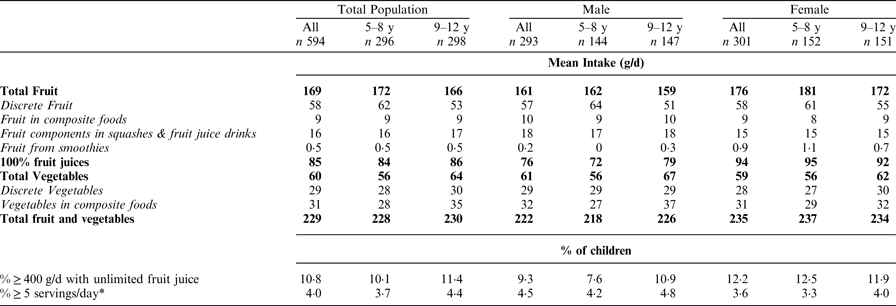
It is recommended in Ireland that children over 5 years of age consume 400 g or five (80 g) servings of fruit and vegetables per day, including no more than 150 ml of unsweetened fruit juice or smoothies as one serving(1, 2). The aim of this analysis was to estimate fruit and vegetable intakes, including those from composite foods, in Irish children aged 5–12 years using data from the National Children's Food Survey (NCFS) (2003–2004) which used a 7-d weighed food diary to collect detailed food and beverage intake data from a representative sample of 594 children (www.iuna.net). Of 1945 food codes consumed during the survey period, 860 had a fruit/vegetable component. These included discrete fruit and vegetables, fruit and vegetables from composite foods, 100 % fruit juices and fruit in smoothies, squashes and fruit juice drinks. The fruit and/or vegetables content in each food code was estimated using standard recipes from McCance and Widdowson's, The Composition of Foods (3), the Irish food composition database(Reference Black, Ireland and Moller4) and manufacturers’ product information. Inedible portions of fruit and vegetables were excluded (Reference Black, Ireland and Moller4). SPSS© v22 was used to calculate mean daily intake (MDI) of fruit and vegetables and percentage of the population meeting recommendations.
*Servings defined by The Healthy Eating Guidelines (including ≤150 ml of unsweetened fruit juice/smoothies as one serving where consumed) (2)
The MDI of total fruit and vegetables from all sources in the population was 229 g/d (equivalent to 2·9 servings) with 10·8% of children having intakes ≥400 g per day. When the contribution of unsweetened fruit juice and smoothies was limited to no more than 150 ml/d, the MDI of fruit and vegetables was 2·6 servings (1·8 from fruit and 0·8 from vegetables) with just 4% of children meeting the recommended intake of 5 servings per day, while 15% had intakes ≥4 servings per day and 36% ≥3 servings per day. Composite foods contributed 31 g/d (52%) of total vegetable intakes but were not as important for fruit (5% of intake). In conclusion, this study has shown that intakes of fruit and vegetables in young children are not meeting the current recommendations and that composite food and dishes should be included in estimates of intakes, particularly for vegetables. These findings may be useful for developing strategies to increase fruit and vegetable intakes in Irish children.
This research was funded by the Irish Department of Agriculture, Food and the Marine under the project ‘National Children's Food Consumption Survey II’ (15/F/673)


