuk and Nazareth2008). According to Meyer's sexual minority stress model, the stressors induced by a homophobic environment specific to the sexual minority status can lead to psychological problems in sexual minorities (Meyer, Reference Meyer2003). Traditional Chinese culture promotes heterosexual marriage, procreation and filial piety, leading to low social acceptance of same-sex behaviours (Steward et al., Reference Steward, Miège and Choi2013). Same-sex marriage, civil unions and other same-sex partnerships are not supported by law in China, nor are there relevant anti-discrimination laws and policies (Zhang and Chu, Reference Zhang and Chu2005; Cao and Guo, Reference Cao and Guo2016). These social and cultural characteristics create a heteronormative and stigmatising environment for Chinese MSM, detrimental to their mental health. A recent review indicated that Chinese MSM have a high prevalence of several mental health issues, including depression, anxiety, suicidal behaviour and alcohol abuse, which can be explained by minority stress (Sun et al., Reference Sun, Pachankis, Li and Operario2020). These psychological problems are conducive to the ‘syndemic’ conditions surrounding human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) transmission risk behaviours and indirectly contribute to the high prevalence of HIV among MSM (Tsai and Burns, Reference Tsai and Burns2015; Safren et al., Reference Safren, Reisner, Herrick, Mimiaga and Stall2010).
Despite an influx of studies focusing on the prevalence of depression, anxiety and suicide among MSM in China, the reported prevalence varies due to methodologies and sample characteristics, indicating the importance of reliable estimates from a pooled prevalence of these psychological problems. With a decade of relevant studies available, enough data exist to obtain a summary prevalence and explore potential sources of heterogeneity via a meta-analysis. Reliable estimates of depression, anxiety and suicidal behaviour are important to identify the precise number of people with psychological problems, better understand the mental health status of the sexual minority population, and develop strategies to improve their psychological well-being. In addition, our work encourages the development of comprehensive strategies, based on psychosomatic medicine and social policies, against the HIV/AIDS epidemic among MSM.
Thus, we conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis of published studies on depressive symptoms, anxiety symptoms and suicide (including suicidal ideation, suicide plans and suicide attempts) among Chinese MSM. The purposes of this meta-analysis were to (1) estimate the prevalence of these psychological problems and (2) identify the underlying methodological and sample characteristic moderators that can contribute to between-study heterogeneity.
Methods
We conducted this meta-analysis in accordance with the standards of Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-analyses (PRISMA) and Meta-analysis of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (MOOSE) (Stroup et al., Reference Stroup, Berlin, Morton, Olkin, Williamson, Rennie, Moher, Becker, Sipe and Thacker2000; Moher et al., Reference Moher, Liberati, Tetzlaff and Altman2009).
Search strategy
Two authors (DW and XY) performed a systematic search of the EMBASE, MEDLINE, PsycINFO, PubMed, CNKI and Wanfang databases, with languages restricted to Chinese and English for studies published before 10 September 2019, on the prevalence of depressive symptoms, anxiety symptoms, suicidal ideation, suicide plans and suicide attempts among Chinese MSM. In addition, the authors screened the reference lists of previous review articles on Google Scholar and Baidu Research to identify relevant studies that might have been missed, and then contacted the corresponding authors of these articles for missing information.
The database search combined terms related to MSM and study design with those related to depression or anxiety or suicidal ideation or suicide plans or suicide attempts, with the regional restriction of China. The keywords were selected based on each database (full details of the search strategy are provided in online Supplementary Table S1).
Study eligibility
We included studies in the meta-analysis that (1) reported original quantitative data on one of our outcomes of interest related to gay, bisexual and other MSM (defined on the basis of self-identity, sexual behaviour or sexual attraction) in China; (2) were published in peer-reviewed journals and (3) used a standardised scale to assess depression and anxiety symptoms.
We excluded studies that (1) did not clearly define the study area in the original article; (2) could not extract the prevalence data by indirect calculation or by contacting the corresponding author; (3) that were conference papers, dissertations, reviews, case studies and qualitative studies and (4) the sample size was less than 30 people. The titles and abstracts of all identified studies were independently screened for eligibility by two authors (DW and XY), and any conflict was resolved by the first author of this study. The eligibility of all studies that successfully passed the title/abstract screening stage was similarly confirmed by the same two authors at the full-text screening stage.
Data extraction
Using an extraction form piloted in three eligible studies, four authors (DW, XY, XY and SP) independently extracted the following data from each article: study design, survey year, study location, screening method used, population characteristics, sample size, recruitment, psychological outcomes and reported prevalence estimates. For longitudinal studies and intervention studies, only the baseline data were extracted. When more than one study used the same MSM sample, only the most comprehensive or most recent publication was included. Initial data extraction was checked by the first author. Immediately before the final analysis, all included data were checked again.
Quality assessment
The Joanna Briggs Institute Critical Appraisal tool for use in JBI Systematic Reviews for prevalence studies (JBI checklist) was used to assess the trustworthiness, relevance and results of all included studies by two authors (DW and XY) independently (Munn et al., Reference Munn, Moola, Lisy, Riitano and Tufanaru2015). We made minor changes to the tool based on the study characteristics (see online Supplementary Table S2 for more details). The final checklist consisted of ten items with a score of 0 ‘not mentioned’, 1 ‘mentioned but not described in detail’ or 2 ‘detailed and comprehensive description’. The higher the total score, the better the quality of the study. Quality scores for all included studies are shown in online Supplementary Table S3.
Data synthesis and analysis
The prevalence estimates with a 95% confidence interval (CI) of depressive symptoms, anxiety symptoms, suicide ideation, suicide plans and suicide attempts were calculated by pooling study-specific estimates using a random-effects meta-analysis accounting for heterogeneity (Borenstein et al., Reference Borenstein, Hedges, Higgins and Rothstein2010). Q-tests and I 2 were used to assess the level of heterogeneity between studies (i.e. the percentage of variability in prevalence estimates due to heterogeneity rather than sampling error or chance, with values ⩾75% indicating considerable heterogeneity) (Higgins and Thompson, Reference Higgins and Thompson2002; Higgins et al., Reference Higgins, Thompson, Deeks and Altman2003). Univariate meta-regression and subgroup analysis based on study-level characteristics (study region, survey year, sampling method, study population, sample size, screening method and recall time for suicidality) were conducted to explore potential sources of heterogeneity. The regional classification was based on China's economic geographic division, including the first developing eastern region, the revitalised northeast region, the rising central region and the developing western region. Sensitivity analysis was performed sequentially, excluding each study, to determine the influence of individual studies on the overall prevalence estimates. Egger's test (Egger et al., Reference Egger, Davey Smith, Schneider and Minder1997) was used to test publication bias, p < 0.05 indicating statistically significant publication bias.16 All analyses were performed using R version 3.6.1 (with meta and metafor packages) (Schwarzer, Reference Schwarzer2007; Viechtbauer, Reference Viechtbauer2010).
Results
Study characteristics
The PRISMA flow diagram outlines the search strategy used to identify the studies (Fig. 1). Sixty-seven studies were included in the final meta-analysis. Among them, 52 studies reported the prevalence of depressive symptoms, with a combined sample of 37 376 people. Twenty-seven studies reported the prevalence of anxiety symptoms, with a combined sample of 10 531 people. Finally, 23, 9 and 19 studies reported the prevalence of suicidal ideation, suicide plans and suicide attempts, with combined samples of 15 034 people, 5271 people and 27 936 people, respectively.
