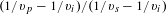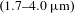Dual-chirped difference frequency generation (DFG) is an advantageous technique for generating the broadband mid-infrared (IR) idler wave, which is inaccessible by a population-inversion-based laser system. In principle, the generated idler wave may even suffer a spectrum broadening compared with the driving pulsed lasers if the pump and signal waves are oppositely chirped. However, broadband phase-matching is always the determining factor for the resulting efficiency and the bandwidth of the generated idler wave. In this study, specific to an oppositely dual-chirped DFG scheme, we derive the precondition to realize broadband frequency conversion, wherein a negative 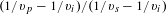 $(1/\unicode[STIX]{x1D710}_{p}-1/\unicode[STIX]{x1D710}_{i})/(1/\unicode[STIX]{x1D710}_{s}-1/\unicode[STIX]{x1D710}_{i})$, in terms of the correlation coefficient of the group velocity (
$(1/\unicode[STIX]{x1D710}_{p}-1/\unicode[STIX]{x1D710}_{i})/(1/\unicode[STIX]{x1D710}_{s}-1/\unicode[STIX]{x1D710}_{i})$, in terms of the correlation coefficient of the group velocity ( $\unicode[STIX]{x1D70E}$), is necessary. However, most birefringence bulk crystals can only provide the required material dispersions in limited spectral regions. We show that the periodically poled lithium niobate crystal that satisfies an inactive Type-II (eo-o) quasi-phase-matching condition has a stable negative
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D70E}$), is necessary. However, most birefringence bulk crystals can only provide the required material dispersions in limited spectral regions. We show that the periodically poled lithium niobate crystal that satisfies an inactive Type-II (eo-o) quasi-phase-matching condition has a stable negative  $\unicode[STIX]{x1D70E}$ and exerts the expected broadband gain characteristic across an ultra-broad idler spectral region
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D70E}$ and exerts the expected broadband gain characteristic across an ultra-broad idler spectral region 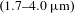 $(1.7{-}4.0~\unicode[STIX]{x03BC}\text{m})$. Finally, we propose and numerically verify a promising DFG configuration to construct a tunable mid-IR spectrum broader based on the broadband phase-matched oppositely dual-chirped DFG scheme.
$(1.7{-}4.0~\unicode[STIX]{x03BC}\text{m})$. Finally, we propose and numerically verify a promising DFG configuration to construct a tunable mid-IR spectrum broader based on the broadband phase-matched oppositely dual-chirped DFG scheme.