In this report, we present results of analytical and numerical calculations of evolution the axis of rotation of planets moving at very close orbits. We consider the evolution of the axis of rotation caused by tidal perturbations of a parent star and obtain estimates of the principal moment of inertia and the dynamical flattening for nine exoplanets. From analysis of evolutionary equations, we obtain the critical values of the kinetic momentum vector, 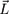 , for different values of orbital eccentricity. We find a general tendency of vector
, for different values of orbital eccentricity. We find a general tendency of vector 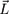 to evolve to the direction perpendicular to the orbital plane.
to evolve to the direction perpendicular to the orbital plane.