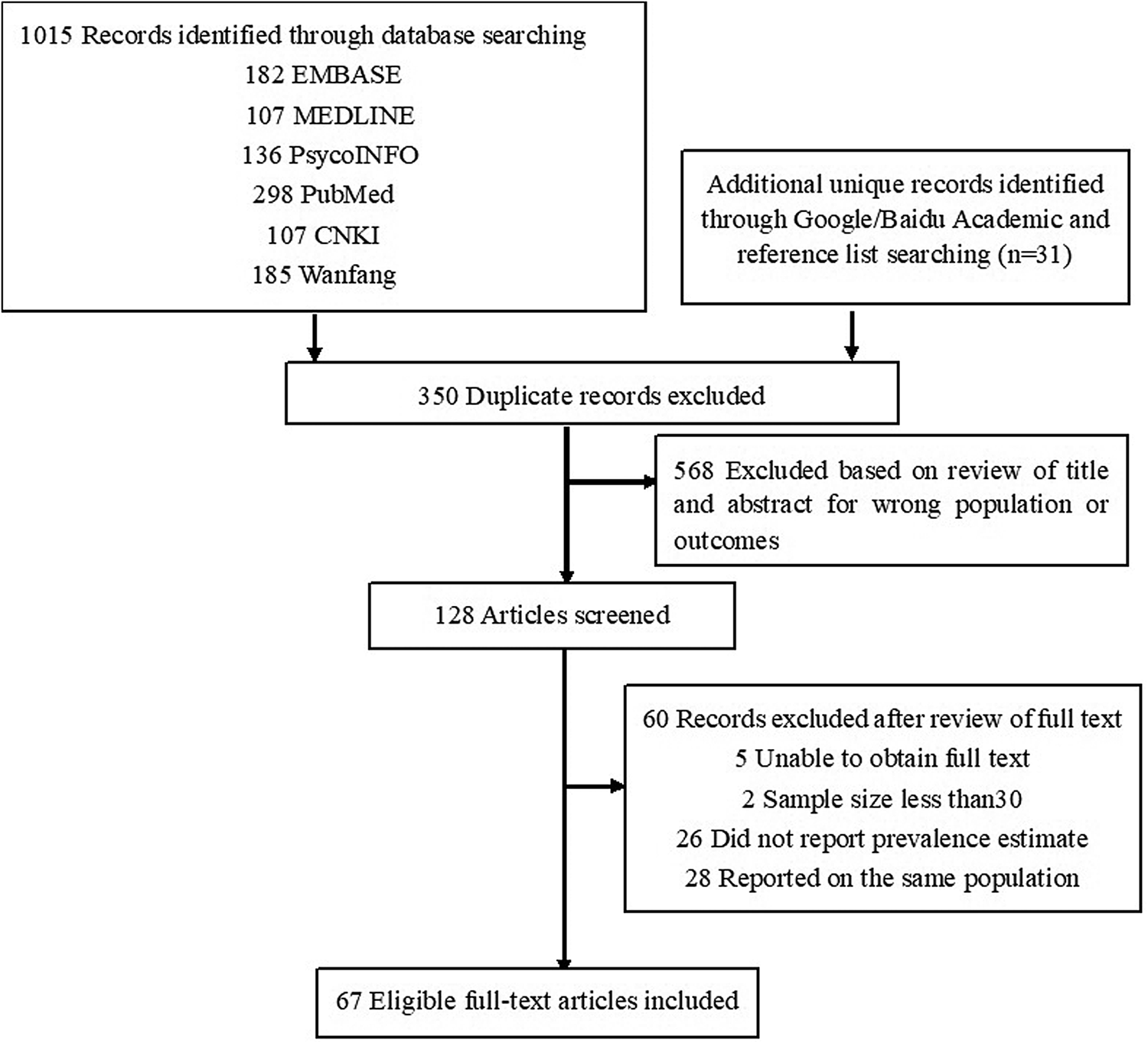
Fig. 1. PRISMA flow diagram detailing the search strategy.
Among these studies, 37 were written in Chinese and 30 in English. In addition, 64 studies used a cross-sectional design, two used a cohort design (Tao et al., Reference Tao, Vermund, Lu, Ruan, Shepherd, Kipp, Amico, Zhang, Shao and Qian2017b; Wang et al., Reference Wang, Wang, Chu, Zhang, Mao, Geng, Jiang, Shang and Xu2018) and one used a randomised-controlled trial design (Tao et al., Reference Tao, Qian, Kipp, Ruan, Shepherd, Amico, Shao, Lu and Vermund2017a). The quality of the included studies varied considerably, with JBI scores ranging from 6 to 19 (mean score = 13).
