Engineered Proteins as Multifunctional Materials
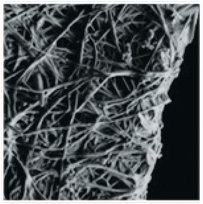
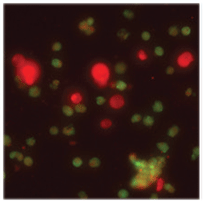
Engineered proteins as multifunctional materials. Living organisms have engineered remarkable protein-based materials through billions of years of evolution. As multifunctional materials, these show unparalleled mechanical, optical, and electronic properties and have served as inspiration for scientists to study and mimic. This issue of MRS Bulletin covers the mechanical and rheological properties of engineered structural protein materials and nanocomposites, advancements in the synthesis and assembly of protein materials, and recent developments in the processing of these materials. The work in the inset on the cover demonstrates that the specifi c penetration energy of a silk/graphene oxide bionanocomposite is signifi cantly higher than that of Kevlar because of the nanoscale morphology and the interactions between the two components. The layer-by-layer bionanocomposite image depicts its brick and mortar structure and an approaching silica sphere in a projectile impact test. Image courtesy of Washington University in St. Louis. The background shows an atomic force microscope image of co-assembled silk and MXene fl akes (Z-scale: 20 nm). The false color shows the silk corona morphology. Image courtesy of Michelle Krecker. See the technical theme that begins on p. 999.
Engineered Proteins as Multifunctional Materials
Engineered proteins as multifunctional materials
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 December 2020, pp. 999-1004
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Proteins and peptides for functional nanomaterials: Current efforts and new opportunities
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 December 2020, pp. 1005-1016
-
- Article
- Export citation
Protein-based functional nanocomposites
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 December 2020, pp. 1017-1026
-
- Article
- Export citation
Proteins for bioinspired optical and electronic materials
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 December 2020, pp. 1027-1033
-
- Article
- Export citation
Engineered proteins and three-dimensional printing of living materials
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 December 2020, pp. 1034-1038
-
- Article
- Export citation
Liquid–liquid phase separation of proteins and peptides derived from biological materials: Discovery, protein engineering, and emerging applications
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 December 2020, pp. 1039-1047
-
- Article
- Export citation
Rheological properties of engineered protein polymer networks
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 December 2020, pp. 1048-1054
-
- Article
- Export citation
Impact Section
Opinion & Perspective
Picturing science and engineering
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 December 2020, pp. 994-998
-
- Article
- Export citation
Energy Quarterly
Editorial
Design for recycling: The circular economy starts here
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 December 2020, p. 989
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Energy Sector Analysis
Sustainable design of fully recyclable all solid-state batteries
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 December 2020, pp. 990-991
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Considerations for leveraging flexible loads to decarbonize electricity and transportation
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 December 2020, pp. 992-993
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Departments
Opinion
Material Matters
Nanotechnology shows promise for next-generation vaccines in the fight against COVID-19
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 December 2020, pp. 981-982
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
News & Analysis
Materials News
Electrochemical high-speed AFM dynamically probes fast-charging battery materials
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 December 2020, pp. 984-985
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Trigonal prismatic cage molecule enables new type of 3D covalent organic framework
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 December 2020, p. 985
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
3D printed colloidal microswimmers with complex shapes propelled catalytically
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 December 2020, p. 986
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Science Policy
Australia launches quantum industry roadmap
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 December 2020, pp. 987-988
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
South Africa's Platinum Valley project to pull hydrogen initiatives into one ecosystem
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 December 2020, p. 988
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Society News
MRS Journal Highlights
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 December 2020, p. 983
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
MRS Bulletin names Raman as Postdoctoral Publication Prize recipient
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 December 2020, p. 1055
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Features
Historical Note
Optical communication systems serve as the backbone of today's technologies
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 December 2020, pp. 1056-1057
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation