Japanese bindweed was found to be one of the most abundant and most difficult-to-control weed species during a 2-yr weed survey in more than 100 winter wheat fields in the North China Plain region. Multivariate data analysis showed that Japanese bindweed is most abundant at sites with comparative low nitrogen (N) fertilization intensities and low crop densities. To gain deeper insights into the biology of Japanese bindweed under various N fertilization intensities, winter wheat seeding rates, herbicide treatments, and their interactions, a 2-yr field experiment was performed. In nonfertilized plots, a herbicide efficacy (based on density reduction) of 22% for 2,4-D, and of 25% for tribenuron-methyl was found. The maximum herbicide efficacy in Nmin-fertilized plots (target N value based on expected crop yield minus soil mineral nitrogen content, 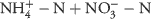 ) was 32% for 2,4-D and 34% for tribenuron-methyl. In plots fertilized according to the farmer's practices, a maximum herbicide efficacy of 72% for 2,4-D and of 64% for tribenuron-methyl could be observed. Furthermore, medium and high seeding rates improved the herbicide efficacy by at least 39% for tribenuron-methyl and 44% for 2,4-D compared to the low seeding rate. Winter wheat yield was not significantly affected by seeding rate itself, whereas at low and medium seeding rates, Nmin fertilization was decreasing winter wheat yield significantly compared to the farmer's usual fertilization practice. At the highest seeding rate, Nmin fertilization resulted in equal yields compared to the farmer's practices of fertilization.
) was 32% for 2,4-D and 34% for tribenuron-methyl. In plots fertilized according to the farmer's practices, a maximum herbicide efficacy of 72% for 2,4-D and of 64% for tribenuron-methyl could be observed. Furthermore, medium and high seeding rates improved the herbicide efficacy by at least 39% for tribenuron-methyl and 44% for 2,4-D compared to the low seeding rate. Winter wheat yield was not significantly affected by seeding rate itself, whereas at low and medium seeding rates, Nmin fertilization was decreasing winter wheat yield significantly compared to the farmer's usual fertilization practice. At the highest seeding rate, Nmin fertilization resulted in equal yields compared to the farmer's practices of fertilization.