The time span of these studies extended from 2001 to 2019, and the study population covered 15 provinces or cities (Shanghai, Beijing, Zhejiang, Guangdong, Jiangsu, Shandong, Tianjin, Liaoning, Anhui, Jiangxi, Hubei, Sichuan, Chongqing, Guangxi and Yunnan) and Taiwan. The sample size ranged from 50 to 15 066, and the target population included general MSM, young sexual minority males (YSMM), HIV-positive, HIV-negative, or serostatus-unknown MSM and money boys (MB, referring to male sex workers in China who engage in sex with men for economic survival). Forty-eight studies used behavioural measures to define their study population as MSM. Four studies (Sun et al., Reference Sun, Wu, Qu, Lu and Wang2014a, Reference Sun, Feng, Xu, Cheng, Zou and Lou2014b; Yu et al., Reference Yu, Li and Wang2016; Xiong et al., Reference Xiong, Zhang, Liu and Yin2018) used self-reported sexual orientation and five studies (Chen et al., Reference Chen, Li, Zhang, Yu, Li, Wang and Yu2012; Hu et al., Reference Hu, Zhong, Wen, Han, Tan, Huang and Peng2016; Wang et al., Reference Wang, Liu, Guo and Zhang2016; Yu and Xiao, Reference Yu and Xiao2017; Gao et al., Reference Gao, Li, Ma, Chen, Ma, Li and Jia2018) used both self-reported homosexual behaviour and sexual orientation to define their study population. In addition, four studies (Huang et al., Reference Huang, Huang, Zhuang, Fang, Li, Ye, Wang and Chen2010; Li et al., Reference Li, Huang, Guo, Wang, Xi, Lei, Luo, Pan, Deng, Zhang and Lu2017; Huang et al., Reference Huang, Li, Guo, Gao, Xu, Huang, Deng and Lu2018a, Reference Huang, Li, Lai, Jia, Xiao, Wang, Guo and Lu2018b) focused on sexual minority adolescents with two study populations, defining the study population using self-reported sex attraction. Six studies (Lv et al., Reference Lv, Cheng and Cheng2014; Shiu et al., Reference Shiu, Chen, Tseng, Chung, Wu, Hsu and Ko2014; Yan et al., Reference Yan, Wong, Zheng, Ning, Ding, Nehl, Lin and He2014; Chen et al., Reference Chen, Li, Wang and Zhang2015; Tao et al., Reference Tao, Qian, Kipp, Ruan, Shepherd, Amico, Shao, Lu and Vermund2017a, Reference Tao, Vermund, Lu, Ruan, Shepherd, Kipp, Amico, Zhang, Shao and Qian2017b) did not report how they identified their study population. Moreover, ten assessment methods were used to measure the prevalence of depressive symptoms, and seven were used to measure the prevalence of anxiety symptoms. The most common screening tools for depression were the Center for Epidemiologic Studies Depression Scale (CES-D) (Radloff, Reference Radloff1977) and the Zung Self-rating Depression Scale (SDS) (Biggs et al., Reference Biggs, Wylie and Ziegler1978), used in 27 and 14 studies, respectively. Anxiety was mainly measured with the Self-rating Anxiety Scale (SAS) (Zung, Reference Zung1971) and the Generalised Anxiety Disorder Scale-7 (GAD-7) (Spitzer et al., Reference Spitzer, Kroenke, Williams and Löwe2006), used in 17 and 4 studies, respectively. The measurement of suicide (suicide ideation, suicide plans or suicide attempts) based on a single item, except for two studies (Yu and Xiao, Reference Yu and Xiao2017; Yu et al., Reference Yu, Li, Liu, Li, Na, An, Zhou, Gu, Bi, Mu, Zhang, Dong and Pan2018), used standardised scales [a section of the World Mental Health Composite International Diagnostic Interview (WMH-CIDI)] (Kessler and Ustün, Reference Kessler and Ustün2004) and a shortened 6-item version of the suicide questionnaire designed by Kessler et al. (Reference Kessler, Berglund, Borges, Nock and Wang2005). The recall time to measure suicide included ‘over the past week’, ‘over the past six months’, ‘over the past year’, ‘since HIV diagnosis’ and ‘lifetime’. The recruitment methods used in these studies included snowball sampling, respondent-driven sampling (RDS), recruitment through voluntary counselling and testing (VCT) clinics, online surveys and recruitment through gay-friendly non-governmental organisations. A summary of the characteristics of included studies is provided in online Supplementary Table S4.
