Multifunctional materials such as the single phase compound Pb(Fe0.5Nb0.5)O3 (PFN), where ferroelectric and antiferromagnetic order coexist, are very promising and have great interest from the academic and technological points of view. In this work, coupling of the ferroelectric and magnetic ordering has been observed. For this study, a combination of the small signal response using the impedance spectroscopy technique and the electromechanical resonance method with the large signal response through standard ferroelectric measurement, has been used with and without an applied magnetic field. The measurements to determine the electrical properties of the ceramic were performed as functions of the bias and poling electric fields. A simultaneous analysis of the complex dielectric constant 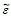 , impedance
, impedance 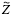 , electric modulus
, electric modulus 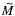 , and the electromechanical coupling factors is presented. The results are correlated with a previous study of structural, morphological, small signal dielectric frequency-temperature response, and the ferroelectric hysteretic, magnetic and magnetodielectric behaviors. The observed shifts of the resonance and antiresonance frequency values can be associated with change of the domain size favored by the readjustment of the oxygen octahedron when the magnetic field is applied.From P-E hysteresis loops obtained without and with an external applied magnetic field a maximum value of dc magnetoelectric coefficient αME = 4 kV/cm T (400 mV/cm Oe) was obtained.
, and the electromechanical coupling factors is presented. The results are correlated with a previous study of structural, morphological, small signal dielectric frequency-temperature response, and the ferroelectric hysteretic, magnetic and magnetodielectric behaviors. The observed shifts of the resonance and antiresonance frequency values can be associated with change of the domain size favored by the readjustment of the oxygen octahedron when the magnetic field is applied.From P-E hysteresis loops obtained without and with an external applied magnetic field a maximum value of dc magnetoelectric coefficient αME = 4 kV/cm T (400 mV/cm Oe) was obtained.