Depressive symptoms
Meta-analytic pooling of the prevalence of depressive symptoms reported in the 52 studies identified yielded a summary prevalence of 43.2% (12 887/37 376 individuals; 95% CI, 38.9–47.5), with significant evidence of between-study heterogeneity (I 2 = 96.6%; Table 1). Sensitivity analysis showed that no individual study significantly affected the overall prevalence. In the subgroup analysis, heterogeneity was found to be reduced for the 2004–2007 period (I 2 = 56.7%) in the MB population (I 2 = 0.0%) and the YSMM population (I 2 = 0.0%) for a sample size <100 (I 2 = 70.6%), and in studies using the CESD-10 with a cut-off score of 10 or above (I 2 = 29.9%) and HADS with a cut-off score of 8 or above (I 2 = 29.7%) to identify significant depression.
Table 1. Estimated depression prevalence among MSM in China

N, not reported; NGO, non-governmental organisation; RDS, respondent-driven sampling; VCT, HIV voluntary counselling and testing; MSM, men who have sex with Men; HNMSM, HIV-negative MSM; UnMSM, serostatus-unknown MSM; HIVMSM, HIV-positive MSM; YSMM, young sexual minority male; MB, money boy; CBDI-II, Chinese version of Beck Depression Inventory; CESD, Center for Epidemiological Studies Depression Scale; DASS: Depression Anxiety and Stress scale; SCL-90: Symptom Checklist 90; DSRSC, Depression Self-Rating Scale for Children; PHQ, Patient Health Questionnaire; SDS, Self-Rating Depression scale.
Subgroup differences were found in different study regions, survey years, sampling methods, study populations and assessment methods (p < 0.001). The estimated prevalence of depressive symptoms was higher in the central region (including Anhui and Jiangxi) in this study (50.2%; 95% CI, 41.2–59.1; Fig. 2). All studies conducted between 2004 and 2007 also had a higher prevalence of depressive symptoms than other sampling periods (59.0%; 95% CI, 53.7–64.0). The pooled prevalence of depressive symptoms varied according to the sampling methods. All studies using venue-based (i.e. sauna, bar; 62.3%; 95% CI, 54.6–69.4) and online (63.9%; 95% CI, 58.2–69.2) recruitment reported a higher prevalence of depressive symptoms than other recruitment methods. In addition, all studies involving HIV-positive MSM (50.5%; 95% CI, 40.7–60.2) and MB (63.1%; 95% CI, 58.0–68.0) reported a higher prevalence of depressive symptoms, while those involving HIV-negative or serostatus-unknown MSM reported a lower prevalence of depressive symptoms, ranging from 29.2 to 32.3%. The prevalence of depressive symptoms also varied with the different measurement and cut-off scores. All studies adopting a CESD-20 cut-off score of 16 or above (48.2%; 95% CI, 42.7–53.7) and an SDS cut-off score of 42 or above (47.7%; 95% CI, 29.4–66.7) reported a similar prevalence. In all univariate meta-regression analyses, only the study population could explain the heterogeneity of the estimates of the prevalence of depressive symptoms (p = 0.007). Publication bias was found in the pooled prevalence analysis (p < 0.001 using Egger's test).

Fig. 2. Pooled prevalence by region.
Anxiety symptoms
The pooled prevalence of anxiety symptoms was 32.2% (3187/10 531 individuals; 95% CI, 28.3–36.6; Table 2). There was substantial heterogeneity between the included studies (I 2 = 95.1%). Sensitivity analysis showed that there was no significant effect of individual studies on the overall prevalence of anxiety symptoms (p < 0.05). In the subgroup analysis, heterogeneity was found to be reduced for the 2004–2007 period (I 2 = 0.0%), in studies using venue-based sampling (I 2 = 0.0%), in the YSMM population (I 2 = 71.0%), for a sample size <100 (I 2 = 38.9%) and in studies using a HADS cut-off score of 8 or above (I 2 = 62.0%).
Table 2. Estimated anxiety prevalence among MSM in China

GAD-7, General Anxiety Disorder-7 item; SAS, Self-Rating Anxiety Scale.
Subgroup analysis showed that the pooled prevalence of anxiety symptoms varied by survey year, sampling method, sample size, study population and measurement (p < 0.05). The estimated prevalence of anxiety symptoms was higher in the central region of China (37.4%; 95% CI, 31.0–45.2; Fig. 2). All studies conducted between 2004 and 2007 also had a higher prevalence of anxiety symptoms than other sampling periods (45.9%; 95% CI, 40.5–52.1). All studies using venue-based recruitment (45.9%; 95% CI, 40.5–52.1) reported a higher prevalence of anxiety symptoms than other recruitment methods. Similarly, all studies involving HIV-positive MSM (38.7%; 95% CI, 32.8–45.7) and MB (46.6%; 95% CI, 38.3–56.6) reported a higher prevalence of anxiety symptoms than those involving HIV-negative or serostatus-unknown MSM (25.6–29.4%). Studies with a smaller sample reported a higher prevalence of anxiety symptoms than those with a larger sample (33.0–44.5% v. 22.2–23.0%). The prevalence of anxiety symptoms measured using the SAS with a cut-off score of 40 or above (31.9%; 95% CI, 26.7–38.1), used in most studies to identify significant anxiety symptoms, was similar to the overall prevalence. In all univariate meta-regression analyses, the sampling methods (p = 0.039, R 2 = 14.6%) and the sample size (p < 0.001, R 2 = 39.2%) partially explained the heterogeneity of the estimates of the prevalence of anxiety symptoms. Egger's test showed that there was no significant publication bias in the pooled prevalence analysis (p = 0.353).
Suicide
As the number of studies on suicide (including suicide ideation, suicide plans and suicide attempts) was small and the recall time used in these studies was different, we reported the combined prevalence of suicidal ideation, suicide plans and suicide attempts at different recall times (Table 3). Among suicidal ideation studies, the most commonly used recall time was ‘over the past week’ (four studies), ‘over the past year’ (seven studies) and ‘lifetime’ (six studies), with a combined prevalence of 20.3% (95% CI, 12.6–32.7), 18.1% (95% CI, 13.0–25.1) and 24.0% (95% CI, 20.1–28.6), respectively. There was significant heterogeneity in each subgroup (I 2 = 90.0–97.3%). Four studies with high heterogeneity (I 2 = 85.6%) reported a combined prevalence of suicide plans over the past year of 5.5% (95% CI, 20.1–28.6). Among the studies reporting suicide attempts, the most commonly used recall time was ‘over the past year’ (six studies) and ‘lifetime’ (four studies), with a combined prevalence of 4.2% (95% CI, 2.2–6.3) and 8.6% (95% CI, 3.8–13.3), respectively. There was significant heterogeneity in each subgroup (I 2 = 92.0–96.6%).
Table 3. Subgroup analysis of suicidality according to different recall times

Discussion
Main findings
The above study showed a high prevalence of depressive symptoms, anxiety symptoms and suicide among Chinese MSM compared with the general population. The meta-analysis revealed that 43.2% (ranging from 18.1 to 70.9%) of all MSM screened positive for depressive symptoms, which was more than double the prevalence in the general Chinese population (16.6%) (Huang et al., Reference Huang, Wang, Wang, Liu, Yu, Yan, Yu, Kou, Xu, Lu, Wang, He, Xu, He, Li, Guo, Tian, Xu, Xu, Ma, Wang, Wang, Yan, Wang, Xiao, Zhou, Li, Tan, Zhang, Ma, Li, Ding, Geng, Jia, Shi, Wang, Zhang, Du, Du and Wu2019) and higher than MSM in other countries (10.6–36.7%) (Mills et al., Reference Mills, Paul, Stall, Pollack, Canchola, Chang, Moskowitz and Catania2004; Parker et al., Reference Parker, Lõhmus, Valk, Mangine and Rüütel2015; Hylton et al., Reference Hylton, Wirtz, Zelaya, Latkin, Peryshkina, Mogilnyi, Dzhigun, Kostetskaya, Galai and Beyrer2017; Semple et al., Reference Semple, Stockman, Goodman-Meza, Pitpitan, Strathdee, Chavarin, Rangel, Torres and Patterson2017; Korhonen et al., Reference Korhonen, Kimani, Wahome, Otieno, Okall, Bailey, Harper, Lorway, Doshi, Mathenge, Kimani, Sanders and Graham2018). Sexual minorities in China are more hidden than in other countries, with only 5% revealing their sexual identity, leaving the public with little awareness and very skeptical about this population. Moreover, traditional family values are deeply rooted in Chinese society and the majority of sexual minorities are excluded from the family. They also face increased difficulties in accessing medical and social services because of their sexual identity. Coupled with the high prevalence of HIV among MSM in China, MSM suffer from a double stigma. All of these factors contribute to the higher prevalence of psychological problems among MSM in China than in other countries (UNDP, 2016; Sun et al., Reference Sun, Pachankis, Li and Operario2020).
The summary prevalence of anxiety symptoms among all MSM was 32.2% (12.2–57.6%), with a higher prevalence among MB (46.6%) and HIV-positive MSM (38.7%). In addition, the prevalence of depression and anxiety symptoms was higher among MSM living in the central region and during the 2004–2007 period. The summary prevalence varied by assessment method, with the most frequently used methods yielding a similar prevalence. Moreover, Chinese MSM reported 18.1 and 24.0% of suicidal ideation in the past year and in their lifetime, 5.5 and 11.5% of suicide plans in the past year and in their lifetime and 4.2 and 8.6% of suicide attempts in the past year and in their lifetime. In comparison, only 3.9 and 0.80% of the general population reported suicide ideation and suicide attempts in their lifetime (Cao et al., Reference Cao, Zhong, Xiang, Ungvari, Lai, Chiu and Caine2015). However, given the methodological limitations of the included studies, these results should be interpreted with caution.
Limitations of included studies
The included studies had several methodological limitations. First, all included studies used different methodologies to investigate sexual identities, including self-reported sexual orientation or sexual attraction, self-reported same-sex sexual encounters, or both. Few studies distinguished between gay, bisexual and homosexual MSM during screening. However, men's mental health status may be influenced by their internal sexual identification, and previous studies have suggested that bisexual men (defined by identity, behaviour or attraction) are more at risk for mental health problems than gay men (Bostwick et al., Reference Bostwick, Boyd, Hughes and Mccabe2010; Conron et al., Reference Conron, Mimiaga and Landers2010). Therefore, additional studies distinguishing between sexual identities are needed.
Second, considering the identity concealment of MSM, it is difficult to obtain a large sample. Some of the included studies used a small sample, which could lead to a biased estimated prevalence. In addition, there were few cross-regional or national studies, and most studies were conducted in developed urban cities. Therefore, cross-regional studies and studies focusing on MSM in the central, western and northeast regions of China are needed to contribute to a more comprehensive understanding of mental health problems among Chinese MSM and develop interventions in the context of regional differences.
Finally, all included studies used different measures for depressive symptoms, anxiety symptoms and suicide. Although these studies used standardised scales, such as the CES-D, the SDS or the SAS, they did not choose the same cut-off score, which greatly affected their final results. In addition, most included studies used a single item to investigate suicide ideation, suicide plans or suicide attempts, with inconsistent statements, and only some studies explicitly defined suicidal ideation, suicide plans or suicide attempts. Unstandardised screening tools and inconsistent definitions of suicide may have led to inaccurate results. To the best of our knowledge, the definition of suicide and related terms vary across cultures and societies, thus there is no universal scale for suicide screening (Xiao and Xu, Reference Xiao and Xu2005). However, we encourage researchers to use standardised scales that have been culturally validated instead of a single item.
Strengths and limitations of this study
Our review involved an extensive literature search with no time restrictions and quantitatively summarised the prevalence of depressive symptoms, anxiety symptoms and suicide among Chinese MSM. When interpreting these findings, it is important to recognise that the data synthesised in this study came from self-reported measures of depressive symptoms, anxiety symptoms and suicide, which were strongly influenced by the sensitivity and specificity of the screening instruments. Meanwhile, the cut-off points set to screen for depressive and anxiety symptoms and the recall time used to estimate suicidal behaviours varied across different studies, leading to significant heterogeneity in overall pooled prevalence. In addition, the factors that can be sources of heterogeneity, such as different sexual orientations or the severity of depressive symptoms or anxiety symptoms, could not be extracted for analysis, leaving substantial heterogeneity between studies largely unexplained by the variables studied. Finally, the studies mainly used a cross-sectional design and only the baseline data were extracted from the cohort studies, whereas longitudinal studies on the change in prevalence were lacking. Therefore, the results of longitudinal studies should be followed in future studies.
Implications for future research
First, further studies should clarify participants' sexual orientation and self-identity during screening, which can help determine the potential impact of internal sexual identification on their mental health status. Second, national studies using probability-based samples are needed to establish more reliable estimates of the prevalence of different psychological problems among MSM. Third, longitudinal studies are also needed to establish the causal pathway between mental health problems and related factors, which are greatly warranted for intervention development. Fourth, for the measurement of depression and anxiety, attention should be paid to the standardised use of the scale and the cut-off score. Fifth, the existing studies basically measure depressive or anxiety symptoms rather than clinically significant depression and anxiety disorders. Further studies should focus on the incidence of depression or anxiety disorders and identify the burden of untreated mental disorders among MSM, so as to provide reference for the allocation of mental health services and medical resources for this population. Sixth, this review highlighted high prevalence of mental health problems of Chinese MSM population and their needs for mental health interventions and services. More intervention studies are needed to find ways to address their poor mental health. Rigorous assessments of the feasibility, effectiveness and sustainability of mental health service and interventions for MSM are also warranted to guide future policies and practices.
Conclusions
Depressive symptoms, anxiety symptoms and suicide are common mental health problems among Chinese MSM. Additional attention is needed to provide mental health services and to identify those at risk of mental health problems and those requiring treatment. Efforts are needed to develop interventions to prevent and alleviate these mental health problems in this population.
Supplementary material
The supplementary material for this article can be found at https://doi.org/10.1017/S2045796020000487.
Data
The data sets used and analysed in the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Acknowledgements
None.
Author contributions
The manuscript has been read and approved by all named authors and all of them have contributed to the development of this research.
Financial support
This work was support by the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province (Grant No. 2017A030310561), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 81803334 and 71774178), a Major Infectious Disease Prevention and Control of the National Science and Technique Major Project (Grant No. 2018ZX10715004), Science and Technology Planning Project of Guangdong Province (Grant No. 2017A020212006), Science and Technology Research Project of Guangzhou (Grant No. 201607010368) and China Medical Board (Grant No. 18-301).
Conflict of interest
There are no known conflicts of interest associated with this publication.
Ethical standards
Ethical approval for the study was obtained from the Ethics Committee of Sun Yat-Sen University ([2018] 049).







